Zhaoyang Ma
Harmonizing Intra-coherence and Inter-divergence in Ensemble Attacks for Adversarial Transferability
May 02, 2025Abstract:The development of model ensemble attacks has significantly improved the transferability of adversarial examples, but this progress also poses severe threats to the security of deep neural networks. Existing methods, however, face two critical challenges: insufficient capture of shared gradient directions across models and a lack of adaptive weight allocation mechanisms. To address these issues, we propose a novel method Harmonized Ensemble for Adversarial Transferability (HEAT), which introduces domain generalization into adversarial example generation for the first time. HEAT consists of two key modules: Consensus Gradient Direction Synthesizer, which uses Singular Value Decomposition to synthesize shared gradient directions; and Dual-Harmony Weight Orchestrator which dynamically balances intra-domain coherence, stabilizing gradients within individual models, and inter-domain diversity, enhancing transferability across models. Experimental results demonstrate that HEAT significantly outperforms existing methods across various datasets and settings, offering a new perspective and direction for adversarial attack research.
A Nested Graph Reinforcement Learning-based Decision-making Strategy for Eco-platooning
Aug 14, 2024Abstract:Platooning technology is renowned for its precise vehicle control, traffic flow optimization, and energy efficiency enhancement. However, in large-scale mixed platoons, vehicle heterogeneity and unpredictable traffic conditions lead to virtual bottlenecks. These bottlenecks result in reduced traffic throughput and increased energy consumption within the platoon. To address these challenges, we introduce a decision-making strategy based on nested graph reinforcement learning. This strategy improves collaborative decision-making, ensuring energy efficiency and alleviating congestion. We propose a theory of nested traffic graph representation that maps dynamic interactions between vehicles and platoons in non-Euclidean spaces. By incorporating spatio-temporal weighted graph into a multi-head attention mechanism, we further enhance the model's capacity to process both local and global data. Additionally, we have developed a nested graph reinforcement learning framework to enhance the self-iterative learning capabilities of platooning. Using the I-24 dataset, we designed and conducted comparative algorithm experiments, generalizability testing, and permeability ablation experiments, thereby validating the proposed strategy's effectiveness. Compared to the baseline, our strategy increases throughput by 10% and decreases energy use by 9%. Specifically, increasing the penetration rate of CAVs significantly enhances traffic throughput, though it also increases energy consumption.
V2X-Real: a Largs-Scale Dataset for Vehicle-to-Everything Cooperative Perception
Mar 24, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) technologies have enabled autonomous vehicles to share sensing information to see through occlusions, greatly boosting the perception capability. However, there are no real-world datasets to facilitate the real V2X cooperative perception research -- existing datasets either only support Vehicle-to-Infrastructure cooperation or Vehicle-to-Vehicle cooperation. In this paper, we propose a dataset that has a mixture of multiple vehicles and smart infrastructure simultaneously to facilitate the V2X cooperative perception development with multi-modality sensing data. Our V2X-Real is collected using two connected automated vehicles and two smart infrastructures, which are all equipped with multi-modal sensors including LiDAR sensors and multi-view cameras. The whole dataset contains 33K LiDAR frames and 171K camera data with over 1.2M annotated bounding boxes of 10 categories in very challenging urban scenarios. According to the collaboration mode and ego perspective, we derive four types of datasets for Vehicle-Centric, Infrastructure-Centric, Vehicle-to-Vehicle, and Infrastructure-to-Infrastructure cooperative perception. Comprehensive multi-class multi-agent benchmarks of SOTA cooperative perception methods are provided. The V2X-Real dataset and benchmark codes will be released.
Zero-Shot Digital Rock Image Segmentation with a Fine-Tuned Segment Anything Model
Nov 17, 2023Abstract:Accurate image segmentation is crucial in reservoir modelling and material characterization, enhancing oil and gas extraction efficiency through detailed reservoir models. This precision offers insights into rock properties, advancing digital rock physics understanding. However, creating pixel-level annotations for complex CT and SEM rock images is challenging due to their size and low contrast, lengthening analysis time. This has spurred interest in advanced semi-supervised and unsupervised segmentation techniques in digital rock image analysis, promising more efficient, accurate, and less labour-intensive methods. Meta AI's Segment Anything Model (SAM) revolutionized image segmentation in 2023, offering interactive and automated segmentation with zero-shot capabilities, essential for digital rock physics with limited training data and complex image features. Despite its advanced features, SAM struggles with rock CT/SEM images due to their absence in its training set and the low-contrast nature of grayscale images. Our research fine-tunes SAM for rock CT/SEM image segmentation, optimizing parameters and handling large-scale images to improve accuracy. Experiments on rock CT and SEM images show that fine-tuning significantly enhances SAM's performance, enabling high-quality mask generation in digital rock image analysis. Our results demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the fine-tuned SAM model (RockSAM) for rock images, offering segmentation without extensive training or complex labelling.
Enhancing Rock Image Segmentation in Digital Rock Physics: A Fusion of Generative AI and State-of-the-Art Neural Networks
Nov 10, 2023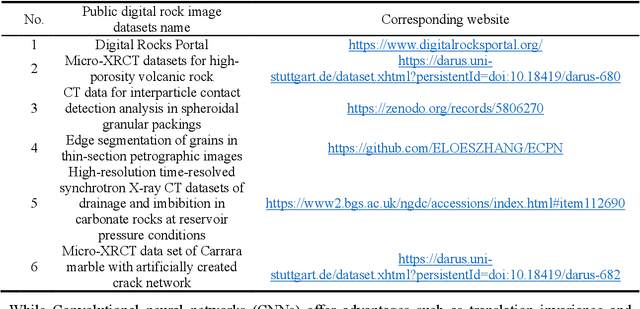
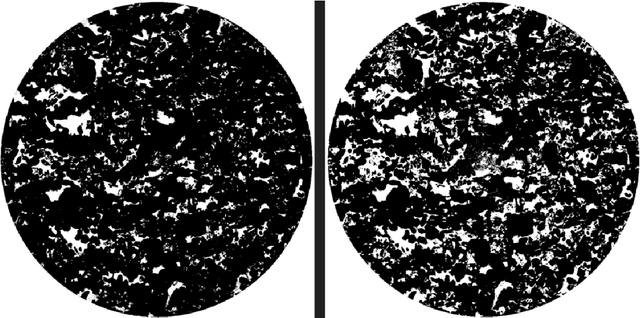

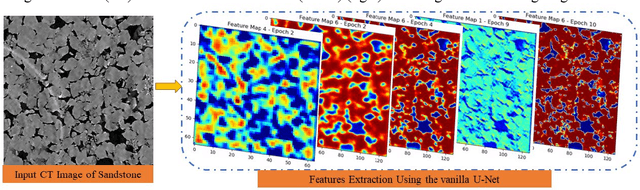
Abstract:In digital rock physics, analysing microstructures from CT and SEM scans is crucial for estimating properties like porosity and pore connectivity. Traditional segmentation methods like thresholding and CNNs often fall short in accurately detailing rock microstructures and are prone to noise. U-Net improved segmentation accuracy but required many expert-annotated samples, a laborious and error-prone process due to complex pore shapes. Our study employed an advanced generative AI model, the diffusion model, to overcome these limitations. This model generated a vast dataset of CT/SEM and binary segmentation pairs from a small initial dataset. We assessed the efficacy of three neural networks: U-Net, Attention-U-net, and TransUNet, for segmenting these enhanced images. The diffusion model proved to be an effective data augmentation technique, improving the generalization and robustness of deep learning models. TransU-Net, incorporating Transformer structures, demonstrated superior segmentation accuracy and IoU metrics, outperforming both U-Net and Attention-U-net. Our research advances rock image segmentation by combining the diffusion model with cutting-edge neural networks, reducing dependency on extensive expert data and boosting segmentation accuracy and robustness. TransU-Net sets a new standard in digital rock physics, paving the way for future geoscience and engineering breakthroughs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge