Letian Gao
V2X-ReaLO: An Open Online Framework and Dataset for Cooperative Perception in Reality
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Cooperative perception enabled by Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication holds significant promise for enhancing the perception capabilities of autonomous vehicles, allowing them to overcome occlusions and extend their field of view. However, existing research predominantly relies on simulated environments or static datasets, leaving the feasibility and effectiveness of V2X cooperative perception especially for intermediate fusion in real-world scenarios largely unexplored. In this work, we introduce V2X-ReaLO, an open online cooperative perception framework deployed on real vehicles and smart infrastructure that integrates early, late, and intermediate fusion methods within a unified pipeline and provides the first practical demonstration of online intermediate fusion's feasibility and performance under genuine real-world conditions. Additionally, we present an open benchmark dataset specifically designed to assess the performance of online cooperative perception systems. This new dataset extends V2X-Real dataset to dynamic, synchronized ROS bags and provides 25,028 test frames with 6,850 annotated key frames in challenging urban scenarios. By enabling real-time assessments of perception accuracy and communication lantency under dynamic conditions, V2X-ReaLO sets a new benchmark for advancing and optimizing cooperative perception systems in real-world applications. The codes and datasets will be released to further advance the field.
RNACG: A Universal RNA Sequence Conditional Generation model based on Flow-Matching
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:RNA plays a crucial role in diverse life processes. In contrast to the rapid advancement of protein design methods, the work related to RNA is more demanding. Most current RNA design approaches concentrate on specified target attributes and rely on extensive experimental searches. However, these methods remain costly and inefficient due to practical limitations. In this paper, we characterize all sequence design issues as conditional generation tasks and offer parameterized representations for multiple problems. For these problems, we have developed a universal RNA sequence generation model based on flow matching, namely RNACG. RNACG can accommodate various conditional inputs and is portable, enabling users to customize the encoding network for conditional inputs as per their requirements and integrate it into the generation network. We evaluated RNACG in RNA 3D structure inverse folding, 2D structure inverse folding, family-specific sequence generation, and 5'UTR translation efficiency prediction. RNACG attains superior or competitive performance on these tasks compared with other methods. RNACG exhibits extensive applicability in sequence generation and property prediction tasks, providing a novel approach to RNA sequence design and potential methods for simulation experiments with large-scale RNA sequence data.
V2X-Real: a Largs-Scale Dataset for Vehicle-to-Everything Cooperative Perception
Mar 24, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) technologies have enabled autonomous vehicles to share sensing information to see through occlusions, greatly boosting the perception capability. However, there are no real-world datasets to facilitate the real V2X cooperative perception research -- existing datasets either only support Vehicle-to-Infrastructure cooperation or Vehicle-to-Vehicle cooperation. In this paper, we propose a dataset that has a mixture of multiple vehicles and smart infrastructure simultaneously to facilitate the V2X cooperative perception development with multi-modality sensing data. Our V2X-Real is collected using two connected automated vehicles and two smart infrastructures, which are all equipped with multi-modal sensors including LiDAR sensors and multi-view cameras. The whole dataset contains 33K LiDAR frames and 171K camera data with over 1.2M annotated bounding boxes of 10 categories in very challenging urban scenarios. According to the collaboration mode and ego perspective, we derive four types of datasets for Vehicle-Centric, Infrastructure-Centric, Vehicle-to-Vehicle, and Infrastructure-to-Infrastructure cooperative perception. Comprehensive multi-class multi-agent benchmarks of SOTA cooperative perception methods are provided. The V2X-Real dataset and benchmark codes will be released.
A Systematic Survey of Control Techniques and Applications: From Autonomous Vehicles to Connected and Automated Vehicles
Mar 10, 2023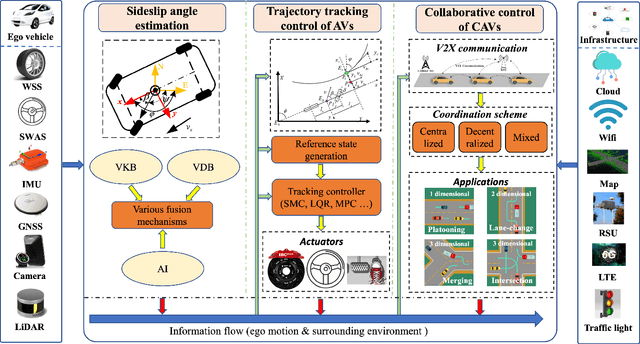
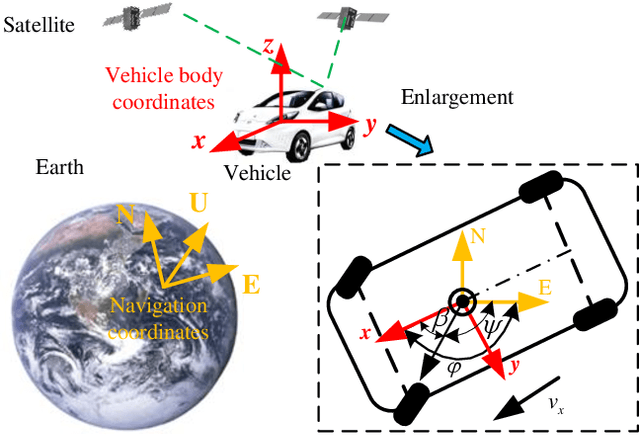
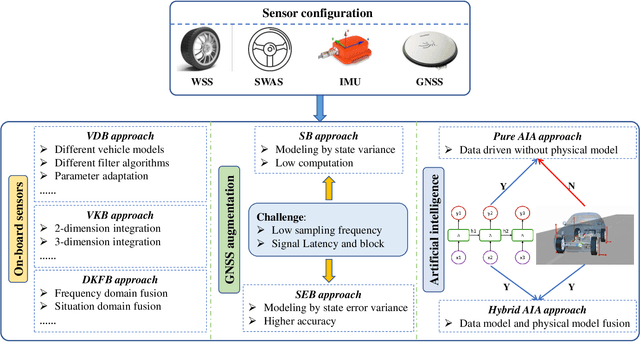
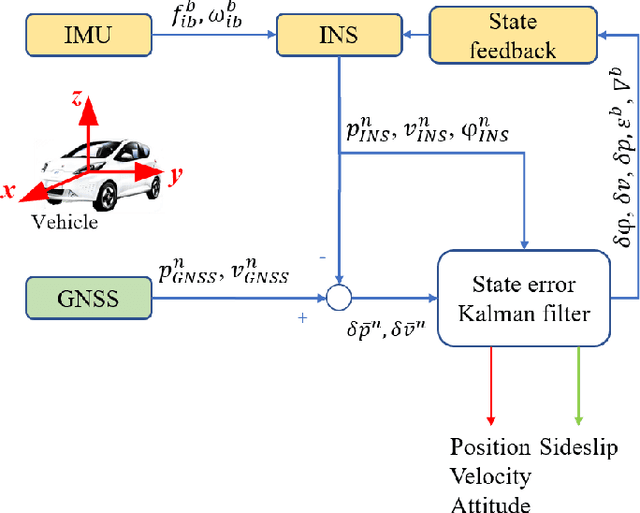
Abstract:Vehicle control is one of the most critical challenges in autonomous vehicles (AVs) and connected and automated vehicles (CAVs), and it is paramount in vehicle safety, passenger comfort, transportation efficiency, and energy saving. This survey attempts to provide a comprehensive and thorough overview of the current state of vehicle control technology, focusing on the evolution from vehicle state estimation and trajectory tracking control in AVs at the microscopic level to collaborative control in CAVs at the macroscopic level. First, this review starts with vehicle key state estimation, specifically vehicle sideslip angle, which is the most pivotal state for vehicle trajectory control, to discuss representative approaches. Then, we present symbolic vehicle trajectory tracking control approaches for AVs. On top of that, we further review the collaborative control frameworks for CAVs and corresponding applications. Finally, this survey concludes with a discussion of future research directions and the challenges. This survey aims to provide a contextualized and in-depth look at state of the art in vehicle control for AVs and CAVs, identifying critical areas of focus and pointing out the potential areas for further exploration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge