Chun Qi
DiffFAS: Face Anti-Spoofing via Generative Diffusion Models
Sep 13, 2024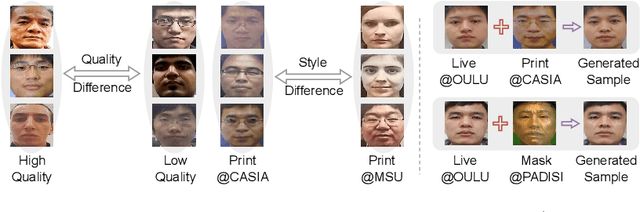
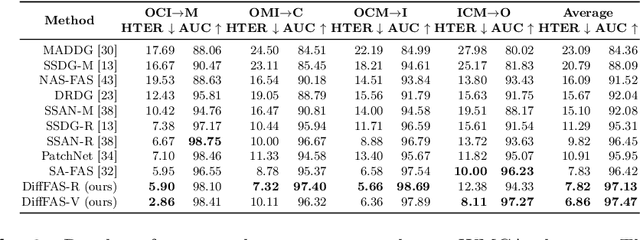
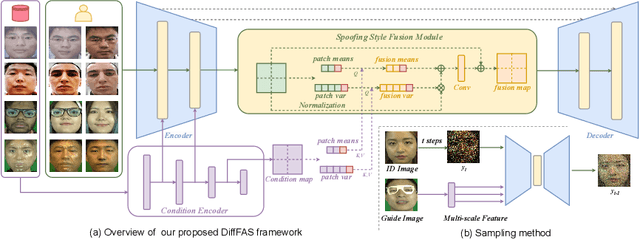
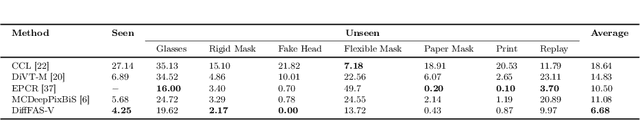
Abstract:Face anti-spoofing (FAS) plays a vital role in preventing face recognition (FR) systems from presentation attacks. Nowadays, FAS systems face the challenge of domain shift, impacting the generalization performance of existing FAS methods. In this paper, we rethink about the inherence of domain shift and deconstruct it into two factors: image style and image quality. Quality influences the purity of the presentation of spoof information, while style affects the manner in which spoof information is presented. Based on our analysis, we propose DiffFAS framework, which quantifies quality as prior information input into the network to counter image quality shift, and performs diffusion-based high-fidelity cross-domain and cross-attack types generation to counter image style shift. DiffFAS transforms easily collectible live faces into high-fidelity attack faces with precise labels while maintaining consistency between live and spoof face identities, which can also alleviate the scarcity of labeled data with novel type attacks faced by nowadays FAS system. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework on challenging cross-domain and cross-attack FAS datasets, achieving the state-of-the-art performance. Available at https://github.com/murphytju/DiffFAS.
Multi-scale multi-modal micro-expression recognition algorithm based on transformer
Jan 11, 2023



Abstract:A micro-expression is a spontaneous unconscious facial muscle movement that can reveal the true emotions people attempt to hide. Although manual methods have made good progress and deep learning is gaining prominence. Due to the short duration of micro-expression and different scales of expressed in facial regions, existing algorithms cannot extract multi-modal multi-scale facial region features while taking into account contextual information to learn underlying features. Therefore, in order to solve the above problems, a multi-modal multi-scale algorithm based on transformer network is proposed in this paper, aiming to fully learn local multi-grained features of micro-expressions through two modal features of micro-expressions - motion features and texture features. To obtain local area features of the face at different scales, we learned patch features at different scales for both modalities, and then fused multi-layer multi-headed attention weights to obtain effective features by weighting the patch features, and combined cross-modal contrastive learning for model optimization. We conducted comprehensive experiments on three spontaneous datasets, and the results show the accuracy of the proposed algorithm in single measurement SMIC database is up to 78.73% and the F1 value on CASMEII of the combined database is up to 0.9071, which is at the leading level.
Reconstruction of compressed spectral imaging based on global structure and spectral correlation
Oct 27, 2022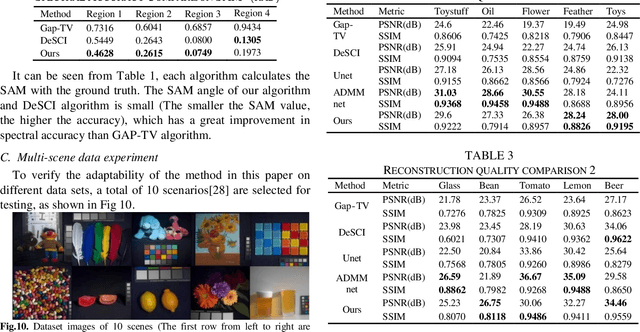
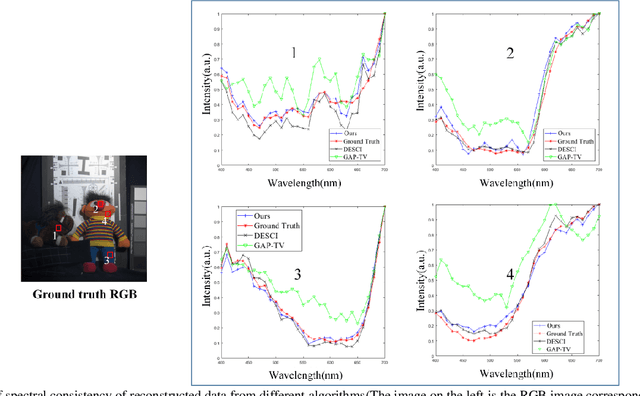
Abstract:In this paper, a convolution sparse coding method based on global structure characteristics and spectral correlation is proposed for the reconstruction of compressive spectral images. The proposed method uses the convolution kernel to operate the global image, which can better preserve image structure information in the spatial dimension. To take full exploration of the constraints between spectra, the coefficients corresponding to the convolution kernel are constrained by the norm to improve spectral accuracy. And, to solve the problem that convolutional sparse coding is insensitive to low frequency, the global total-variation (TV) constraint is added to estimate the low-frequency components. It not only ensures the effective estimation of the low-frequency but also transforms the convolutional sparse coding into a de-noising process, which makes the reconstructing process simpler. Simulations show that compared with the current mainstream optimization methods (DeSCI and Gap-TV), the proposed method improves the reconstruction quality by up to 7 dB in PSNR and 10% in SSIM, and has a great improvement in the details of the reconstructed image.
A Dynamic 3D Spontaneous Micro-expression Database: Establishment and Evaluation
Aug 22, 2021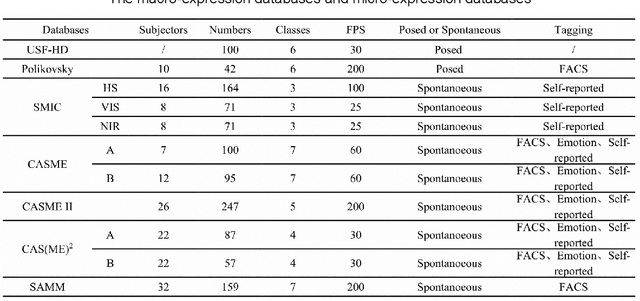
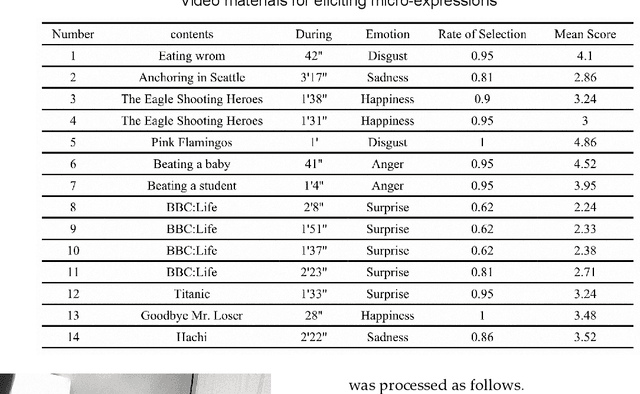


Abstract:Micro-expressions are spontaneous, unconscious facial movements that show people's true inner emotions and have great potential in related fields of psychological testing. Since the face is a 3D deformation object, the occurrence of an expression can arouse spatial deformation of the face, but limited by the available databases are 2D videos, lacking the description of 3D spatial information of micro-expressions. Therefore, we proposed a new micro-expression database containing 2D video sequences and 3D point clouds sequences. The database includes 259 micro-expressions sequences, and these samples were classified using the objective method based on facial action coding system, as well as the non-objective method that combines video contents and participants' self-reports. We extracted 2D and 3D features using the local binary patterns on three orthogonal planes (LBP-TOP) and curvature algorithms, respectively, and evaluated the classification accuracies of these two features and their fusion results with leave-one-subject-out (LOSO) and 10-fold cross-validation. Further, we performed various neural network algorithms for database classification, the results show that classification accuracies are improved by fusing 3D features than using only 2D features. The database offers original and cropped micro-expression samples, which will facilitate the exploration and research on 3D Spatio-temporal features of micro-expressions.
CNN Retrieval based Unsupervised Metric Learning for Near-Duplicated Video Retrieval
May 30, 2021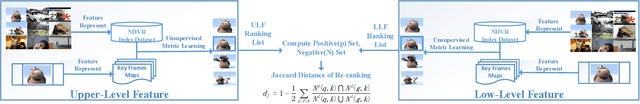
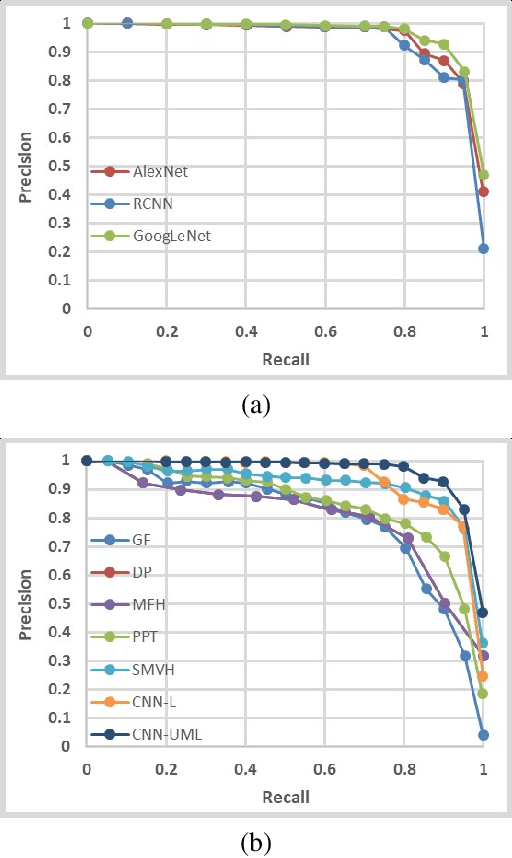
Abstract:As important data carriers, the drastically increasing number of multimedia videos often brings many duplicate and near-duplicate videos in the top results of search. Near-duplicate video retrieval (NDVR) can cluster and filter out the redundant contents. In this paper, the proposed NDVR approach extracts the frame-level video representation based on convolutional neural network (CNN) features from fully-connected layer and aggregated intermediate convolutional layers. Unsupervised metric learning is used for similarity measurement and feature matching. An efficient re-ranking algorithm combined with k-nearest neighborhood fuses the retrieval results from two levels of features and further improves the retrieval performance. Extensive experiments on the widely used CC\_WEB\_VIDEO dataset shows that the proposed approach exhibits superior performance over the state-of-the-art.
Kernel based low-rank sparse model for single image super-resolution
Sep 27, 2018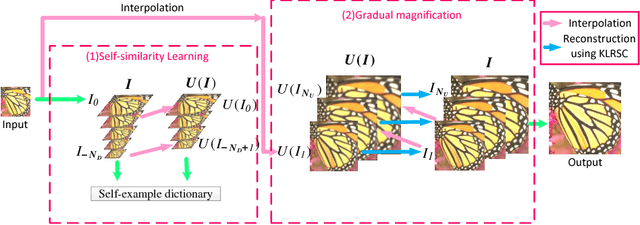
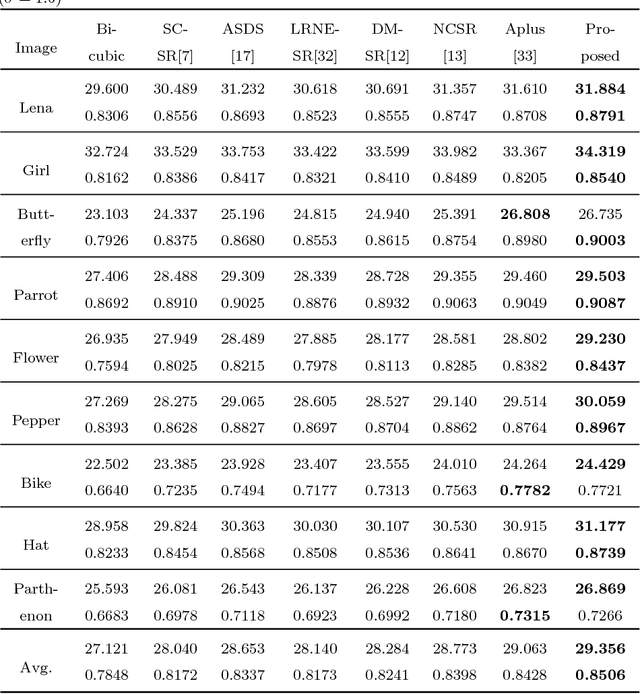
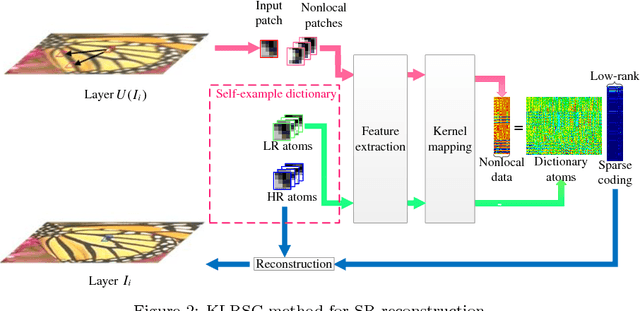
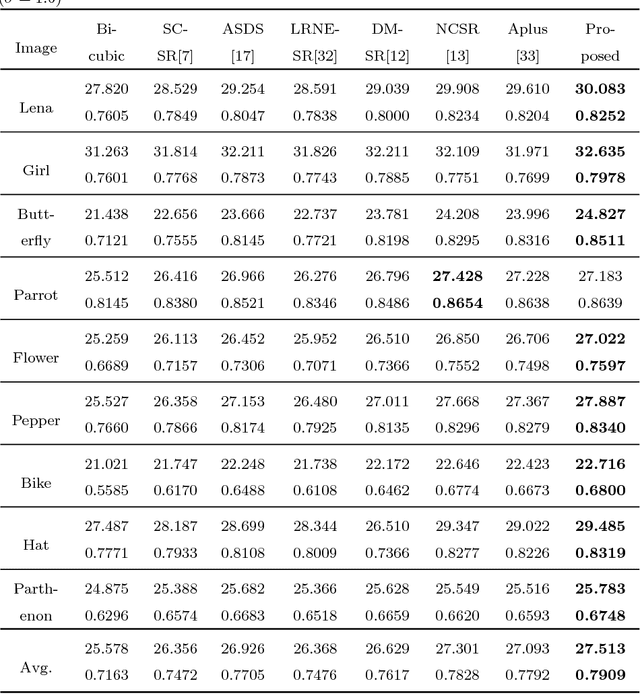
Abstract:Self-similarity learning has been recognized as a promising method for single image super-resolution (SR) to produce high-resolution (HR) image in recent years. The performance of learning based SR reconstruction, however, highly depends on learned representation coeffcients. Due to the degradation of input image, conventional sparse coding is prone to produce unfaithful representation coeffcients. To this end, we propose a novel kernel based low-rank sparse model with self-similarity learning for single image SR which incorporates nonlocalsimilarity prior to enforce similar patches having similar representation weights. We perform a gradual magnification scheme, using self-examples extracted from the degraded input image and up-scaled versions. To exploit nonlocal-similarity, we concatenate the vectorized input patch and its nonlocal neighbors at different locations into a data matrix which consists of similar components. Then we map the nonlocal data matrix into a high-dimensional feature space by kernel method to capture their nonlinear structures. Under the assumption that the sparse coeffcients for the nonlocal data in the kernel space should be low-rank, we impose low-rank constraint on sparse coding to share similarities among representation coeffcients and remove outliers in order that stable weights for SR reconstruction can be obtained. Experimental results demonstrate the advantage of our proposed method in both visual quality and reconstruction error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge