Huai-Qian Khor
Infused Suppression Of Magnification Artefacts For Micro-AU Detection
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:Facial micro-expressions are spontaneous, brief and subtle facial motions that unveil the underlying, suppressed emotions. Detecting Action Units (AUs) in micro-expressions is crucial because it yields a finer representation of facial motions than categorical emotions, effectively resolving the ambiguity among different expressions. One of the difficulties in micro-expression analysis is that facial motions are subtle and brief, thereby increasing the difficulty in correlating facial motion features to AU occurrence. To bridge the subtlety issue, flow-related features and motion magnification are a few common approaches as they can yield descriptive motion changes and increased motion amplitude respectively. While motion magnification can amplify the motion changes, it also accounts for illumination changes and projection errors during the amplification process, thereby creating motion artefacts that confuse the model to learn inauthentic magnified motion features. The problem is further aggravated in the context of a more complicated task where more AU classes are analyzed in cross-database settings. To address this issue, we propose InfuseNet, a layer-wise unitary feature infusion framework that leverages motion context to constrain the Action Unit (AU) learning within an informative facial movement region, thereby alleviating the influence of magnification artefacts. On top of that, we propose leveraging magnified latent features instead of reconstructing magnified samples to limit the distortion and artefacts caused by the projection inaccuracy in the motion reconstruction process. Via alleviating the magnification artefacts, InfuseNet has surpassed the state-of-the-art results in the CD6ME protocol. Further quantitative studies have also demonstrated the efficacy of motion artefacts alleviation.
Towards Consistent and Controllable Image Synthesis for Face Editing
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:Current face editing methods mainly rely on GAN-based techniques, but recent focus has shifted to diffusion-based models due to their success in image reconstruction. However, diffusion models still face challenges in manipulating fine-grained attributes and preserving consistency of attributes that should remain unchanged. To address these issues and facilitate more convenient editing of face images, we propose a novel approach that leverages the power of Stable-Diffusion models and crude 3D face models to control the lighting, facial expression and head pose of a portrait photo. We observe that this task essentially involve combinations of target background, identity and different face attributes. We aim to sufficiently disentangle the control of these factors to enable high-quality of face editing. Specifically, our method, coined as RigFace, contains: 1) A Spatial Arrtibute Encoder that provides presise and decoupled conditions of background, pose, expression and lighting; 2) An Identity Encoder that transfers identity features to the denoising UNet of a pre-trained Stable-Diffusion model; 3) An Attribute Rigger that injects those conditions into the denoising UNet. Our model achieves comparable or even superior performance in both identity preservation and photorealism compared to existing face editing models.
MagicFace: High-Fidelity Facial Expression Editing with Action-Unit Control
Jan 04, 2025



Abstract:We address the problem of facial expression editing by controling the relative variation of facial action-unit (AU) from the same person. This enables us to edit this specific person's expression in a fine-grained, continuous and interpretable manner, while preserving their identity, pose, background and detailed facial attributes. Key to our model, which we dub MagicFace, is a diffusion model conditioned on AU variations and an ID encoder to preserve facial details of high consistency. Specifically, to preserve the facial details with the input identity, we leverage the power of pretrained Stable-Diffusion models and design an ID encoder to merge appearance features through self-attention. To keep background and pose consistency, we introduce an efficient Attribute Controller by explicitly informing the model of current background and pose of the target. By injecting AU variations into a denoising UNet, our model can animate arbitrary identities with various AU combinations, yielding superior results in high-fidelity expression editing compared to other facial expression editing works. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/weimengting/MagicFace.
Towards Localized Fine-Grained Control for Facial Expression Generation
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:Generative models have surged in popularity recently due to their ability to produce high-quality images and video. However, steering these models to produce images with specific attributes and precise control remains challenging. Humans, particularly their faces, are central to content generation due to their ability to convey rich expressions and intent. Current generative models mostly generate flat neutral expressions and characterless smiles without authenticity. Other basic expressions like anger are possible, but are limited to the stereotypical expression, while other unconventional facial expressions like doubtful are difficult to reliably generate. In this work, we propose the use of AUs (action units) for facial expression control in face generation. AUs describe individual facial muscle movements based on facial anatomy, allowing precise and localized control over the intensity of facial movements. By combining different action units, we unlock the ability to create unconventional facial expressions that go beyond typical emotional models, enabling nuanced and authentic reactions reflective of real-world expressions. The proposed method can be seamlessly integrated with both text and image prompts using adapters, offering precise and intuitive control of the generated results. Code and dataset are available in {https://github.com/tvaranka/fineface}.
Revealing the Invisible with Model and Data Shrinking for Composite-database Micro-expression Recognition
Jun 17, 2020



Abstract:Composite-database micro-expression recognition is attracting increasing attention as it is more practical to real-world applications. Though the composite database provides more sample diversity for learning good representation models, the important subtle dynamics are prone to disappearing in the domain shift such that the models greatly degrade their performance, especially for deep models. In this paper, we analyze the influence of learning complexity, including the input complexity and model complexity, and discover that the lower-resolution input data and shallower-architecture model are helpful to ease the degradation of deep models in composite-database task. Based on this, we propose a recurrent convolutional network (RCN) to explore the shallower-architecture and lower-resolution input data, shrinking model and input complexities simultaneously. Furthermore, we develop three parameter-free modules (i.e., wide expansion, shortcut connection and attention unit) to integrate with RCN without increasing any learnable parameters. These three modules can enhance the representation ability in various perspectives while preserving not-very-deep architecture for lower-resolution data. Besides, three modules can further be combined by an automatic strategy (a neural architecture search strategy) and the searched architecture becomes more robust. Extensive experiments on MEGC2019 dataset (composited of existing SMIC, CASME II and SAMM datasets) have verified the influence of learning complexity and shown that RCNs with three modules and the searched combination outperform the state-of-the-art approaches.
A Shallow Triple Stream Three-dimensional CNN for Micro-expression Recognition System
Feb 10, 2019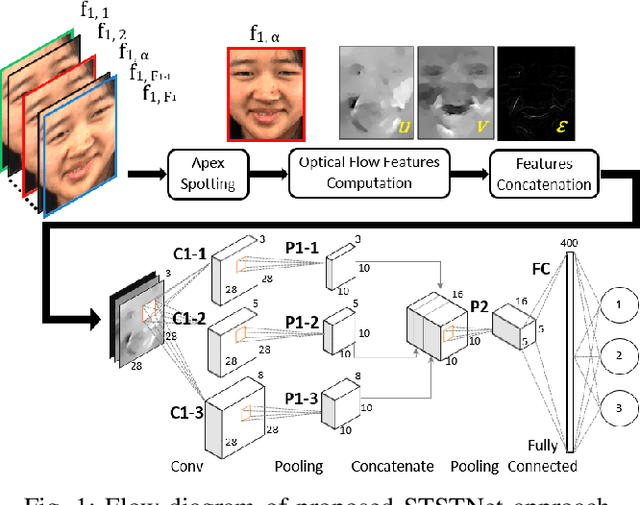
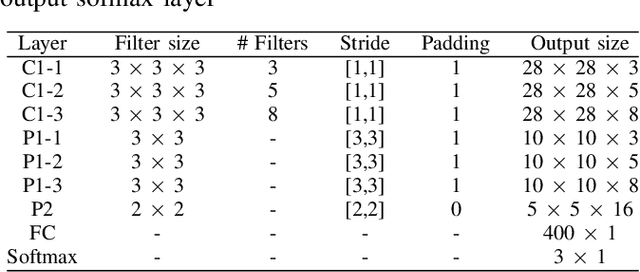
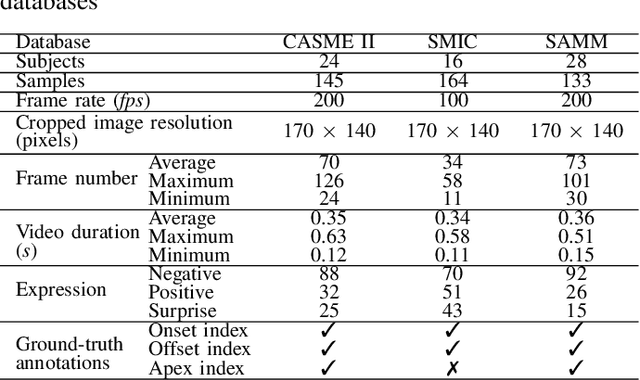
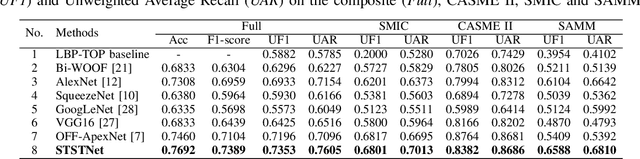
Abstract:In the recent year, the state-of-the-arts of facial micro-expression recognition task have been significantly advanced by the emergence of data-driven approaches based on deep learning. Due to the superb learning capacity of deep learning, it generates promising performance beyond the traditional handcrafted approaches. Recently, many researchers have focused on developing better networks by increasing its depth, as deep networks can effectively approximate certain function classes more efficiently than shallow ones. In this paper, we aim to design a shallow network to extract the high level features of the micro-expression details. Specifically, a two-layer neural network, namely Shallow Triple Stream Three-dimensional CNN (STSTNet) is proposed. The network is capable to learn the features from three optical flow features (i.e., optical strain, horizontal and vertical optical flow images) computed from the onset and apex frames from each video. Our experimental results demonstrate the viability of the proposed STSTNet, which exhibits the UAR recognition results of 76.05%, 70.13%, 86.86% and 68.10% in composite, SMIC, CASME II and SAMM databases, respectively.
Enriched Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network for Facial Micro-Expression Recognition
May 22, 2018



Abstract:Facial micro-expression (ME) recognition has posed a huge challenge to researchers for its subtlety in motion and limited databases. Recently, handcrafted techniques have achieved superior performance in micro-expression recognition but at the cost of domain specificity and cumbersome parametric tunings. In this paper, we propose an Enriched Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network (ELRCN) that first encodes each micro-expression frame into a feature vector through CNN module(s), then predicts the micro-expression by passing the feature vector through a Long Short-term Memory (LSTM) module. The framework contains two different network variants: (1) Channel-wise stacking of input data for spatial enrichment, (2) Feature-wise stacking of features for temporal enrichment. We demonstrate that the proposed approach is able to achieve reasonably good performance, without data augmentation. In addition, we also present ablation studies conducted on the framework and visualizations of what CNN "sees" when predicting the micro-expression classes.
Lost in Time: Temporal Analytics for Long-Term Video Surveillance
Dec 20, 2017



Abstract:Video surveillance is a well researched area of study with substantial work done in the aspects of object detection, tracking and behavior analysis. With the abundance of video data captured over a long period of time, we can understand patterns in human behavior and scene dynamics through data-driven temporal analytics. In this work, we propose two schemes to perform descriptive and predictive analytics on long-term video surveillance data. We generate heatmap and footmap visualizations to describe spatially pooled trajectory patterns with respect to time and location. We also present two approaches for anomaly prediction at the day-level granularity: a trajectory-based statistical approach, and a time-series based approach. Experimentation with one year data from a single camera demonstrates the ability to uncover interesting insights about the scene and to predict anomalies reasonably well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge