Xiaobai Li
Vision Large Language Models Are Good Noise Handlers in Engagement Analysis
Nov 18, 2025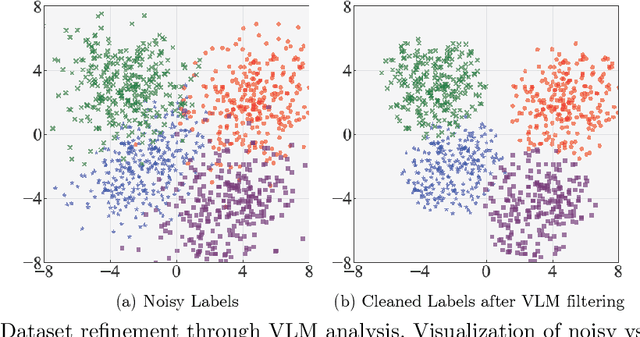
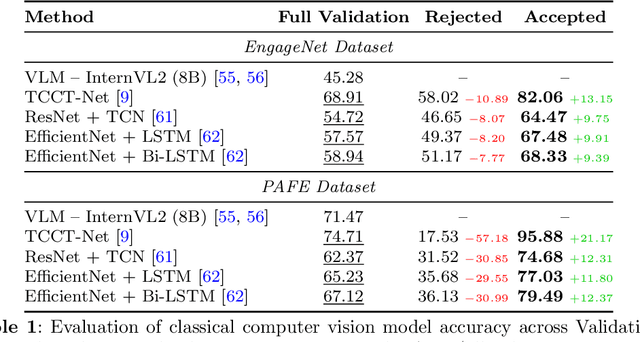
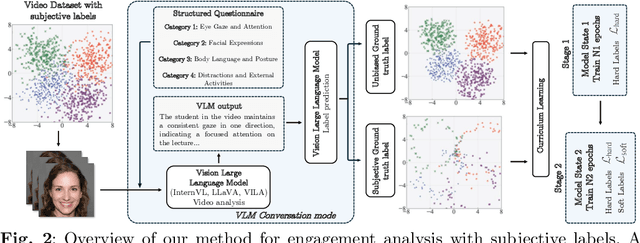
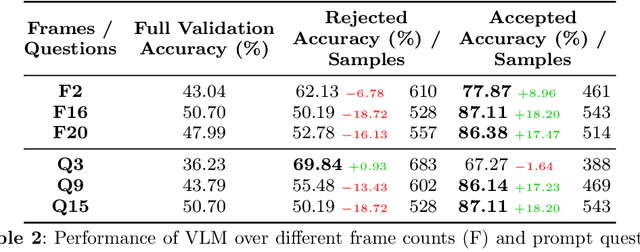
Abstract:Engagement recognition in video datasets, unlike traditional image classification tasks, is particularly challenged by subjective labels and noise limiting model performance. To overcome the challenges of subjective and noisy engagement labels, we propose a framework leveraging Vision Large Language Models (VLMs) to refine annotations and guide the training process. Our framework uses a questionnaire to extract behavioral cues and split data into high- and low-reliability subsets. We also introduce a training strategy combining curriculum learning with soft label refinement, gradually incorporating ambiguous samples while adjusting supervision to reflect uncertainty. We demonstrate that classical computer vision models trained on refined high-reliability subsets and enhanced with our curriculum strategy show improvements, highlighting benefits of addressing label subjectivity with VLMs. This method surpasses prior state of the art across engagement benchmarks such as EngageNet (three of six feature settings, maximum improvement of +1.21%), and DREAMS / PAFE with F1 gains of +0.22 / +0.06.
Radar-APLANC: Unsupervised Radar-based Heartbeat Sensing via Augmented Pseudo-Label and Noise Contrast
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radars can measure subtle chest wall oscillations to enable non-contact heartbeat sensing. However, traditional radar-based heartbeat sensing methods face performance degradation due to noise. Learning-based radar methods achieve better noise robustness but require costly labeled signals for supervised training. To overcome these limitations, we propose the first unsupervised framework for radar-based heartbeat sensing via Augmented Pseudo-Label and Noise Contrast (Radar-APLANC). We propose to use both the heartbeat range and noise range within the radar range matrix to construct the positive and negative samples, respectively, for improved noise robustness. Our Noise-Contrastive Triplet (NCT) loss only utilizes positive samples, negative samples, and pseudo-label signals generated by the traditional radar method, thereby avoiding dependence on expensive ground-truth physiological signals. We further design a pseudo-label augmentation approach featuring adaptive noise-aware label selection to improve pseudo-label signal quality. Extensive experiments on the Equipleth dataset and our collected radar dataset demonstrate that our unsupervised method achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art supervised methods. Our code, dataset, and supplementary materials can be accessed from https://github.com/RadarHRSensing/Radar-APLANC.
MEGC2025: Micro-Expression Grand Challenge on Spot Then Recognize and Visual Question Answering
Jun 18, 2025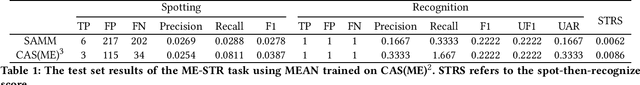
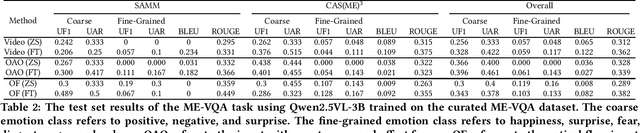
Abstract:Facial micro-expressions (MEs) are involuntary movements of the face that occur spontaneously when a person experiences an emotion but attempts to suppress or repress the facial expression, typically found in a high-stakes environment. In recent years, substantial advancements have been made in the areas of ME recognition, spotting, and generation. However, conventional approaches that treat spotting and recognition as separate tasks are suboptimal, particularly for analyzing long-duration videos in realistic settings. Concurrently, the emergence of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and large vision-language models (LVLMs) offers promising new avenues for enhancing ME analysis through their powerful multimodal reasoning capabilities. The ME grand challenge (MEGC) 2025 introduces two tasks that reflect these evolving research directions: (1) ME spot-then-recognize (ME-STR), which integrates ME spotting and subsequent recognition in a unified sequential pipeline; and (2) ME visual question answering (ME-VQA), which explores ME understanding through visual question answering, leveraging MLLMs or LVLMs to address diverse question types related to MEs. All participating algorithms are required to run on this test set and submit their results on a leaderboard. More details are available at https://megc2025.github.io.
Active Multimodal Distillation for Few-shot Action Recognition
Jun 16, 2025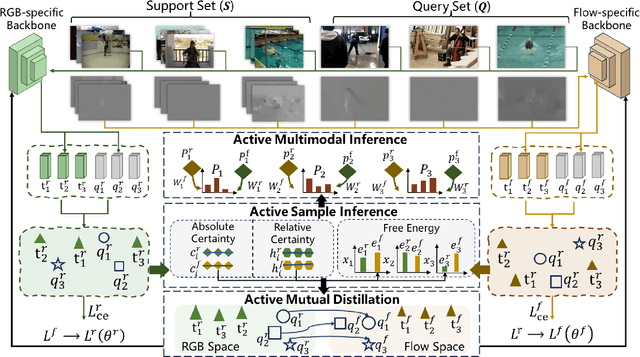
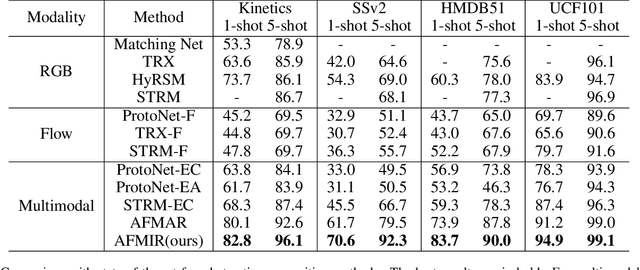
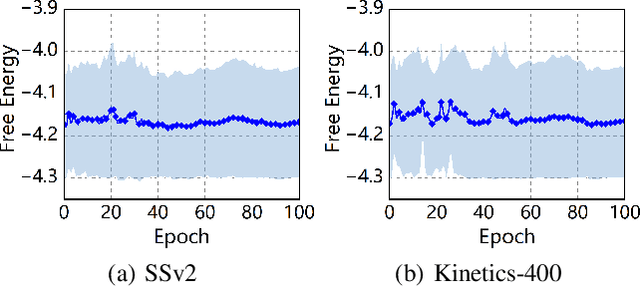
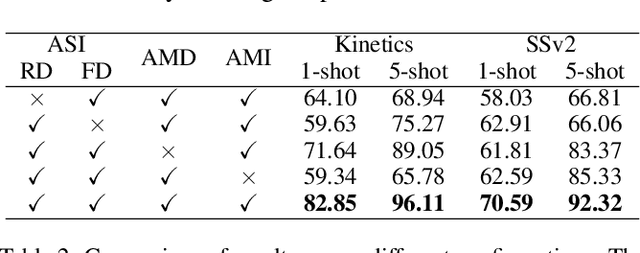
Abstract:Owing to its rapid progress and broad application prospects, few-shot action recognition has attracted considerable interest. However, current methods are predominantly based on limited single-modal data, which does not fully exploit the potential of multimodal information. This paper presents a novel framework that actively identifies reliable modalities for each sample using task-specific contextual cues, thus significantly improving recognition performance. Our framework integrates an Active Sample Inference (ASI) module, which utilizes active inference to predict reliable modalities based on posterior distributions and subsequently organizes them accordingly. Unlike reinforcement learning, active inference replaces rewards with evidence-based preferences, making more stable predictions. Additionally, we introduce an active mutual distillation module that enhances the representation learning of less reliable modalities by transferring knowledge from more reliable ones. Adaptive multimodal inference is employed during the meta-test to assign higher weights to reliable modalities. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches.
A Benchmark for Incremental Micro-expression Recognition
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Micro-expression recognition plays a pivotal role in understanding hidden emotions and has applications across various fields. Traditional recognition methods assume access to all training data at once, but real-world scenarios involve continuously evolving data streams. To respond to the requirement of adapting to new data while retaining previously learned knowledge, we introduce the first benchmark specifically designed for incremental micro-expression recognition. Our contributions include: Firstly, we formulate the incremental learning setting tailored for micro-expression recognition. Secondly, we organize sequential datasets with carefully curated learning orders to reflect real-world scenarios. Thirdly, we define two cross-evaluation-based testing protocols, each targeting distinct evaluation objectives. Finally, we provide six baseline methods and their corresponding evaluation results. This benchmark lays the groundwork for advancing incremental micro-expression recognition research. All code used in this study will be made publicly available.
PsyDraw: A Multi-Agent Multimodal System for Mental Health Screening in Left-Behind Children
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Left-behind children (LBCs), numbering over 66 million in China, face severe mental health challenges due to parental migration for work. Early screening and identification of at-risk LBCs is crucial, yet challenging due to the severe shortage of mental health professionals, especially in rural areas. While the House-Tree-Person (HTP) test shows higher child participation rates, its requirement for expert interpretation limits its application in resource-scarce regions. To address this challenge, we propose PsyDraw, a multi-agent system based on Multimodal Large Language Models that assists mental health professionals in analyzing HTP drawings. The system employs specialized agents for feature extraction and psychological interpretation, operating in two stages: comprehensive feature analysis and professional report generation. Evaluation of HTP drawings from 290 primary school students reveals that 71.03% of the analyzes achieved High Consistency with professional evaluations, 26.21% Moderate Consistency and only 2.41% Low Consistency. The system identified 31.03% of cases requiring professional attention, demonstrating its effectiveness as a preliminary screening tool. Currently deployed in pilot schools, \method shows promise in supporting mental health professionals, particularly in resource-limited areas, while maintaining high professional standards in psychological assessment.
VisioPhysioENet: Multimodal Engagement Detection using Visual and Physiological Signals
Sep 24, 2024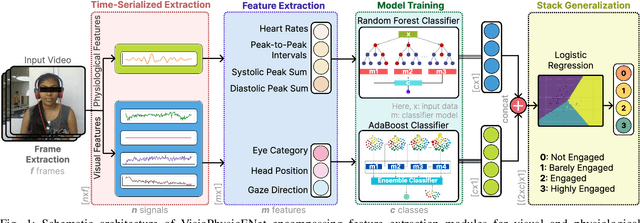
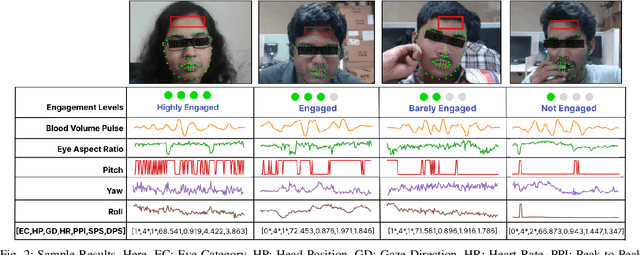
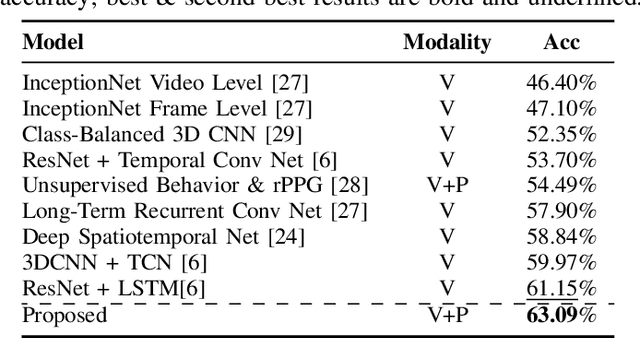

Abstract:This paper presents VisioPhysioENet, a novel multimodal system that leverages visual cues and physiological signals to detect learner engagement. It employs a two-level approach for visual feature extraction using the Dlib library for facial landmark extraction and the OpenCV library for further estimations. This is complemented by extracting physiological signals using the plane-orthogonal-to-skin method to assess cardiovascular activity. These features are integrated using advanced machine learning classifiers, enhancing the detection of various engagement levels. We rigorously evaluate VisioPhysioENet on the DAiSEE dataset, where it achieves an accuracy of 63.09%, demonstrating a superior ability to discern various levels of engagement compared to existing methodologies. The proposed system's code can be accessed at https://github.com/MIntelligence-Group/VisioPhysioENet.
Biometric Authentication Based on Enhanced Remote Photoplethysmography Signal Morphology
Jul 04, 2024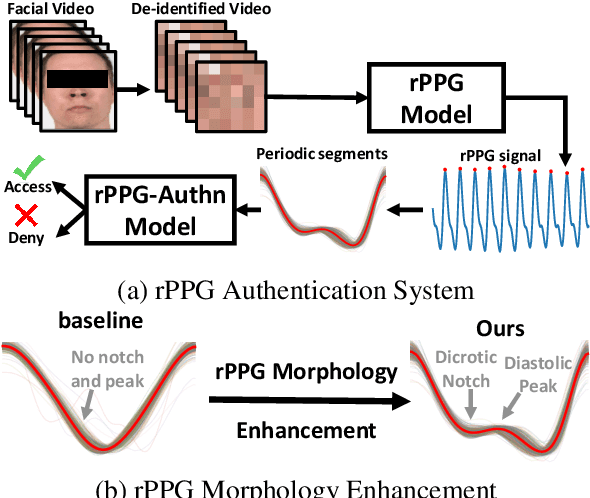
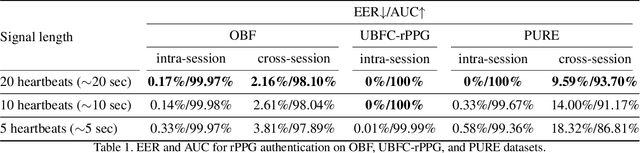
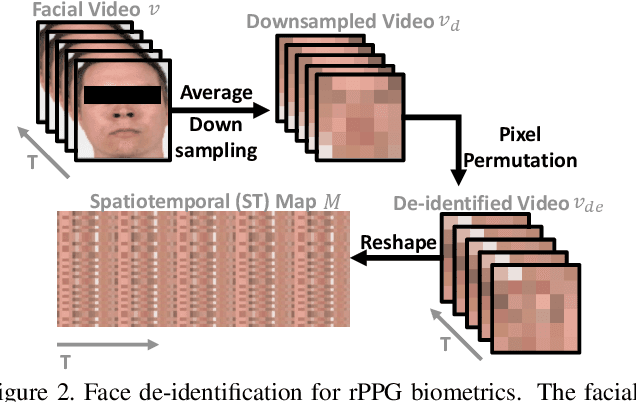
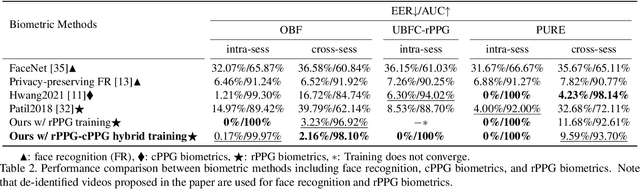
Abstract:Remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) is a non-contact method for measuring cardiac signals from facial videos, offering a convenient alternative to contact photoplethysmography (cPPG) obtained from contact sensors. Recent studies have shown that each individual possesses a unique cPPG signal morphology that can be utilized as a biometric identifier, which has inspired us to utilize the morphology of rPPG signals extracted from facial videos for person authentication. Since the facial appearance and rPPG are mixed in the facial videos, we first de-identify facial videos to remove facial appearance while preserving the rPPG information, which protects facial privacy and guarantees that only rPPG is used for authentication. The de-identified videos are fed into an rPPG model to get the rPPG signal morphology for authentication. In the first training stage, unsupervised rPPG training is performed to get coarse rPPG signals. In the second training stage, an rPPG-cPPG hybrid training is performed by incorporating external cPPG datasets to achieve rPPG biometric authentication and enhance rPPG signal morphology. Our approach needs only de-identified facial videos with subject IDs to train rPPG authentication models. The experimental results demonstrate that rPPG signal morphology hidden in facial videos can be used for biometric authentication. The code is available at https://github.com/zhaodongsun/rppg_biometrics.
TCCT-Net: Two-Stream Network Architecture for Fast and Efficient Engagement Estimation via Behavioral Feature Signals
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Engagement analysis finds various applications in healthcare, education, advertisement, services. Deep Neural Networks, used for analysis, possess complex architecture and need large amounts of input data, computational power, inference time. These constraints challenge embedding systems into devices for real-time use. To address these limitations, we present a novel two-stream feature fusion "Tensor-Convolution and Convolution-Transformer Network" (TCCT-Net) architecture. To better learn the meaningful patterns in the temporal-spatial domain, we design a "CT" stream that integrates a hybrid convolutional-transformer. In parallel, to efficiently extract rich patterns from the temporal-frequency domain and boost processing speed, we introduce a "TC" stream that uses Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT) to represent information in a 2D tensor form. Evaluated on the EngageNet dataset, the proposed method outperforms existing baselines, utilizing only two behavioral features (head pose rotations) compared to the 98 used in baseline models. Furthermore, comparative analysis shows TCCT-Net's architecture offers an order-of-magnitude improvement in inference speed compared to state-of-the-art image-based Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) methods. The code will be released at https://github.com/vedernikovphoto/TCCT_Net.
Analyzing Participants' Engagement during Online Meetings Using Unsupervised Remote Photoplethysmography with Behavioral Features
Apr 05, 2024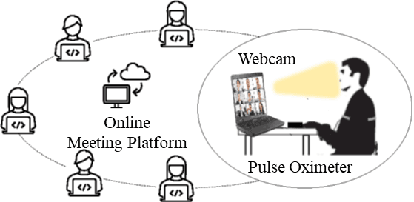

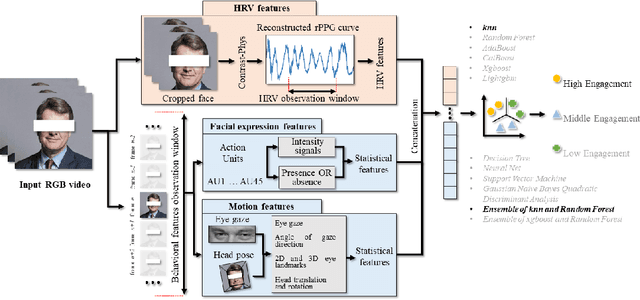

Abstract:Engagement measurement finds application in healthcare, education, advertisement, and services. The use of physiological and behavioral features is viable, but the impracticality of traditional physiological measurement arises due to the need for contact sensors. We demonstrate the feasibility of unsupervised remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) as an alternative for contact sensors in deriving heart rate variability (HRV) features, then fusing these with behavioral features to measure engagement in online group meetings. Firstly, a unique Engagement Dataset of online interactions among social workers is collected with granular engagement labels, offering insight into virtual meeting dynamics. Secondly, a pre-trained rPPG model is customized to reconstruct accurate rPPG signals from video meetings in an unsupervised manner, enabling the calculation of HRV features. Thirdly, the feasibility of estimating engagement from HRV features using short observation windows, with a notable enhancement when using longer observation windows of two to four minutes, is demonstrated. Fourthly, the effectiveness of behavioral cues is evaluated and fused with physiological data, which further enhances engagement estimation performance. An accuracy of 94% is achieved when only HRV features are used, eliminating the need for contact sensors or ground truth signals. The incorporation of behavioral cues raises the accuracy to 96%. Facial video analysis offers precise engagement measurement, beneficial for future applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge