Juyong Zhang
Channel Knowledge Map Construction: Recent Advances and Open Challenges
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Channel knowledge map (CKM) has emerged as a pivotal technology for environment-aware wireless communications and sensing, which provides a priori location-specific channel knowledge to facilitate network optimization. Efficient CKM construction is an important technical problem for its effective implementation. This article provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in CKM construction. First, we examine classical interpolation-based CKM construction methods, highlighting their limitations in practical deployments. Next, we explore image processing and generative artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, which leverage feature extraction to construct CKMs based on environmental knowledge. Furthermore, we present emerging wireless radiance field (WRF) frameworks that exploit neural radiance fields or Gaussian splatting to construct high-fidelity CKMs from sparse measurement data. Finally, we outline various future research directions in real-time and cross-domain CKM construction, as well as cost-efficient deployment of CKMs.
6D Channel Knowledge Map Construction via Bidirectional Wireless Gaussian Splatting
Oct 30, 2025
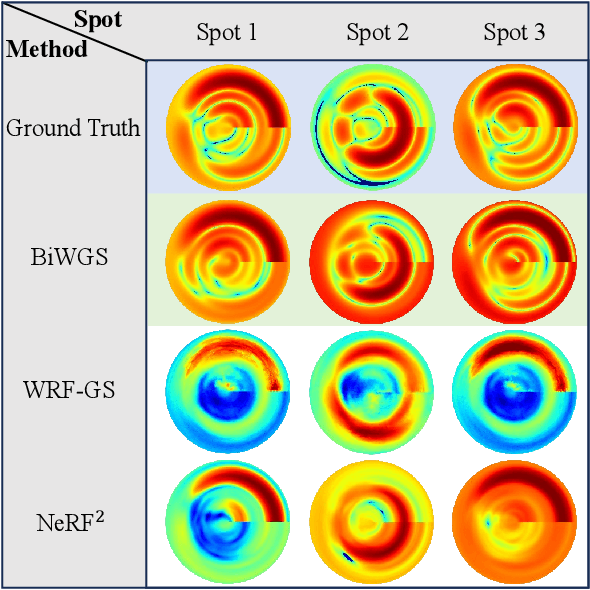
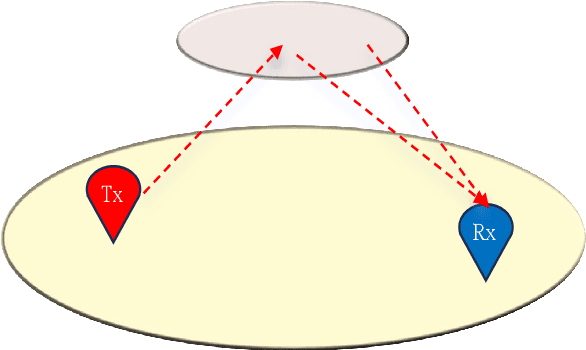
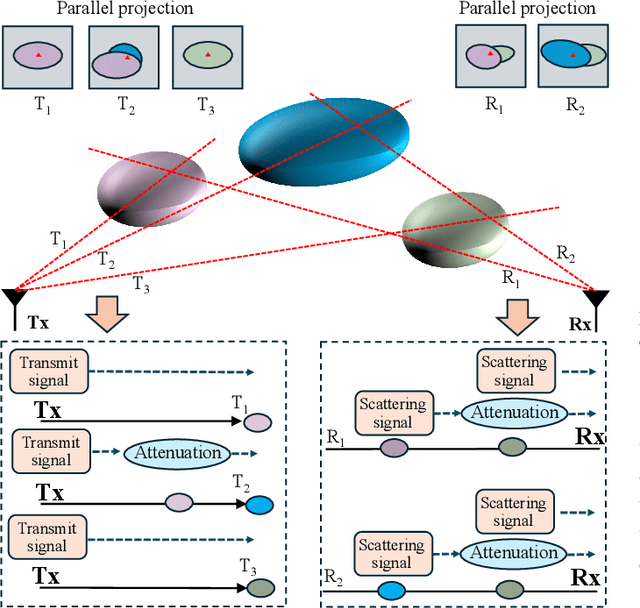
Abstract:This paper investigates the construction of channel knowledge map (CKM) from sparse channel measurements. Dif ferent from conventional two-/three-dimensional (2D/3D) CKM approaches assuming fixed base station configurations, we present a six-dimensional (6D) CKM framework named bidirectional wireless Gaussian splatting (BiWGS), which is capable of mod eling wireless channels across dynamic transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) positions in 3D space. BiWGS uses Gaussian el lipsoids to represent virtual scatterer clusters and environmental obstacles in the wireless environment. By properly learning the bidirectional scattering patterns and complex attenuation profiles based on channel measurements, these ellipsoids inherently cap ture the electromagnetic transmission characteristics of wireless environments, thereby accurately modeling signal transmission under varying transceiver configurations. Experiment results show that BiWGS significantly outperforms classic multi-layer perception (MLP) for the construction of 6D channel power gain map with varying Tx-Rx positions, and achieves spatial spectrum prediction accuracy comparable to the state-of-the art wireless radiation field Gaussian splatting (WRF-GS) for 3D CKM construction. This validates the capability of the proposed BiWGS in accomplishing dimensional expansion of 6D CKM construction, without compromising fidelity.
Joint Deblurring and 3D Reconstruction for Macrophotography
Oct 02, 2025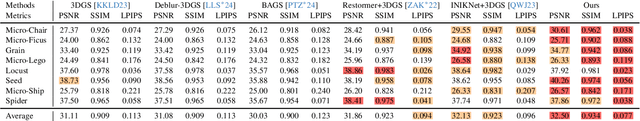
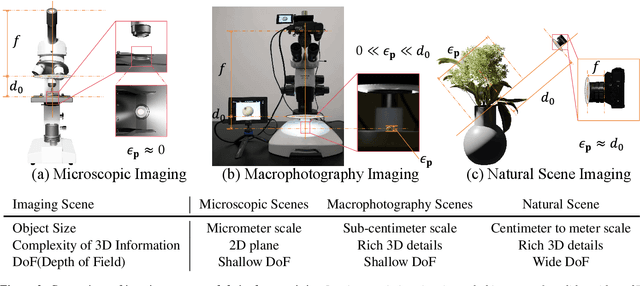
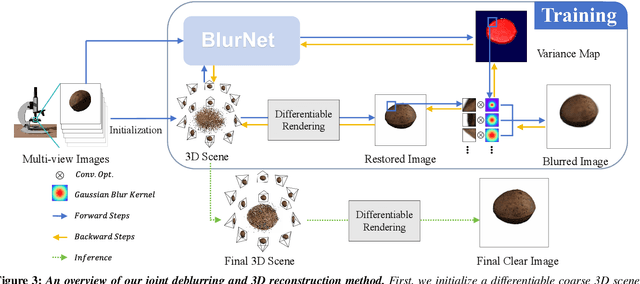

Abstract:Macro lens has the advantages of high resolution and large magnification, and 3D modeling of small and detailed objects can provide richer information. However, defocus blur in macrophotography is a long-standing problem that heavily hinders the clear imaging of the captured objects and high-quality 3D reconstruction of them. Traditional image deblurring methods require a large number of images and annotations, and there is currently no multi-view 3D reconstruction method for macrophotography. In this work, we propose a joint deblurring and 3D reconstruction method for macrophotography. Starting from multi-view blurry images captured, we jointly optimize the clear 3D model of the object and the defocus blur kernel of each pixel. The entire framework adopts a differentiable rendering method to self-supervise the optimization of the 3D model and the defocus blur kernel. Extensive experiments show that from a small number of multi-view images, our proposed method can not only achieve high-quality image deblurring but also recover high-fidelity 3D appearance.
DualReg: Dual-Space Filtering and Reinforcement for Rigid Registration
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Rigid registration, aiming to estimate a rigid transformation to align source and target data, play a crucial role in applications such as SLAM and 3D reconstruction. However, noisy, partially overlapping data and the need for real-time processing pose major challenges for rigid registration. Considering that feature-based matching can handle large transformation differences but suffers from limited accuracy, while local geometry-based matching can achieve fine-grained local alignment but relies heavily on a good initial transformation, we propose a novel dual-space paradigm to fully leverage the strengths of both approaches. First, we introduce an efficient filtering mechanism that incorporates a computationally lightweight single-point RANSAC algorithm followed by a refinement module to eliminate unreliable feature-based correspondences. Subsequently, we treat filtered correspondences as anchor points, extract geometric proxies, and formulates an effective objective function with a tailored solver to estimate the transformation. Experiments verify our method's effectiveness, as shown by achieving up to a 32x CPU-time speedup over MAC on KITTI with comparable accuracy.
Controlling Avatar Diffusion with Learnable Gaussian Embedding
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have made significant progress in digital human generation. However, most existing models still struggle to maintain 3D consistency, temporal coherence, and motion accuracy. A key reason for these shortcomings is the limited representation ability of commonly used control signals(e.g., landmarks, depth maps, etc.). In addition, the lack of diversity in identity and pose variations in public datasets further hinders progress in this area. In this paper, we analyze the shortcomings of current control signals and introduce a novel control signal representation that is optimizable, dense, expressive, and 3D consistent. Our method embeds a learnable neural Gaussian onto a parametric head surface, which greatly enhances the consistency and expressiveness of diffusion-based head models. Regarding the dataset, we synthesize a large-scale dataset with multiple poses and identities. In addition, we use real/synthetic labels to effectively distinguish real and synthetic data, minimizing the impact of imperfections in synthetic data on the generated head images. Extensive experiments show that our model outperforms existing methods in terms of realism, expressiveness, and 3D consistency. Our code, synthetic datasets, and pre-trained models will be released in our project page: https://ustc3dv.github.io/Learn2Control/
Scalable and High-Quality Neural Implicit Representation for 3D Reconstruction
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Various SDF-based neural implicit surface reconstruction methods have been proposed recently, and have demonstrated remarkable modeling capabilities. However, due to the global nature and limited representation ability of a single network, existing methods still suffer from many drawbacks, such as limited accuracy and scale of the reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a versatile, scalable and high-quality neural implicit representation to address these issues. We integrate a divide-and-conquer approach into the neural SDF-based reconstruction. Specifically, we model the object or scene as a fusion of multiple independent local neural SDFs with overlapping regions. The construction of our representation involves three key steps: (1) constructing the distribution and overlap relationship of the local radiance fields based on object structure or data distribution, (2) relative pose registration for adjacent local SDFs, and (3) SDF blending. Thanks to the independent representation of each local region, our approach can not only achieve high-fidelity surface reconstruction, but also enable scalable scene reconstruction. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and practicality of our proposed method.
Matching Free Depth Recovery from Structured Light
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:We present a novel approach for depth estimation from images captured by structured light systems. Unlike many previous methods that rely on image matching process, our approach uses a density voxel grid to represent scene geometry, which is trained via self-supervised differentiable volume rendering. Our method leverages color fields derived from projected patterns in structured light systems during the rendering process, enabling the isolated optimization of the geometry field. This contributes to faster convergence and high-quality output. Additionally, we incorporate normalized device coordinates (NDC), a distortion loss, and a novel surface-based color loss to enhance geometric fidelity. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing matching-based techniques in geometric performance for few-shot scenarios, achieving approximately a 60% reduction in average estimated depth errors on synthetic scenes and about 30% on real-world captured scenes. Furthermore, our approach delivers fast training, with a speed roughly three times faster than previous matching-free methods that employ implicit representations.
D$^3$-Human: Dynamic Disentangled Digital Human from Monocular Video
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:We introduce D$^3$-Human, a method for reconstructing Dynamic Disentangled Digital Human geometry from monocular videos. Past monocular video human reconstruction primarily focuses on reconstructing undecoupled clothed human bodies or only reconstructing clothing, making it difficult to apply directly in applications such as animation production. The challenge in reconstructing decoupled clothing and body lies in the occlusion caused by clothing over the body. To this end, the details of the visible area and the plausibility of the invisible area must be ensured during the reconstruction process. Our proposed method combines explicit and implicit representations to model the decoupled clothed human body, leveraging the robustness of explicit representations and the flexibility of implicit representations. Specifically, we reconstruct the visible region as SDF and propose a novel human manifold signed distance field (hmSDF) to segment the visible clothing and visible body, and then merge the visible and invisible body. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that, compared with existing reconstruction schemes, D$^3$-Human can achieve high-quality decoupled reconstruction of the human body wearing different clothing, and can be directly applied to clothing transfer and animation.
SparseLGS: Sparse View Language Embedded Gaussian Splatting
Dec 03, 2024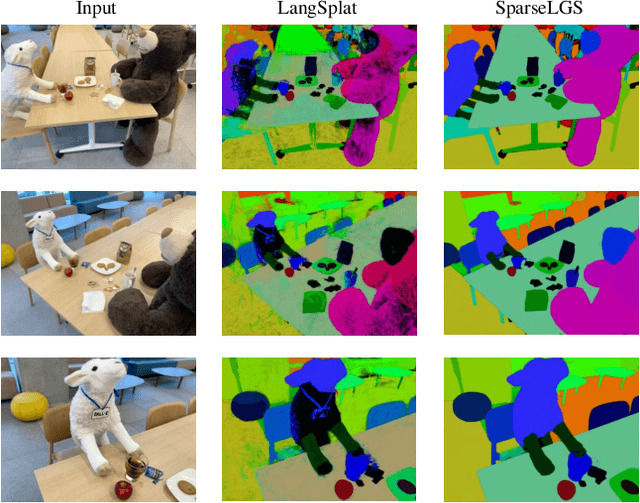
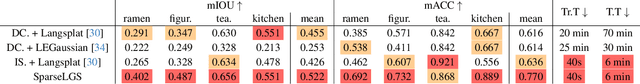
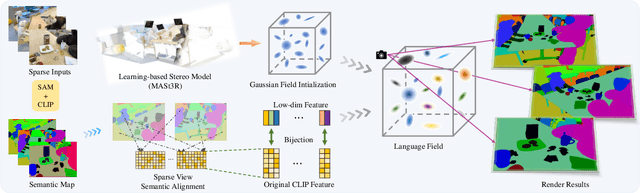
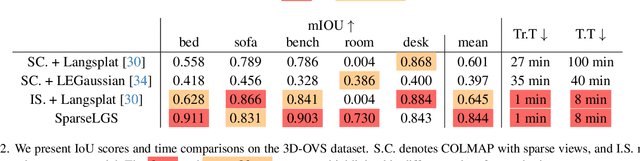
Abstract:Recently, several studies have combined Gaussian Splatting to obtain scene representations with language embeddings for open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding. While these methods perform well, they essentially require very dense multi-view inputs, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. In this work, we propose SparseLGS to address the challenge of 3D scene understanding with pose-free and sparse view input images. Our method leverages a learning-based dense stereo model to handle pose-free and sparse inputs, and a three-step region matching approach to address the multi-view semantic inconsistency problem, which is especially important for sparse inputs. Different from directly learning high-dimensional CLIP features, we extract low-dimensional information and build bijections to avoid excessive learning and storage costs. We introduce a reconstruction loss during semantic training to improve Gaussian positions and shapes. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to address the 3D semantic field problem with sparse pose-free inputs. Experimental results show that SparseLGS achieves comparable quality when reconstructing semantic fields with fewer inputs (3-4 views) compared to previous SOTA methods with dense input. Besides, when using the same sparse input, SparseLGS leads significantly in quality and heavily improves the computation speed (5$\times$ speedup). Project page: {\tt\small \url{https://ustc3dv.github.io/SparseLGS}}
One Shot, One Talk: Whole-body Talking Avatar from a Single Image
Dec 02, 2024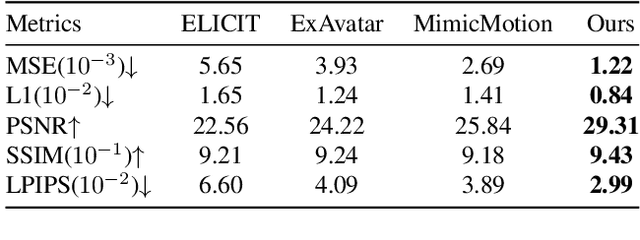
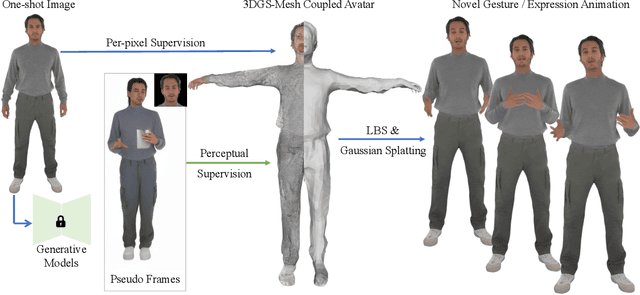
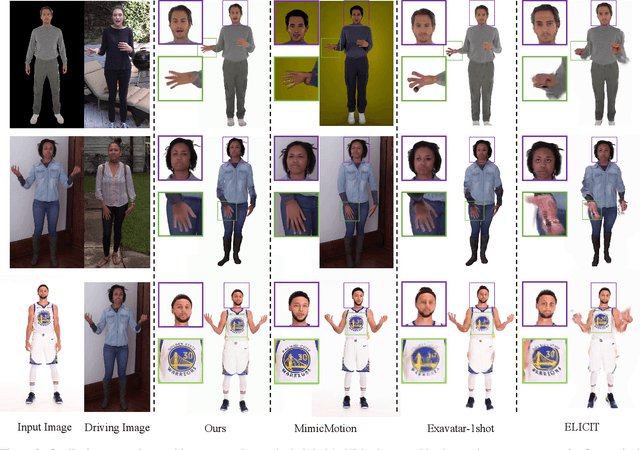

Abstract:Building realistic and animatable avatars still requires minutes of multi-view or monocular self-rotating videos, and most methods lack precise control over gestures and expressions. To push this boundary, we address the challenge of constructing a whole-body talking avatar from a single image. We propose a novel pipeline that tackles two critical issues: 1) complex dynamic modeling and 2) generalization to novel gestures and expressions. To achieve seamless generalization, we leverage recent pose-guided image-to-video diffusion models to generate imperfect video frames as pseudo-labels. To overcome the dynamic modeling challenge posed by inconsistent and noisy pseudo-videos, we introduce a tightly coupled 3DGS-mesh hybrid avatar representation and apply several key regularizations to mitigate inconsistencies caused by imperfect labels. Extensive experiments on diverse subjects demonstrate that our method enables the creation of a photorealistic, precisely animatable, and expressive whole-body talking avatar from just a single image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge