Su Yang
Fudan University
Robust Moment Identification for Nonlinear PDEs via a Neural ODE Approach
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:We propose a data-driven framework for learning reduced-order moment dynamics from PDE-governed systems using Neural ODEs. In contrast to derivative-based methods like SINDy, which necessitate densely sampled data and are sensitive to noise, our approach based on Neural ODEs directly models moment trajectories, enabling robust learning from sparse and potentially irregular time series. Using as an application platform the nonlinear Schr\"{o}dinger equation, the framework accurately recovers governing moment dynamics when closure is available, even with limited and irregular observations. For systems without analytical closure, we introduce a data-driven coordinate transformation strategy based on Stiefel manifold optimization, enabling the discovery of low-dimensional representations in which the moment dynamics become closed, facilitating interpretable and reliable modeling. We also explore cases where a closure model is not known, such as a Fisher-KPP reaction-diffusion system. Here we demonstrate that Neural ODEs can still effectively approximate the unclosed moment dynamics and achieve superior extrapolation accuracy compared to physical-expert-derived ODE models. This advantage remains robust even under sparse and irregular sampling, highlighting the method's robustness in data-limited settings. Our results highlight the Neural ODE framework as a powerful and flexible tool for learning interpretable, low-dimensional moment dynamics in complex PDE-governed systems.
Promoting SAM for Camouflaged Object Detection via Selective Key Point-based Guidance
May 14, 2025Abstract:Big model has emerged as a new research paradigm that can be applied to various down-stream tasks with only minor effort for domain adaption. Correspondingly, this study tackles Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) leveraging the Segment Anything Model (SAM). The previous studies declared that SAM is not workable for COD but this study reveals that SAM works if promoted properly, for which we devise a new framework to render point promotions: First, we develop the Promotion Point Targeting Network (PPT-net) to leverage multi-scale features in predicting the probabilities of camouflaged objects' presences at given candidate points over the image. Then, we develop a key point selection (KPS) algorithm to deploy both positive and negative point promotions contrastively to SAM to guide the segmentation. It is the first work to facilitate big model for COD and achieves plausible results experimentally over the existing methods on 3 data sets under 6 metrics. This study demonstrates an off-the-shelf methodology for COD by leveraging SAM, which gains advantage over designing professional models from scratch, not only in performance, but also in turning the problem to a less challenging task, that is, seeking informative but not exactly precise promotions.
SimMIL: A Universal Weakly Supervised Pre-Training Framework for Multi-Instance Learning in Whole Slide Pathology Images
May 10, 2025Abstract:Various multi-instance learning (MIL) based approaches have been developed and successfully applied to whole-slide pathological images (WSI). Existing MIL methods emphasize the importance of feature aggregators, but largely neglect the instance-level representation learning. They assume that the availability of a pre-trained feature extractor can be directly utilized or fine-tuned, which is not always the case. This paper proposes to pre-train feature extractor for MIL via a weakly-supervised scheme, i.e., propagating the weak bag-level labels to the corresponding instances for supervised learning. To learn effective features for MIL, we further delve into several key components, including strong data augmentation, a non-linear prediction head and the robust loss function. We conduct experiments on common large-scale WSI datasets and find it achieves better performance than other pre-training schemes (e.g., ImageNet pre-training and self-supervised learning) in different downstream tasks. We further show the compatibility and scalability of the proposed scheme by deploying it in fine-tuning the pathological-specific models and pre-training on merged multiple datasets. To our knowledge, this is the first work focusing on the representation learning for MIL.
Learning Compositional Transferability of Time Series for Source-Free Domain Adaptation
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Domain adaptation is challenging for time series classification due to the highly dynamic nature. This study tackles the most difficult subtask when both target labels and source data are inaccessible, namely, source-free domain adaptation. To reuse the classification backbone pre-trained on source data, time series reconstruction is a sound solution that aligns target and source time series by minimizing the reconstruction errors of both. However, simply fine-tuning the source pre-trained reconstruction model on target data may lose the learnt priori, and it struggles to accommodate domain varying temporal patterns in a single encoder-decoder. Therefore, this paper tries to disentangle the composition of domain transferability by using a compositional architecture for time series reconstruction. Here, the preceding component is a U-net frozen since pre-trained, the output of which during adaptation is the initial reconstruction of a given target time series, acting as a coarse step to prompt the subsequent finer adaptation. The following pipeline for finer adaptation includes two parallel branches: The source replay branch using a residual link to preserve the output of U-net, and the offset compensation branch that applies an additional autoencoder (AE) to further warp U-net's output. By deploying a learnable factor on either branch to scale their composition in the final output of reconstruction, the data transferability is disentangled and the learnt reconstructive capability from source data is retained. During inference, aside from the batch-level optimization in the training, we search at test time stability-aware rescaling of source replay branch to tolerate instance-wise variation. The experimental results show that such compositional architecture of time series reconstruction leads to SOTA performance on 3 widely used benchmarks.
ColonScopeX: Leveraging Explainable Expert Systems with Multimodal Data for Improved Early Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks as the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths and the third most prevalent malignant tumour worldwide. Early detection of CRC remains problematic due to its non-specific and often embarrassing symptoms, which patients frequently overlook or hesitate to report to clinicians. Crucially, the stage at which CRC is diagnosed significantly impacts survivability, with a survival rate of 80-95\% for Stage I and a stark decline to 10\% for Stage IV. Unfortunately, in the UK, only 14.4\% of cases are diagnosed at the earliest stage (Stage I). In this study, we propose ColonScopeX, a machine learning framework utilizing explainable AI (XAI) methodologies to enhance the early detection of CRC and pre-cancerous lesions. Our approach employs a multimodal model that integrates signals from blood sample measurements, processed using the Savitzky-Golay algorithm for fingerprint smoothing, alongside comprehensive patient metadata, including medication history, comorbidities, age, weight, and BMI. By leveraging XAI techniques, we aim to render the model's decision-making process transparent and interpretable, thereby fostering greater trust and understanding in its predictions. The proposed framework could be utilised as a triage tool or a screening tool of the general population. This research highlights the potential of combining diverse patient data sources and explainable machine learning to tackle critical challenges in medical diagnostics.
From Attributes to Natural Language: A Survey and Foresight on Text-based Person Re-identification
Jul 31, 2024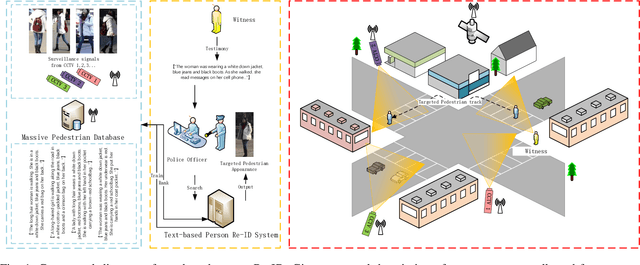
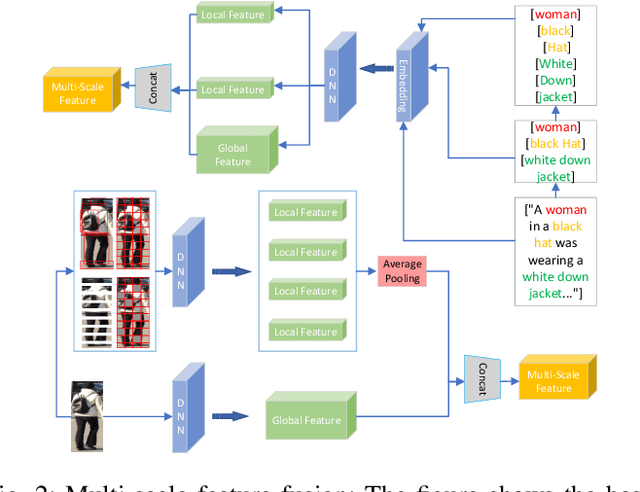
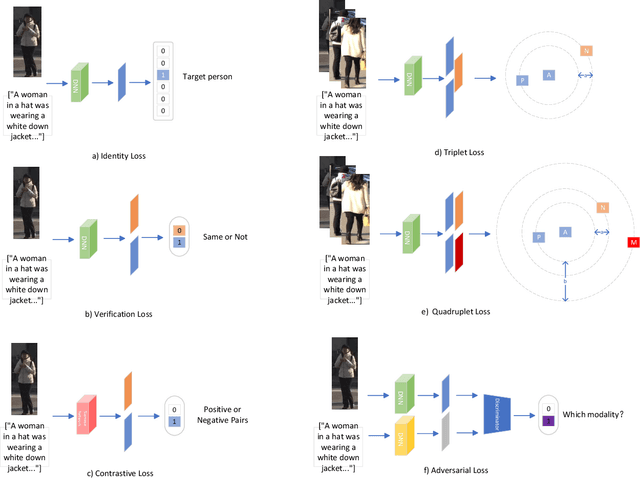
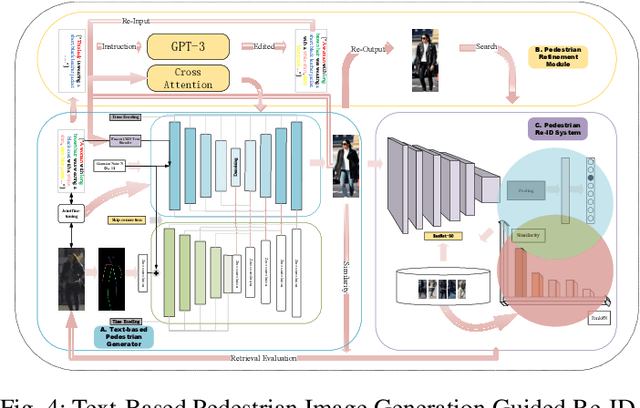
Abstract:Text-based person re-identification (Re-ID) is a challenging topic in the field of complex multimodal analysis, its ultimate aim is to recognize specific pedestrians by scrutinizing attributes/natural language descriptions. Despite the wide range of applicable areas such as security surveillance, video retrieval, person tracking, and social media analytics, there is a notable absence of comprehensive reviews dedicated to summarizing the text-based person Re-ID from a technical perspective. To address this gap, we propose to introduce a taxonomy spanning Evaluation, Strategy, Architecture, and Optimization dimensions, providing a comprehensive survey of the text-based person Re-ID task. We start by laying the groundwork for text-based person Re-ID, elucidating fundamental concepts related to attribute/natural language-based identification. Then a thorough examination of existing benchmark datasets and metrics is presented. Subsequently, we further delve into prevalent feature extraction strategies employed in text-based person Re-ID research, followed by a concise summary of common network architectures within the domain. Prevalent loss functions utilized for model optimization and modality alignment in text-based person Re-ID are also scrutinized. To conclude, we offer a concise summary of our findings, pinpointing challenges in text-based person Re-ID. In response to these challenges, we outline potential avenues for future open-set text-based person Re-ID and present a baseline architecture for text-based pedestrian image generation-guided re-identification(TBPGR).
LLaMandement: Large Language Models for Summarization of French Legislative Proposals
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:This report introduces LLaMandement, a state-of-the-art Large Language Model, fine-tuned by the French government and designed to enhance the efficiency and efficacy of processing parliamentary sessions (including the production of bench memoranda and documents required for interministerial meetings) by generating neutral summaries of legislative proposals. Addressing the administrative challenges of manually processing a growing volume of legislative amendments, LLaMandement stands as a significant legal technological milestone, providing a solution that exceeds the scalability of traditional human efforts while matching the robustness of a specialized legal drafter. We release all our fine-tuned models and training data to the community.
Predicting Token Impact Towards Efficient Vision Transformer
May 24, 2023Abstract:Token filtering to reduce irrelevant tokens prior to self-attention is a straightforward way to enable efficient vision Transformer. This is the first work to view token filtering from a feature selection perspective, where we weigh the importance of a token according to how much it can change the loss once masked. If the loss changes greatly after masking a token of interest, it means that such a token has a significant impact on the final decision and is thus relevant. Otherwise, the token is less important for the final decision, so it can be filtered out. After applying the token filtering module generalized from the whole training data, the token number fed to the self-attention module can be obviously reduced in the inference phase, leading to much fewer computations in all the subsequent self-attention layers. The token filter can be realized using a very simple network, where we utilize multi-layer perceptron. Except for the uniqueness of performing token filtering only once from the very beginning prior to self-attention, the other core feature making our method different from the other token filters lies in the predictability of token impact from a feature selection point of view. The experiments show that the proposed method provides an efficient way to approach a light weighted model after optimized with a backbone by means of fine tune, which is easy to be deployed in comparison with the existing methods based on training from scratch.
SIEDOB: Semantic Image Editing by Disentangling Object and Background
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:Semantic image editing provides users with a flexible tool to modify a given image guided by a corresponding segmentation map. In this task, the features of the foreground objects and the backgrounds are quite different. However, all previous methods handle backgrounds and objects as a whole using a monolithic model. Consequently, they remain limited in processing content-rich images and suffer from generating unrealistic objects and texture-inconsistent backgrounds. To address this issue, we propose a novel paradigm, \textbf{S}emantic \textbf{I}mage \textbf{E}diting by \textbf{D}isentangling \textbf{O}bject and \textbf{B}ackground (\textbf{SIEDOB}), the core idea of which is to explicitly leverages several heterogeneous subnetworks for objects and backgrounds. First, SIEDOB disassembles the edited input into background regions and instance-level objects. Then, we feed them into the dedicated generators. Finally, all synthesized parts are embedded in their original locations and utilize a fusion network to obtain a harmonized result. Moreover, to produce high-quality edited images, we propose some innovative designs, including Semantic-Aware Self-Propagation Module, Boundary-Anchored Patch Discriminator, and Style-Diversity Object Generator, and integrate them into SIEDOB. We conduct extensive experiments on Cityscapes and ADE20K-Room datasets and exhibit that our method remarkably outperforms the baselines, especially in synthesizing realistic and diverse objects and texture-consistent backgrounds.
Reference-Guided Large-Scale Face Inpainting with Identity and Texture Control
Mar 13, 2023Abstract:Face inpainting aims at plausibly predicting missing pixels of face images within a corrupted region. Most existing methods rely on generative models learning a face image distribution from a big dataset, which produces uncontrollable results, especially with large-scale missing regions. To introduce strong control for face inpainting, we propose a novel reference-guided face inpainting method that fills the large-scale missing region with identity and texture control guided by a reference face image. However, generating high-quality results under imposing two control signals is challenging. To tackle such difficulty, we propose a dual control one-stage framework that decouples the reference image into two levels for flexible control: High-level identity information and low-level texture information, where the identity information figures out the shape of the face and the texture information depicts the component-aware texture. To synthesize high-quality results, we design two novel modules referred to as Half-AdaIN and Component-Wise Style Injector (CWSI) to inject the two kinds of control information into the inpainting processing. Our method produces realistic results with identity and texture control faithful to reference images. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first work to concurrently apply identity and component-level controls in face inpainting to promise more precise and controllable results. Code is available at https://github.com/WuyangLuo/RefFaceInpainting
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge