Daji Ergu
SSS: Semi-Supervised SAM-2 with Efficient Prompting for Medical Imaging Segmentation
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:In the era of information explosion, efficiently leveraging large-scale unlabeled data while minimizing the reliance on high-quality pixel-level annotations remains a critical challenge in the field of medical imaging. Semi-supervised learning (SSL) enhances the utilization of unlabeled data by facilitating knowledge transfer, significantly improving the performance of fully supervised models and emerging as a highly promising research direction in medical image analysis. Inspired by the ability of Vision Foundation Models (e.g., SAM-2) to provide rich prior knowledge, we propose SSS (Semi-Supervised SAM-2), a novel approach that leverages SAM-2's robust feature extraction capabilities to uncover latent knowledge in unlabeled medical images, thus effectively enhancing feature support for fully supervised medical image segmentation. Specifically, building upon the single-stream "weak-to-strong" consistency regularization framework, this paper introduces a Discriminative Feature Enhancement (DFE) mechanism to further explore the feature discrepancies introduced by various data augmentation strategies across multiple views. By leveraging feature similarity and dissimilarity across multi-scale augmentation techniques, the method reconstructs and models the features, thereby effectively optimizing the salient regions. Furthermore, a prompt generator is developed that integrates Physical Constraints with a Sliding Window (PCSW) mechanism to generate input prompts for unlabeled data, fulfilling SAM-2's requirement for additional prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method for semi-supervised medical image segmentation on two multi-label datasets, i.e., ACDC and BHSD. Notably, SSS achieves an average Dice score of 53.15 on BHSD, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art method by +3.65 Dice. Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/SSS.
DOEI: Dual Optimization of Embedding Information for Attention-Enhanced Class Activation Maps
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) typically utilizes limited semantic annotations to obtain initial Class Activation Maps (CAMs). However, due to the inadequate coupling between class activation responses and semantic information in high-dimensional space, the CAM is prone to object co-occurrence or under-activation, resulting in inferior recognition accuracy. To tackle this issue, we propose DOEI, Dual Optimization of Embedding Information, a novel approach that reconstructs embedding representations through semantic-aware attention weight matrices to optimize the expression capability of embedding information. Specifically, DOEI amplifies tokens with high confidence and suppresses those with low confidence during the class-to-patch interaction. This alignment of activation responses with semantic information strengthens the propagation and decoupling of target features, enabling the generated embeddings to more accurately represent target features in high-level semantic space. In addition, we propose a hybrid-feature alignment module in DOEI that combines RGB values, embedding-guided features, and self-attention weights to increase the reliability of candidate tokens. Comprehensive experiments show that DOEI is an effective plug-and-play module that empowers state-of-the-art visual transformer-based WSSS models to significantly improve the quality of CAMs and segmentation performance on popular benchmarks, including PASCAL VOC (+3.6%, +1.5%, +1.2% mIoU) and MS COCO (+1.2%, +1.6% mIoU). Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/DOEI.
SegKAN: High-Resolution Medical Image Segmentation with Long-Distance Dependencies
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Hepatic vessels in computed tomography scans often suffer from image fragmentation and noise interference, making it difficult to maintain vessel integrity and posing significant challenges for vessel segmentation. To address this issue, we propose an innovative model: SegKAN. First, we improve the conventional embedding module by adopting a novel convolutional network structure for image embedding, which smooths out image noise and prevents issues such as gradient explosion in subsequent stages. Next, we transform the spatial relationships between Patch blocks into temporal relationships to solve the problem of capturing positional relationships between Patch blocks in traditional Vision Transformer models. We conducted experiments on a Hepatic vessel dataset, and compared to the existing state-of-the-art model, the Dice score improved by 1.78%. These results demonstrate that the proposed new structure effectively enhances the segmentation performance of high-resolution extended objects. Code will be available at https://github.com/goblin327/SegKAN
Medical AI for Early Detection of Lung Cancer: A Survey
Oct 18, 2024



Abstract:Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, making early diagnosis critical for improving therapeutic outcomes and patient prognosis. Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems, which analyze CT images, have proven effective in detecting and classifying pulmonary nodules, significantly enhancing the detection rate of early-stage lung cancer. Although traditional machine learning algorithms have been valuable, they exhibit limitations in handling complex sample data. The recent emergence of deep learning has revolutionized medical image analysis, driving substantial advancements in this field. This review focuses on recent progress in deep learning for pulmonary nodule detection, segmentation, and classification. Traditional machine learning methods, such as SVM and KNN, have shown limitations, paving the way for advanced approaches like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), and Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). The integration of ensemble models and novel techniques is also discussed, emphasizing the latest developments in lung cancer diagnosis. Deep learning algorithms, combined with various analytical techniques, have markedly improved the accuracy and efficiency of pulmonary nodule analysis, surpassing traditional methods, particularly in nodule classification. Although challenges remain, continuous technological advancements are expected to further strengthen the role of deep learning in medical diagnostics, especially for early lung cancer detection and diagnosis. A comprehensive list of lung cancer detection models reviewed in this work is available at https://github.com/CaiGuoHui123/Awesome-Lung-Cancer-Detection
MSDet: Receptive Field Enhanced Multiscale Detection for Tiny Pulmonary Nodule
Sep 21, 2024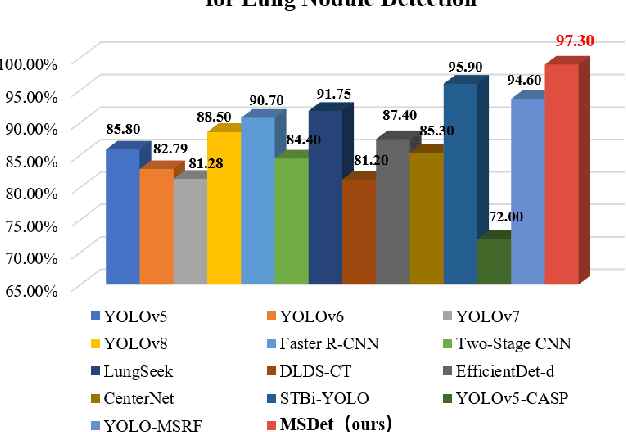
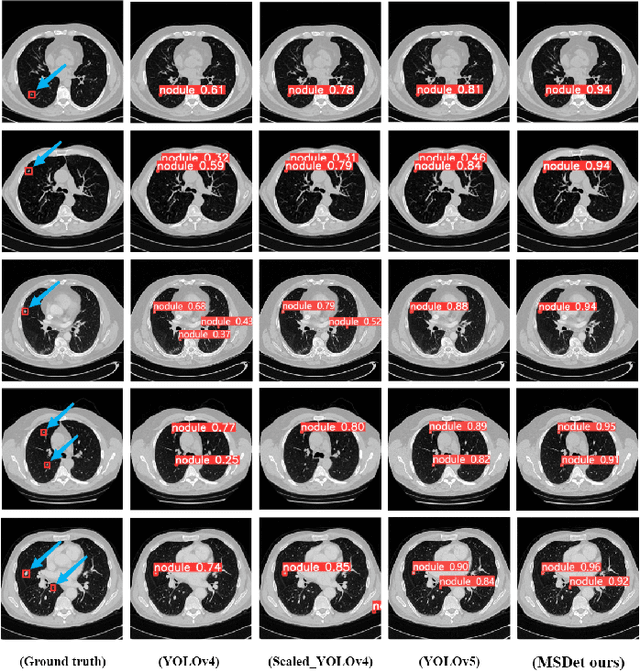
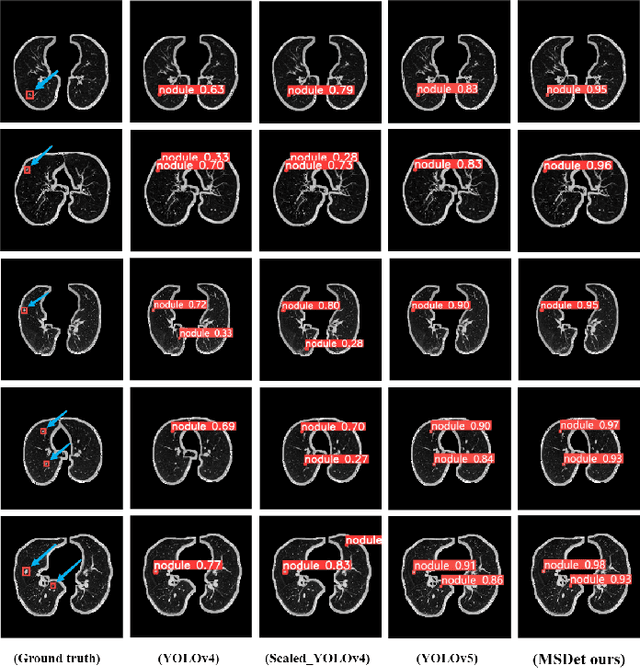
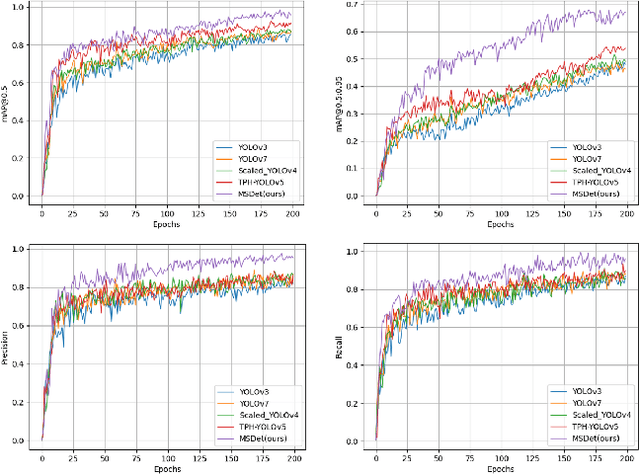
Abstract:Pulmonary nodules are critical indicators for the early diagnosis of lung cancer, making their detection essential for timely treatment. However, traditional CT imaging methods suffered from cumbersome procedures, low detection rates, and poor localization accuracy. The subtle differences between pulmonary nodules and surrounding tissues in complex lung CT images, combined with repeated downsampling in feature extraction networks, often lead to missed or false detections of small nodules. Existing methods such as FPN, with its fixed feature fusion and limited receptive field, struggle to effectively overcome these issues. To address these challenges, our paper proposed three key contributions: Firstly, we proposed MSDet, a multiscale attention and receptive field network for detecting tiny pulmonary nodules. Secondly, we proposed the extended receptive domain (ERD) strategy to capture richer contextual information and reduce false positives caused by nodule occlusion. We also proposed the position channel attention mechanism (PCAM) to optimize feature learning and reduce multiscale detection errors, and designed the tiny object detection block (TODB) to enhance the detection of tiny nodules. Lastly, we conducted thorough experiments on the public LUNA16 dataset, achieving state-of-the-art performance, with an mAP improvement of 8.8% over the previous state-of-the-art method YOLOv8. These advancements significantly boosted detection accuracy and reliability, providing a more effective solution for early lung cancer diagnosis. The code will be available at https://github.com/CaiGuoHui123/MSDet
MedDet: Generative Adversarial Distillation for Efficient Cervical Disc Herniation Detection
Aug 30, 2024Abstract:Cervical disc herniation (CDH) is a prevalent musculoskeletal disorder that significantly impacts health and requires labor-intensive analysis from experts. Despite advancements in automated detection of medical imaging, two significant challenges hinder the real-world application of these methods. First, the computational complexity and resource demands present a significant gap for real-time application. Second, noise in MRI reduces the effectiveness of existing methods by distorting feature extraction. To address these challenges, we propose three key contributions: Firstly, we introduced MedDet, which leverages the multi-teacher single-student knowledge distillation for model compression and efficiency, meanwhile integrating generative adversarial training to enhance performance. Additionally, we customize the second-order nmODE to improve the model's resistance to noise in MRI. Lastly, we conducted comprehensive experiments on the CDH-1848 dataset, achieving up to a 5% improvement in mAP compared to previous methods. Our approach also delivers over 5 times faster inference speed, with approximately 67.8% reduction in parameters and 36.9% reduction in FLOPs compared to the teacher model. These advancements significantly enhance the performance and efficiency of automated CDH detection, demonstrating promising potential for future application in clinical practice. See project website https://steve-zeyu-zhang.github.io/MedDet
SegStitch: Multidimensional Transformer for Robust and Efficient Medical Imaging Segmentation
Aug 01, 2024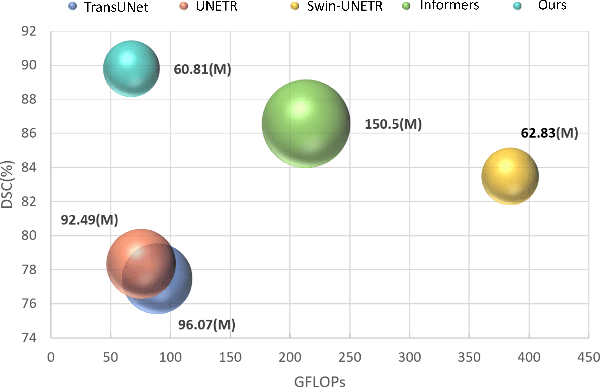

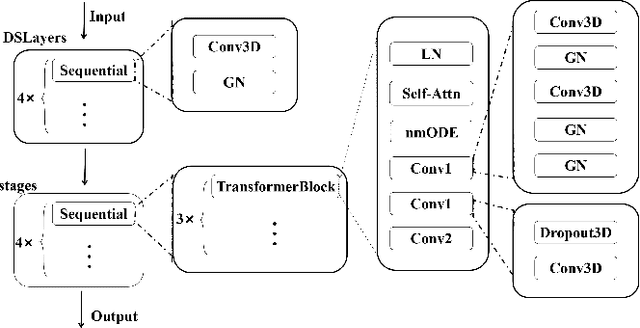
Abstract:Medical imaging segmentation plays a significant role in the automatic recognition and analysis of lesions. State-of-the-art methods, particularly those utilizing transformers, have been prominently adopted in 3D semantic segmentation due to their superior performance in scalability and generalizability. However, plain vision transformers encounter challenges due to their neglect of local features and their high computational complexity. To address these challenges, we introduce three key contributions: Firstly, we proposed SegStitch, an innovative architecture that integrates transformers with denoising ODE blocks. Instead of taking whole 3D volumes as inputs, we adapt axial patches and customize patch-wise queries to ensure semantic consistency. Additionally, we conducted extensive experiments on the BTCV and ACDC datasets, achieving improvements up to 11.48% and 6.71% respectively in mDSC, compared to state-of-the-art methods. Lastly, our proposed method demonstrates outstanding efficiency, reducing the number of parameters by 36.7% and the number of FLOPS by 10.7% compared to UNETR. This advancement holds promising potential for adapting our method to real-world clinical practice. The code will be available at https://github.com/goblin327/SegStitch
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge