Binhang Yuan
IMMACULATE: A Practical LLM Auditing Framework via Verifiable Computation
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:Commercial large language models are typically deployed as black-box API services, requiring users to trust providers to execute inference correctly and report token usage honestly. We present IMMACULATE, a practical auditing framework that detects economically motivated deviations-such as model substitution, quantization abuse, and token overbilling-without trusted hardware or access to model internals. IMMACULATE selectively audits a small fraction of requests using verifiable computation, achieving strong detection guarantees while amortizing cryptographic overhead. Experiments on dense and MoE models show that IMMACULATE reliably distinguishes benign and malicious executions with under 1% throughput overhead. Our code is published at https://github.com/guo-yanpei/Immaculate.
S2SServiceBench: A Multimodal Benchmark for Last-Mile S2S Climate Services
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Subseasonal-to-seasonal (S2S) forecasts play an essential role in providing a decision-critical weeks-to-months planning window for climate resilience and sustainability, yet a growing bottleneck is the last-mile gap: translating scientific forecasts into trusted, actionable climate services, requiring reliable multimodal understanding and decision-facing reasoning under uncertainty. Meanwhile, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and corresponding agentic paradigms have made rapid progress in supporting various workflows, but it remains unclear whether they can reliably generate decision-making deliverables from operational service products (e.g., actionable signal comprehension, decision-making handoff, and decision analysis & planning) under uncertainty. We introduce S2SServiceBench, a multimodal benchmark for last-mile S2S climate services curated from an operational climate-service system to evaluate this capability. S2SServiceBenchcovers 10 service products with about 150+ expert-selected cases in total, spanning six application domains - Agriculture, Disasters, Energy, Finance, Health, and Shipping. Each case is instantiated at three service levels, yielding around 500 tasks and 1,000+ evaluation items across climate resilience and sustainability applications. Using S2SServiceBench, we benchmark state-of-the-art MLLMs and agents, and analyze performance across products and service levels, revealing persistent challenges in S2S service plot understanding and reasoning - namely, actionable signal comprehension, operationalizing uncertainty into executable handoffs, and stable, evidence-grounded analysis and planning for dynamic hazards-while offering actionable guidance for building future climate-service agents.
AREAL-DTA: Dynamic Tree Attention for Efficient Reinforcement Learning of Large Language Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) based post-training for large language models (LLMs) is computationally expensive, as it generates many rollout sequences that could frequently share long token prefixes. Existing RL frameworks usually process these sequences independently, repeatedly recomputing identical prefixes during forward and backward passes during policy model training, leading to substantial inefficiencies in computation and memory usage. Although prefix sharing naturally induces a tree structure over rollouts, prior tree-attention-based solutions rely on fully materialized attention masks and scale poorly in RL settings. In this paper, we introduce AREAL-DTA to efficiently exploit prefix sharing in RL training. AREAL-DTA employs a depth-first-search (DFS)-based execution strategy that dynamically traverses the rollout prefix tree during both forward and backward computation, materializing only a single root-to-leaf path at a time. To further improve scalability, AREAL-DTA incorporates a load-balanced distributed batching mechanism that dynamically constructs and processes prefix trees across multiple GPUs. Across the popular RL post-training workload, AREAL-DTA achieves up to $8.31\times$ in $τ^2$-bench higher training throughput.
Flash Sparse Attention: An Alternative Efficient Implementation of Native Sparse Attention Kernel
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in sparse attention mechanisms has demonstrated strong potential for reducing the computational cost of long-context training and inference in large language models (LLMs). Native Sparse Attention (NSA), a state-of-the-art approach, introduces natively trainable, hardware-aligned sparse attention that delivers substantial system-level performance gains while maintaining accuracy comparable to full attention. However, the kernel implementation of NSA relies on a query-grouping strategy that is efficient only with large Grouped Query Attention (GQA) sizes, whereas modern LLMs typically adopt much smaller GQA groups, which limits the applicability of this sparse algorithmic advance. In this work, we propose Flash Sparse Attention (FSA), which includes an alternative kernel design that enables efficient NSA computation across a wide range of popular LLMs with varied smaller GQA group sizes on modern GPUs. Compared to vanilla NSA kernel implementation, our empirical evaluation demonstrates that FSA achieves (i) up to 3.5$\times$ and on average 1.6$\times$ kernel-level latency reduction, (ii) up to 1.25$\times$ and 1.09$\times$ on average end-to-end training speedup on state-of-the-art LLMs, and (iii) up to 1.36$\times$ and 1.11$\times$ on average end-to-end prefill speedup on state-of-the-art LLMs. The source code is open-sourced and publicly available at https://github.com/Relaxed-System-Lab/Flash-Sparse-Attention.
Hallucination at a Glance: Controlled Visual Edits and Fine-Grained Multimodal Learning
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved strong performance on vision-language tasks but still struggle with fine-grained visual differences, leading to hallucinations or missed semantic shifts. We attribute this to limitations in both training data and learning objectives. To address these issues, we propose a controlled data generation pipeline that produces minimally edited image pairs with semantically aligned captions. Using this pipeline, we construct the Micro Edit Dataset (MED), containing over 50K image-text pairs spanning 11 fine-grained edit categories, including attribute, count, position, and object presence changes. Building on MED, we introduce a supervised fine-tuning (SFT) framework with a feature-level consistency loss that promotes stable visual embeddings under small edits. We evaluate our approach on the Micro Edit Detection benchmark, which includes carefully balanced evaluation pairs designed to test sensitivity to subtle visual variations across the same edit categories. Our method improves difference detection accuracy and reduces hallucinations compared to strong baselines, including GPT-4o. Moreover, it yields consistent gains on standard vision-language tasks such as image captioning and visual question answering. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of combining targeted data and alignment objectives for enhancing fine-grained visual reasoning in MLLMs.
Multi-Step Visual Reasoning with Visual Tokens Scaling and Verification
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable capabilities by integrating visual perception with language understanding, enabling applications such as image-grounded dialogue, visual question answering, and scientific analysis. However, most MLLMs adopt a static inference paradigm, encoding the entire image into fixed visual tokens upfront, which limits their ability to iteratively refine understanding or adapt to context during inference. This contrasts sharply with human perception, which is dynamic, selective, and feedback-driven. In this work, we introduce a novel framework for inference-time visual token scaling that enables MLLMs to perform iterative, verifier-guided reasoning over visual content. We formulate the problem as a Markov Decision Process, involving a reasoner that proposes visual actions and a verifier, which is trained via multi-step Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), that evaluates these actions and determines when reasoning should terminate. To support this, we present a new dataset, VTS, comprising supervised reasoning trajectories (VTS-SFT) and preference-labeled reasoning comparisons (VTS-DPO). Our method significantly outperforms existing approaches across diverse visual reasoning benchmarks, offering not only improved accuracy but also more interpretable and grounded reasoning processes. These results demonstrate the promise of dynamic inference mechanisms for enabling fine-grained, context-aware visual reasoning in next-generation MLLMs.
AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning
May 30, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a trending paradigm for training large language models (LLMs), particularly for reasoning tasks. Effective RL for LLMs requires massive parallelization and poses an urgent need for efficient training systems. Most existing large-scale RL systems for LLMs are synchronous by alternating generation and training in a batch setting, where the rollouts in each training batch are generated by the same (or latest) model. This stabilizes RL training but suffers from severe system-level inefficiency. Generation must wait until the longest output in the batch is completed before model update, resulting in GPU underutilization. We present AReaL, a \emph{fully asynchronous} RL system that completely decouples generation from training. Rollout workers in AReaL continuously generate new outputs without waiting, while training workers update the model whenever a batch of data is collected. AReaL also incorporates a collection of system-level optimizations, leading to substantially higher GPU utilization. To stabilize RL training, AReaL balances the workload of rollout and training workers to control data staleness, and adopts a staleness-enhanced PPO variant to better handle outdated training samples. Extensive experiments on math and code reasoning benchmarks show that AReaL achieves \textbf{up to 2.57$\times$ training speedup} compared to the best synchronous systems with the same number of GPUs and matched or even improved final performance. The code of AReaL is available at https://github.com/inclusionAI/AReaL/.
MLKV: Efficiently Scaling up Large Embedding Model Training with Disk-based Key-Value Storage
Apr 02, 2025
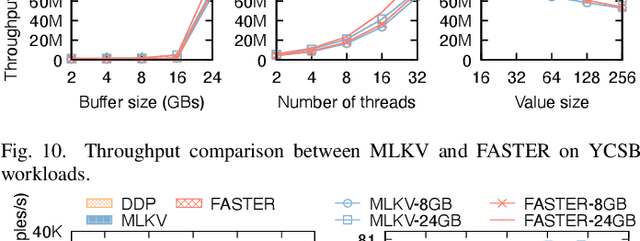
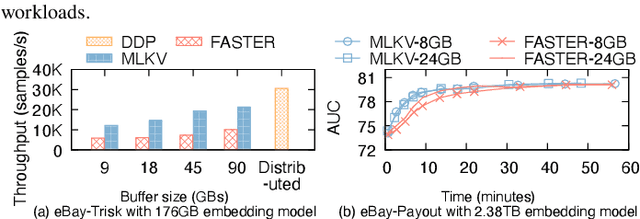
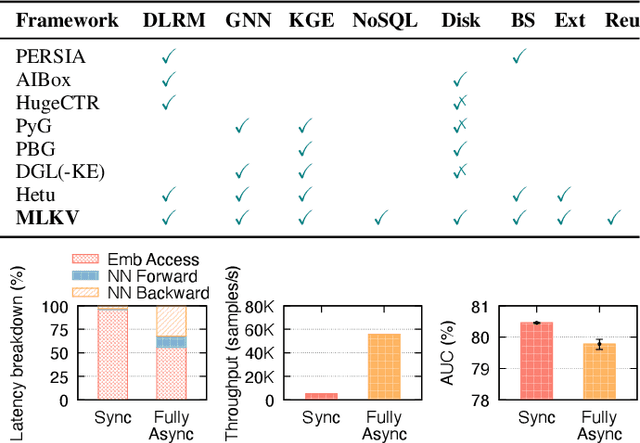
Abstract:Many modern machine learning (ML) methods rely on embedding models to learn vector representations (embeddings) for a set of entities (embedding tables). As increasingly diverse ML applications utilize embedding models and embedding tables continue to grow in size and number, there has been a surge in the ad-hoc development of specialized frameworks targeted to train large embedding models for specific tasks. Although the scalability issues that arise in different embedding model training tasks are similar, each of these frameworks independently reinvents and customizes storage components for specific tasks, leading to substantial duplicated engineering efforts in both development and deployment. This paper presents MLKV, an efficient, extensible, and reusable data storage framework designed to address the scalability challenges in embedding model training, specifically data stall and staleness. MLKV augments disk-based key-value storage by democratizing optimizations that were previously exclusive to individual specialized frameworks and provides easy-to-use interfaces for embedding model training tasks. Extensive experiments on open-source workloads, as well as applications in eBay's payment transaction risk detection and seller payment risk detection, show that MLKV outperforms offloading strategies built on top of industrial-strength key-value stores by 1.6-12.6x. MLKV is open-source at https://github.com/llm-db/MLKV.
AtmosSci-Bench: Evaluating the Recent Advance of Large Language Model for Atmospheric Science
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs), particularly in their reasoning capabilities, hold transformative potential for addressing complex challenges in atmospheric science. However, leveraging LLMs effectively in this domain requires a robust and comprehensive evaluation benchmark. To address this need, we present AtmosSci-Bench, a novel benchmark designed to systematically assess LLM performance across five core categories of atmospheric science problems: hydrology, atmospheric dynamics, atmospheric physics, geophysics, and physical oceanography. We employ a template-based question generation framework, enabling scalable and diverse multiple-choice questions curated from graduate-level atmospheric science problems. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of representative LLMs, categorized into four groups: instruction-tuned models, advanced reasoning models, math-augmented models, and domain-specific climate models. Our analysis provides some interesting insights into the reasoning and problem-solving capabilities of LLMs in atmospheric science. We believe AtmosSci-Bench can serve as a critical step toward advancing LLM applications in climate service by offering a standard and rigorous evaluation framework. Our source codes are currently available at https://github.com/Relaxed-System-Lab/AtmosSci-Bench.
CE-LoRA: Computation-Efficient LoRA Fine-Tuning for Language Models
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional performance across various tasks but demand substantial computational resources even for fine-tuning computation. Although Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) significantly alleviates memory consumption during fine-tuning, its impact on computational cost reduction is limited. This paper identifies the computation of activation gradients as the primary bottleneck in LoRA's backward propagation and introduces the Computation-Efficient LoRA (CE-LoRA) algorithm, which enhances computational efficiency while preserving memory efficiency. CE-LoRA leverages two key techniques: Approximated Matrix Multiplication, which replaces dense multiplications of large and complete matrices with sparse multiplications involving only critical rows and columns, and the Double-LoRA technique, which reduces error propagation in activation gradients. Theoretically, CE-LoRA converges at the same rate as LoRA, $ \mathcal{O}(1/\sqrt{T}) $, where $T$ is the number of iteartions. Empirical evaluations confirm that CE-LoRA significantly reduces computational costs compared to LoRA without notable performance degradation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge