Yingqian Wang
Dynamic High-frequency Convolution for Infrared Small Target Detection
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Infrared small targets are typically tiny and locally salient, which belong to high-frequency components (HFCs) in images. Single-frame infrared small target (SIRST) detection is challenging, since there are many HFCs along with targets, such as bright corners, broken clouds, and other clutters. Current learning-based methods rely on the powerful capabilities of deep networks, but neglect explicit modeling and discriminative representation learning of various HFCs, which is important to distinguish targets from other HFCs. To address the aforementioned issues, we propose a dynamic high-frequency convolution (DHiF) to translate the discriminative modeling process into the generation of a dynamic local filter bank. Especially, DHiF is sensitive to HFCs, owing to the dynamic parameters of its generated filters being symmetrically adjusted within a zero-centered range according to Fourier transformation properties. Combining with standard convolution operations, DHiF can adaptively and dynamically process different HFC regions and capture their distinctive grayscale variation characteristics for discriminative representation learning. DHiF functions as a drop-in replacement for standard convolution and can be used in arbitrary SIRST detection networks without significant decrease in computational efficiency. To validate the effectiveness of our DHiF, we conducted extensive experiments across different SIRST detection networks on real-scene datasets. Compared to other state-of-the-art convolution operations, DHiF exhibits superior detection performance with promising improvement. Codes are available at https://github.com/TinaLRJ/DHiF.
Probing Deep into Temporal Profile Makes the Infrared Small Target Detector Much Better
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Infrared small target (IRST) detection is challenging in simultaneously achieving precise, universal, robust and efficient performance due to extremely dim targets and strong interference. Current learning-based methods attempt to leverage ``more" information from both the spatial and the short-term temporal domains, but suffer from unreliable performance under complex conditions while incurring computational redundancy. In this paper, we explore the ``more essential" information from a more crucial domain for the detection. Through theoretical analysis, we reveal that the global temporal saliency and correlation information in the temporal profile demonstrate significant superiority in distinguishing target signals from other signals. To investigate whether such superiority is preferentially leveraged by well-trained networks, we built the first prediction attribution tool in this field and verified the importance of the temporal profile information. Inspired by the above conclusions, we remodel the IRST detection task as a one-dimensional signal anomaly detection task, and propose an efficient deep temporal probe network (DeepPro) that only performs calculations in the time dimension for IRST detection. We conducted extensive experiments to fully validate the effectiveness of our method. The experimental results are exciting, as our DeepPro outperforms existing state-of-the-art IRST detection methods on widely-used benchmarks with extremely high efficiency, and achieves a significant improvement on dim targets and in complex scenarios. We provide a new modeling domain, a new insight, a new method, and a new performance, which can promote the development of IRST detection. Codes are available at https://github.com/TinaLRJ/DeepPro.
Heterogeneous Graph Transformer for Multiple Tiny Object Tracking in RGB-T Videos
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Tracking multiple tiny objects is highly challenging due to their weak appearance and limited features. Existing multi-object tracking algorithms generally focus on single-modality scenes, and overlook the complementary characteristics of tiny objects captured by multiple remote sensors. To enhance tracking performance by integrating complementary information from multiple sources, we propose a novel framework called {HGT-Track (Heterogeneous Graph Transformer based Multi-Tiny-Object Tracking)}. Specifically, we first employ a Transformer-based encoder to embed images from different modalities. Subsequently, we utilize Heterogeneous Graph Transformer to aggregate spatial and temporal information from multiple modalities to generate detection and tracking features. Additionally, we introduce a target re-detection module (ReDet) to ensure tracklet continuity by maintaining consistency across different modalities. Furthermore, this paper introduces the first benchmark VT-Tiny-MOT (Visible-Thermal Tiny Multi-Object Tracking) for RGB-T fused multiple tiny object tracking. Extensive experiments are conducted on VT-Tiny-MOT, and the results have demonstrated the effectiveness of our method. Compared to other state-of-the-art methods, our method achieves better performance in terms of MOTA (Multiple-Object Tracking Accuracy) and ID-F1 score. The code and dataset will be made available at https://github.com/xuqingyu26/HGTMT.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Stereo Image Super-Resolution: Methods and Results
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:This paper summarizes the 3rd NTIRE challenge on stereo image super-resolution (SR) with a focus on new solutions and results. The task of this challenge is to super-resolve a low-resolution stereo image pair to a high-resolution one with a magnification factor of x4 under a limited computational budget. Compared with single image SR, the major challenge of this challenge lies in how to exploit additional information in another viewpoint and how to maintain stereo consistency in the results. This challenge has 2 tracks, including one track on bicubic degradation and one track on real degradations. In total, 108 and 70 participants were successfully registered for each track, respectively. In the test phase, 14 and 13 teams successfully submitted valid results with PSNR (RGB) scores better than the baseline. This challenge establishes a new benchmark for stereo image SR.
Visible-Thermal Tiny Object Detection: A Benchmark Dataset and Baselines
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:Small object detection (SOD) has been a longstanding yet challenging task for decades, with numerous datasets and algorithms being developed. However, they mainly focus on either visible or thermal modality, while visible-thermal (RGBT) bimodality is rarely explored. Although some RGBT datasets have been developed recently, the insufficient quantity, limited category, misaligned images and large target size cannot provide an impartial benchmark to evaluate multi-category visible-thermal small object detection (RGBT SOD) algorithms. In this paper, we build the first large-scale benchmark with high diversity for RGBT SOD (namely RGBT-Tiny), including 115 paired sequences, 93K frames and 1.2M manual annotations. RGBT-Tiny contains abundant targets (7 categories) and high-diversity scenes (8 types that cover different illumination and density variations). Note that, over 81% of targets are smaller than 16x16, and we provide paired bounding box annotations with tracking ID to offer an extremely challenging benchmark with wide-range applications, such as RGBT fusion, detection and tracking. In addition, we propose a scale adaptive fitness (SAFit) measure that exhibits high robustness on both small and large targets. The proposed SAFit can provide reasonable performance evaluation and promote detection performance. Based on the proposed RGBT-Tiny dataset and SAFit measure, extensive evaluations have been conducted, including 23 recent state-of-the-art algorithms that cover four different types (i.e., visible generic detection, visible SOD, thermal SOD and RGBT object detection). Project is available at https://github.com/XinyiYing24/RGBT-Tiny.
SpecDETR: A Transformer-based Hyperspectral Point Object Detection Network
May 16, 2024



Abstract:Hyperspectral target detection (HTD) aims to identify specific materials based on spectral information in hyperspectral imagery and can detect point targets, some of which occupy a smaller than one-pixel area. However, existing HTD methods are developed based on per-pixel binary classification, which limits the feature representation capability for point targets. In this paper, we rethink the hyperspectral point target detection from the object detection perspective, and focus more on the object-level prediction capability rather than the pixel classification capability. Inspired by the token-based processing flow of Detection Transformer (DETR), we propose the first specialized network for hyperspectral multi-class point object detection, SpecDETR. Without the backbone part of the current object detection framework, SpecDETR treats the spectral features of each pixel in hyperspectral images as a token and utilizes a multi-layer Transformer encoder with local and global coordination attention modules to extract deep spatial-spectral joint features. SpecDETR regards point object detection as a one-to-many set prediction problem, thereby achieving a concise and efficient DETR decoder that surpasses the current state-of-the-art DETR decoder in terms of parameters and accuracy in point object detection. We develop a simulated hyperSpectral Point Object Detection benchmark termed SPOD, and for the first time, evaluate and compare the performance of current object detection networks and HTD methods on hyperspectral multi-class point object detection. SpecDETR demonstrates superior performance as compared to current object detection networks and HTD methods on the SPOD dataset. Additionally, we validate on a public HTD dataset that by using data simulation instead of manual annotation, SpecDETR can detect real-world single-spectral point objects directly.
LFSRDiff: Light Field Image Super-Resolution via Diffusion Models
Nov 27, 2023



Abstract:Light field (LF) image super-resolution (SR) is a challenging problem due to its inherent ill-posed nature, where a single low-resolution (LR) input LF image can correspond to multiple potential super-resolved outcomes. Despite this complexity, mainstream LF image SR methods typically adopt a deterministic approach, generating only a single output supervised by pixel-wise loss functions. This tendency often results in blurry and unrealistic results. Although diffusion models can capture the distribution of potential SR results by iteratively predicting Gaussian noise during the denoising process, they are primarily designed for general images and struggle to effectively handle the unique characteristics and information present in LF images. To address these limitations, we introduce LFSRDiff, the first diffusion-based LF image SR model, by incorporating the LF disentanglement mechanism. Our novel contribution includes the introduction of a disentangled U-Net for diffusion models, enabling more effective extraction and fusion of both spatial and angular information within LF images. Through comprehensive experimental evaluations and comparisons with the state-of-the-art LF image SR methods, the proposed approach consistently produces diverse and realistic SR results. It achieves the highest perceptual metric in terms of LPIPS. It also demonstrates the ability to effectively control the trade-off between perception and distortion. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/chaowentao/LFSRDiff}.
OccCasNet: Occlusion-aware Cascade Cost Volume for Light Field Depth Estimation
May 28, 2023



Abstract:Light field (LF) depth estimation is a crucial task with numerous practical applications. However, mainstream methods based on the multi-view stereo (MVS) are resource-intensive and time-consuming as they need to construct a finer cost volume. To address this issue and achieve a better trade-off between accuracy and efficiency, we propose an occlusion-aware cascade cost volume for LF depth (disparity) estimation. Our cascaded strategy reduces the sampling number while keeping the sampling interval constant during the construction of a finer cost volume. We also introduce occlusion maps to enhance accuracy in constructing the occlusion-aware cost volume. Specifically, we first obtain the coarse disparity map through the coarse disparity estimation network. Then, the sub-aperture images (SAIs) of side views are warped to the center view based on the initial disparity map. Next, we propose photo-consistency constraints between the warped SAIs and the center SAI to generate occlusion maps for each SAI. Finally, we introduce the coarse disparity map and occlusion maps to construct an occlusion-aware refined cost volume, enabling the refined disparity estimation network to yield a more precise disparity map. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Compared with state-of-the-art methods, our method achieves a superior balance between accuracy and efficiency and ranks first in terms of MSE and Q25 metrics among published methods on the HCI 4D benchmark. The code and model of the proposed method are available at https://github.com/chaowentao/OccCasNet.
Learning Remote Sensing Object Detection with Single Point Supervision
May 23, 2023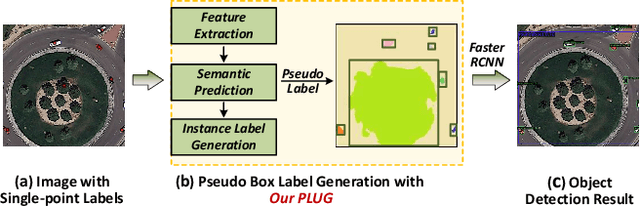
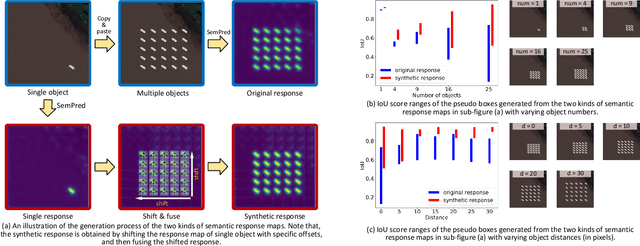
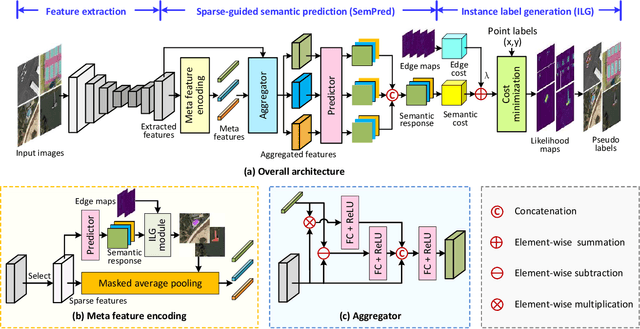

Abstract:Pointly Supervised Object Detection (PSOD) has attracted considerable interests due to its lower labeling cost as compared to box-level supervised object detection. However, the complex scenes, densely packed and dynamic-scale objects in Remote Sensing (RS) images hinder the development of PSOD methods in RS field. In this paper, we make the first attempt to achieve RS object detection with single point supervision, and propose a PSOD framework tailored with RS images. Specifically, we design a point label upgrader (PLUG) to generate pseudo box labels from single point labels, and then use the pseudo boxes to supervise the optimization of existing detectors. Moreover, to handle the challenge of the densely packed objects in RS images, we propose a sparse feature guided semantic prediction module which can generate high-quality semantic maps by fully exploiting informative cues from sparse objects. Extensive ablation studies on the DOTA dataset have validated the effectiveness of our method. Our method can achieve significantly better performance as compared to state-of-the-art image-level and point-level supervised detection methods, and reduce the performance gap between PSOD and box-level supervised object detection. Code will be available at https://github.com/heshitian/PLUG.
NTIRE 2023 Challenge on Light Field Image Super-Resolution: Dataset, Methods and Results
Apr 20, 2023Abstract:In this report, we summarize the first NTIRE challenge on light field (LF) image super-resolution (SR), which aims at super-resolving LF images under the standard bicubic degradation with a magnification factor of 4. This challenge develops a new LF dataset called NTIRE-2023 for validation and test, and provides a toolbox called BasicLFSR to facilitate model development. Compared with single image SR, the major challenge of LF image SR lies in how to exploit complementary angular information from plenty of views with varying disparities. In total, 148 participants have registered the challenge, and 11 teams have successfully submitted results with PSNR scores higher than the baseline method LF-InterNet \cite{LF-InterNet}. These newly developed methods have set new state-of-the-art in LF image SR, e.g., the winning method achieves around 1 dB PSNR improvement over the existing state-of-the-art method DistgSSR \cite{DistgLF}. We report the solutions proposed by the participants, and summarize their common trends and useful tricks. We hope this challenge can stimulate future research and inspire new ideas in LF image SR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge