Miao Li
Wuhan University
Bridging Speech, Emotion, and Motion: a VLM-based Multimodal Edge-deployable Framework for Humanoid Robots
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Effective human-robot interaction requires emotionally rich multimodal expressions, yet most humanoid robots lack coordinated speech, facial expressions, and gestures. Meanwhile, real-world deployment demands on-device solutions that can operate autonomously without continuous cloud connectivity. To bridging \underline{\textit{S}}peech, \underline{\textit{E}}motion, and \underline{\textit{M}}otion, we present \textit{SeM$^2$}, a Vision Language Model-based framework that orchestrates emotionally coherent multimodal interactions through three key components: a multimodal perception module capturing user contextual cues, a Chain-of-Thought reasoning for response planning, and a novel Semantic-Sequence Aligning Mechanism (SSAM) that ensures precise temporal coordination between verbal content and physical expressions. We implement both cloud-based and \underline{\textit{e}}dge-deployed versions (\textit{SeM$^2_e$}), with the latter knowledge distilled to operate efficiently on edge hardware while maintaining 95\% of the relative performance. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms unimodal baselines in naturalness, emotional clarity, and modal coherence, advancing socially expressive humanoid robotics for diverse real-world environments.
Dynamic High-frequency Convolution for Infrared Small Target Detection
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Infrared small targets are typically tiny and locally salient, which belong to high-frequency components (HFCs) in images. Single-frame infrared small target (SIRST) detection is challenging, since there are many HFCs along with targets, such as bright corners, broken clouds, and other clutters. Current learning-based methods rely on the powerful capabilities of deep networks, but neglect explicit modeling and discriminative representation learning of various HFCs, which is important to distinguish targets from other HFCs. To address the aforementioned issues, we propose a dynamic high-frequency convolution (DHiF) to translate the discriminative modeling process into the generation of a dynamic local filter bank. Especially, DHiF is sensitive to HFCs, owing to the dynamic parameters of its generated filters being symmetrically adjusted within a zero-centered range according to Fourier transformation properties. Combining with standard convolution operations, DHiF can adaptively and dynamically process different HFC regions and capture their distinctive grayscale variation characteristics for discriminative representation learning. DHiF functions as a drop-in replacement for standard convolution and can be used in arbitrary SIRST detection networks without significant decrease in computational efficiency. To validate the effectiveness of our DHiF, we conducted extensive experiments across different SIRST detection networks on real-scene datasets. Compared to other state-of-the-art convolution operations, DHiF exhibits superior detection performance with promising improvement. Codes are available at https://github.com/TinaLRJ/DHiF.
When Attention Betrays: Erasing Backdoor Attacks in Robotic Policies by Reconstructing Visual Tokens
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Downstream fine-tuning of vision-language-action (VLA) models enhances robotics, yet exposes the pipeline to backdoor risks. Attackers can pretrain VLAs on poisoned data to implant backdoors that remain stealthy but can trigger harmful behavior during inference. However, existing defenses either lack mechanistic insight into multimodal backdoors or impose prohibitive computational costs via full-model retraining. To this end, we uncover a deep-layer attention grabbing mechanism: backdoors redirect late-stage attention and form compact embedding clusters near the clean manifold. Leveraging this insight, we introduce Bera, a test-time backdoor erasure framework that detects tokens with anomalous attention via latent-space localization, masks suspicious regions using deep-layer cues, and reconstructs a trigger-free image to break the trigger-unsafe-action mapping while restoring correct behavior. Unlike prior defenses, Bera requires neither retraining of VLAs nor any changes to the training pipeline. Extensive experiments across multiple embodied platforms and tasks show that Bera effectively maintains nominal performance, significantly reduces attack success rates, and consistently restores benign behavior from backdoored outputs, thereby offering a robust and practical defense mechanism for securing robotic systems.
Plan, Verify and Fill: A Structured Parallel Decoding Approach for Diffusion Language Models
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Language Models (DLMs) present a promising non-sequential paradigm for text generation, distinct from standard autoregressive (AR) approaches. However, current decoding strategies often adopt a reactive stance, underutilizing the global bidirectional context to dictate global trajectories. To address this, we propose Plan-Verify-Fill (PVF), a training-free paradigm that grounds planning via quantitative validation. PVF actively constructs a hierarchical skeleton by prioritizing high-leverage semantic anchors and employs a verification protocol to operationalize pragmatic structural stopping where further deliberation yields diminishing returns. Extensive evaluations on LLaDA-8B-Instruct and Dream-7B-Instruct demonstrate that PVF reduces the Number of Function Evaluations (NFE) by up to 65% compared to confidence-based parallel decoding across benchmark datasets, unlocking superior efficiency without compromising accuracy.
Generalizable Geometric Prior and Recurrent Spiking Feature Learning for Humanoid Robot Manipulation
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Humanoid robot manipulation is a crucial research area for executing diverse human-level tasks, involving high-level semantic reasoning and low-level action generation. However, precise scene understanding and sample-efficient learning from human demonstrations remain critical challenges, severely hindering the applicability and generalizability of existing frameworks. This paper presents a novel RGMP-S, Recurrent Geometric-prior Multimodal Policy with Spiking features, facilitating both high-level skill reasoning and data-efficient motion synthesis. To ground high-level reasoning in physical reality, we leverage lightweight 2D geometric inductive biases to enable precise 3D scene understanding within the vision-language model. Specifically, we construct a Long-horizon Geometric Prior Skill Selector that effectively aligns the semantic instructions with spatial constraints, ultimately achieving robust generalization in unseen environments. For the data efficiency issue in robotic action generation, we introduce a Recursive Adaptive Spiking Network. We parameterize robot-object interactions via recursive spiking for spatiotemporal consistency, fully distilling long-horizon dynamic features while mitigating the overfitting issue in sparse demonstration scenarios. Extensive experiments are conducted across the Maniskill simulation benchmark and three heterogeneous real-world robotic systems, encompassing a custom-developed humanoid, a desktop manipulator, and a commercial robotic platform. Empirical results substantiate the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art baselines and validate the efficacy of the proposed modules in diverse generalization scenarios. To facilitate reproducibility, the source code and video demonstrations are publicly available at https://github.com/xtli12/RGMP-S.git.
Learning Generalizable Hand-Object Tracking from Synthetic Demonstrations
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We present a system for learning generalizable hand-object tracking controllers purely from synthetic data, without requiring any human demonstrations. Our approach makes two key contributions: (1) HOP, a Hand-Object Planner, which can synthesize diverse hand-object trajectories; and (2) HOT, a Hand-Object Tracker that bridges synthetic-to-physical transfer through reinforcement learning and interaction imitation learning, delivering a generalizable controller conditioned on target hand-object states. Our method extends to diverse object shapes and hand morphologies. Through extensive evaluations, we show that our approach enables dexterous hands to track challenging, long-horizon sequences including object re-arrangement and agile in-hand reorientation. These results represent a significant step toward scalable foundation controllers for manipulation that can learn entirely from synthetic data, breaking the data bottleneck that has long constrained progress in dexterous manipulation.
RGMP: Recurrent Geometric-prior Multimodal Policy for Generalizable Humanoid Robot Manipulation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots exhibit significant potential in executing diverse human-level skills. However, current research predominantly relies on data-driven approaches that necessitate extensive training datasets to achieve robust multimodal decision-making capabilities and generalizable visuomotor control. These methods raise concerns due to the neglect of geometric reasoning in unseen scenarios and the inefficient modeling of robot-target relationships within the training data, resulting in significant waste of training resources. To address these limitations, we present the Recurrent Geometric-prior Multimodal Policy (RGMP), an end-to-end framework that unifies geometric-semantic skill reasoning with data-efficient visuomotor control. For perception capabilities, we propose the Geometric-prior Skill Selector, which infuses geometric inductive biases into a vision language model, producing adaptive skill sequences for unseen scenes with minimal spatial common sense tuning. To achieve data-efficient robotic motion synthesis, we introduce the Adaptive Recursive Gaussian Network, which parameterizes robot-object interactions as a compact hierarchy of Gaussian processes that recursively encode multi-scale spatial relationships, yielding dexterous, data-efficient motion synthesis even from sparse demonstrations. Evaluated on both our humanoid robot and desktop dual-arm robot, the RGMP framework achieves 87% task success in generalization tests and exhibits 5x greater data efficiency than the state-of-the-art model. This performance underscores its superior cross-domain generalization, enabled by geometric-semantic reasoning and recursive-Gaussion adaptation.
Which Similarity-Sensitive Entropy?
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:A canonical step in quantifying a system is to measure its entropy. Shannon entropy and other traditional entropy measures capture only the information encoded in the frequencies of a system's elements. Recently, Leinster, Cobbold, and Reeve (LCR) introduced a method that also captures the rich information encoded in the similarities and differences among elements, yielding similarity-sensitive entropy. More recently, the Vendi score (VS) was introduced as an alternative, raising the question of how LCR and VS compare, and which is preferable. Here we address these questions conceptually, analytically, and experimentally, using 53 machine-learning datasets. We show that LCR and VS can differ by orders of magnitude and can capture complementary information about a system, except in limiting cases. We demonstrate that both LCR and VS depend on how similarities are scaled and introduce the concept of ``half distance'' to parameterize this dependence. We prove that VS provides an upper bound on LCR for several values of the Rényi-Hill order parameter and conjecture that this bound holds for all values. We conclude that VS is preferable only when interpreting elements as linear combinations of a more fundamental set of ``ur-elements'' or when the system or dataset possesses a quantum-mechanical character. In the broader circumstance where one seeks simply to capture the rich information encoded by similarity, LCR is favored; nevertheless, for certain half-distances the two methods can complement each other.
Constraint-Informed Active Learning for End-to-End ACOPF Optimization Proxies
Nov 09, 2025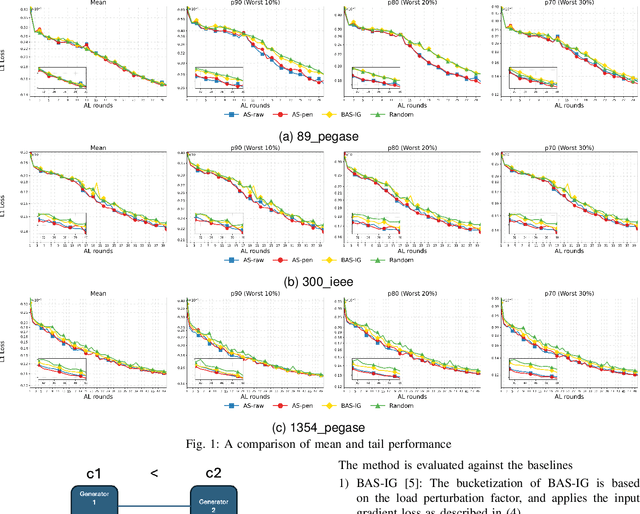
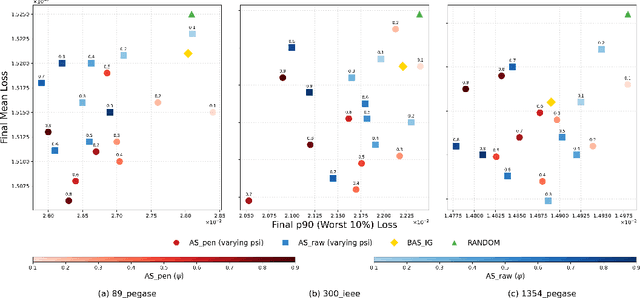
Abstract:This paper studies optimization proxies, machine learning (ML) models trained to efficiently predict optimal solutions for AC Optimal Power Flow (ACOPF) problems. While promising, optimization proxy performance heavily depends on training data quality. To address this limitation, this paper introduces a novel active sampling framework for ACOPF optimization proxies designed to generate realistic and diverse training data. The framework actively explores varied, flexible problem specifications reflecting plausible operational realities. More importantly, the approach uses optimization-specific quantities (active constraint sets) that better capture the salient features of an ACOPF that lead to the optimal solution. Numerical results show superior generalization over existing sampling methods with an equivalent training budget, significantly advancing the state-of-practice for trustworthy ACOPF optimization proxies.
ManiDP: Manipulability-Aware Diffusion Policy for Posture-Dependent Bimanual Manipulation
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Recent work has demonstrated the potential of diffusion models in robot bimanual skill learning. However, existing methods ignore the learning of posture-dependent task features, which are crucial for adapting dual-arm configurations to meet specific force and velocity requirements in dexterous bimanual manipulation. To address this limitation, we propose Manipulability-Aware Diffusion Policy (ManiDP), a novel imitation learning method that not only generates plausible bimanual trajectories, but also optimizes dual-arm configurations to better satisfy posture-dependent task requirements. ManiDP achieves this by extracting bimanual manipulability from expert demonstrations and encoding the encapsulated posture features using Riemannian-based probabilistic models. These encoded posture features are then incorporated into a conditional diffusion process to guide the generation of task-compatible bimanual motion sequences. We evaluate ManiDP on six real-world bimanual tasks, where the experimental results demonstrate a 39.33$\%$ increase in average manipulation success rate and a 0.45 improvement in task compatibility compared to baseline methods. This work highlights the importance of integrating posture-relevant robotic priors into bimanual skill diffusion to enable human-like adaptability and dexterity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge