Mengyuan Li
A Systematic Study of Model Extraction Attacks on Graph Foundation Models
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Graph machine learning has advanced rapidly in tasks such as link prediction, anomaly detection, and node classification. As models scale up, pretrained graph models have become valuable intellectual assets because they encode extensive computation and domain expertise. Building on these advances, Graph Foundation Models (GFMs) mark a major step forward by jointly pretraining graph and text encoders on massive and diverse data. This unifies structural and semantic understanding, enables zero-shot inference, and supports applications such as fraud detection and biomedical analysis. However, the high pretraining cost and broad cross-domain knowledge in GFMs also make them attractive targets for model extraction attacks (MEAs). Prior work has focused only on small graph neural networks trained on a single graph, leaving the security implications for large-scale and multimodal GFMs largely unexplored. This paper presents the first systematic study of MEAs against GFMs. We formalize a black-box threat model and define six practical attack scenarios covering domain-level and graph-specific extraction goals, architectural mismatch, limited query budgets, partial node access, and training data discrepancies. To instantiate these attacks, we introduce a lightweight extraction method that trains an attacker encoder using supervised regression of graph embeddings. Even without contrastive pretraining data, this method learns an encoder that stays aligned with the victim text encoder and preserves its zero-shot inference ability on unseen graphs. Experiments on seven datasets show that the attacker can approximate the victim model using only a tiny fraction of its original training cost, with almost no loss in accuracy. These findings reveal that GFMs greatly expand the MEA surface and highlight the need for deployment-aware security defenses in large-scale graph learning systems.
PySlyde: A Lightweight, Open-Source Toolkit for Pathology Preprocessing
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into pathology is advancing precision medicine by improving diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient outcomes. Digitised whole-slide images (WSIs) capture rich spatial and morphological information vital for understanding disease biology, yet their gigapixel scale and variability pose major challenges for standardisation and analysis. Robust preprocessing, covering tissue detection, tessellation, stain normalisation, and annotation parsing is critical but often limited by fragmented and inconsistent workflows. We present PySlyde, a lightweight, open-source Python toolkit built on OpenSlide to simplify and standardise WSI preprocessing. PySlyde provides an intuitive API for slide loading, annotation management, tissue detection, tiling, and feature extraction, compatible with modern pathology foundation models. By unifying these processes, it streamlines WSI preprocessing, enhances reproducibility, and accelerates the generation of AI-ready datasets, enabling researchers to focus on model development and downstream analysis.
GLIP-OOD: Zero-Shot Graph OOD Detection with Foundation Model
Apr 29, 2025



Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of machine learning systems, particularly in dynamic and open-world environments. In the vision and text domains, zero-shot OOD detection - which requires no training on in-distribution (ID) data - has made significant progress through the use of large-scale pretrained models such as vision-language models (VLMs) and large language models (LLMs). However, zero-shot OOD detection in graph-structured data remains largely unexplored, primarily due to the challenges posed by complex relational structures and the absence of powerful, large-scale pretrained models for graphs. In this work, we take the first step toward enabling zero-shot graph OOD detection by leveraging a graph foundation model (GFM). We show that, when provided only with class label names, the GFM can perform OOD detection without any node-level supervision - outperforming existing supervised methods across multiple datasets. To address the more practical setting where OOD label names are unavailable, we introduce GLIP-OOD, a novel framework that employs LLMs to generate semantically informative pseudo-OOD labels from unlabeled data. These labels enable the GFM to capture nuanced semantic boundaries between ID and OOD classes and perform fine-grained OOD detection - without requiring any labeled nodes. Our approach is the first to enable node-level graph OOD detection in a fully zero-shot setting, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on four benchmark text-attributed graph datasets.
Graph Synthetic Out-of-Distribution Exposure with Large Language Models
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection in graphs is critical for ensuring model robustness in open-world and safety-sensitive applications. Existing approaches to graph OOD detection typically involve training an in-distribution (ID) classifier using only ID data, followed by the application of post-hoc OOD scoring techniques. Although OOD exposure - introducing auxiliary OOD samples during training - has proven to be an effective strategy for enhancing detection performance, current methods in the graph domain generally assume access to a set of real OOD nodes. This assumption, however, is often impractical due to the difficulty and cost of acquiring representative OOD samples. In this paper, we introduce GOE-LLM, a novel framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for OOD exposure in graph OOD detection without requiring real OOD nodes. GOE-LLM introduces two pipelines: (1) identifying pseudo-OOD nodes from the initially unlabeled graph using zero-shot LLM annotations, and (2) generating semantically informative synthetic OOD nodes via LLM-prompted text generation. These pseudo-OOD nodes are then used to regularize the training of the ID classifier for improved OOD awareness. We evaluate our approach across multiple benchmark datasets, showing that GOE-LLM significantly outperforms state-of-the-art graph OOD detection methods that do not use OOD exposure and achieves comparable performance to those relying on real OOD data.
AnyTSR: Any-Scale Thermal Super-Resolution for UAV
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Thermal imaging can greatly enhance the application of intelligent unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) in challenging environments. However, the inherent low resolution of thermal sensors leads to insufficient details and blurred boundaries. Super-resolution (SR) offers a promising solution to address this issue, while most existing SR methods are designed for fixed-scale SR. They are computationally expensive and inflexible in practical applications. To address above issues, this work proposes a novel any-scale thermal SR method (AnyTSR) for UAV within a single model. Specifically, a new image encoder is proposed to explicitly assign specific feature code to enable more accurate and flexible representation. Additionally, by effectively embedding coordinate offset information into the local feature ensemble, an innovative any-scale upsampler is proposed to better understand spatial relationships and reduce artifacts. Moreover, a novel dataset (UAV-TSR), covering both land and water scenes, is constructed for thermal SR tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across all scaling factors as well as generates more accurate and detailed high-resolution images. The code is located at https://github.com/vision4robotics/AnyTSR.
Few-Shot Graph Out-of-Distribution Detection with LLMs
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Existing methods for graph out-of-distribution (OOD) detection typically depend on training graph neural network (GNN) classifiers using a substantial amount of labeled in-distribution (ID) data. However, acquiring high-quality labeled nodes in text-attributed graphs (TAGs) is challenging and costly due to their complex textual and structural characteristics. Large language models (LLMs), known for their powerful zero-shot capabilities in textual tasks, show promise but struggle to naturally capture the critical structural information inherent to TAGs, limiting their direct effectiveness. To address these challenges, we propose LLM-GOOD, a general framework that effectively combines the strengths of LLMs and GNNs to enhance data efficiency in graph OOD detection. Specifically, we first leverage LLMs' strong zero-shot capabilities to filter out likely OOD nodes, significantly reducing the human annotation burden. To minimize the usage and cost of the LLM, we employ it only to annotate a small subset of unlabeled nodes. We then train a lightweight GNN filter using these noisy labels, enabling efficient predictions of ID status for all other unlabeled nodes by leveraging both textual and structural information. After obtaining node embeddings from the GNN filter, we can apply informativeness-based methods to select the most valuable nodes for precise human annotation. Finally, we train the target ID classifier using these accurately annotated ID nodes. Extensive experiments on four real-world TAG datasets demonstrate that LLM-GOOD significantly reduces human annotation costs and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of both ID classification accuracy and OOD detection performance.
Keypoint Detection Empowered Near-Field User Localization and Channel Reconstruction
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:In the near-field region of an extremely large-scale multiple-input multiple-output (XL MIMO) system, channel reconstruction is typically addressed through sparse parameter estimation based on compressed sensing (CS) algorithms after converting the received pilot signals into the transformed domain. However, the exhaustive search on the codebook in CS algorithms consumes significant computational resources and running time, particularly when a large number of antennas are equipped at the base station (BS). To overcome this challenge, we propose a novel scheme to replace the high-cost exhaustive search procedure. We visualize the sparse channel matrix in the transformed domain as a channel image and design the channel keypoint detection network (CKNet) to locate the user and scatterers in high speed. Subsequently, we use a small-scale newtonized orthogonal matching pursuit (NOMP) based refiner to further enhance the precision. Our method is applicable to both the Cartesian domain and the Polar domain. Additionally, to deal with scenarios with a flexible number of propagation paths, we further design FlexibleCKNet to predict both locations and confidence scores. Our experimental results validate that the CKNet and FlexibleCKNet-empowered channel reconstruction scheme can significantly reduce the computational complexity while maintaining high accuracy in both user and scatterer localization and channel reconstruction tasks.
Mask Conditional Synthetic Satellite Imagery
Feb 08, 2023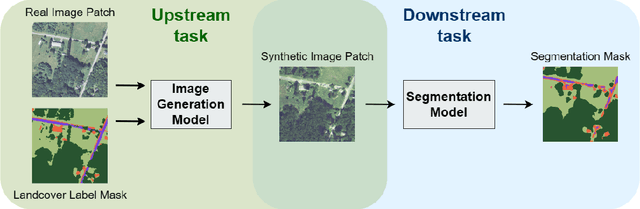
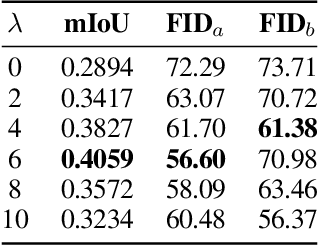


Abstract:In this paper we propose a mask-conditional synthetic image generation model for creating synthetic satellite imagery datasets. Given a dataset of real high-resolution images and accompanying land cover masks, we show that it is possible to train an upstream conditional synthetic imagery generator, use that generator to create synthetic imagery with the land cover masks, then train a downstream model on the synthetic imagery and land cover masks that achieves similar test performance to a model that was trained with the real imagery. Further, we find that incorporating a mixture of real and synthetic imagery acts as a data augmentation method, producing better models than using only real imagery (0.5834 vs. 0.5235 mIoU). Finally, we find that encouraging diversity of outputs in the upstream model is a necessary component for improved downstream task performance. We have released code for reproducing our work on GitHub, see https://github.com/ms-synthetic-satellite-image/synthetic-satellite-imagery .
Efficient and Accurate Quantized Image Super-Resolution on Mobile NPUs, Mobile AI & AIM 2022 challenge: Report
Nov 07, 2022
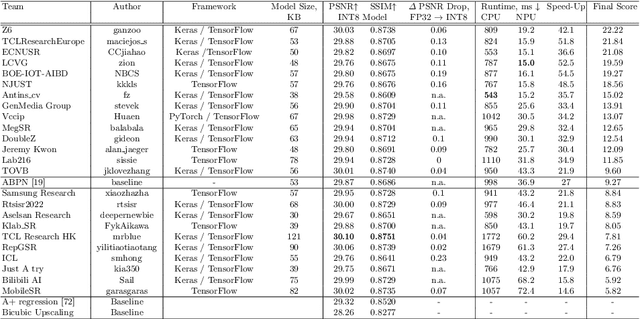
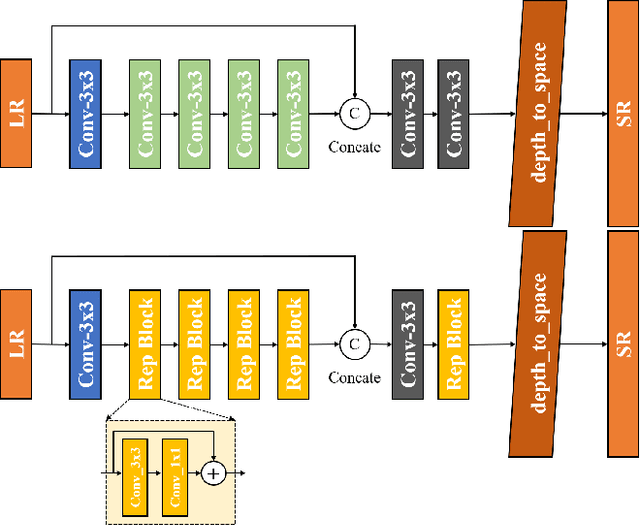
Abstract:Image super-resolution is a common task on mobile and IoT devices, where one often needs to upscale and enhance low-resolution images and video frames. While numerous solutions have been proposed for this problem in the past, they are usually not compatible with low-power mobile NPUs having many computational and memory constraints. In this Mobile AI challenge, we address this problem and propose the participants to design an efficient quantized image super-resolution solution that can demonstrate a real-time performance on mobile NPUs. The participants were provided with the DIV2K dataset and trained INT8 models to do a high-quality 3X image upscaling. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the Synaptics VS680 Smart Home board with a dedicated edge NPU capable of accelerating quantized neural networks. All proposed solutions are fully compatible with the above NPU, demonstrating an up to 60 FPS rate when reconstructing Full HD resolution images. A detailed description of all models developed in the challenge is provided in this paper.
Associative Memory Based Experience Replay for Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jul 16, 2022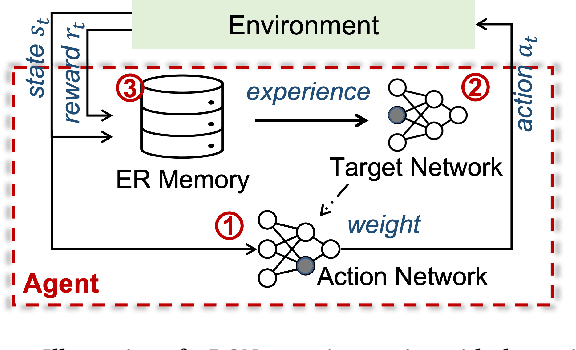
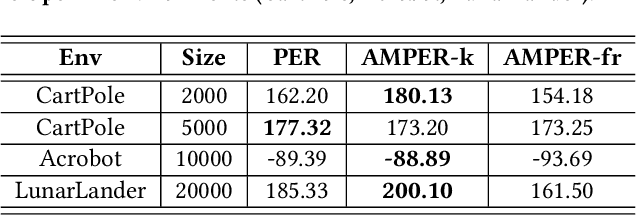
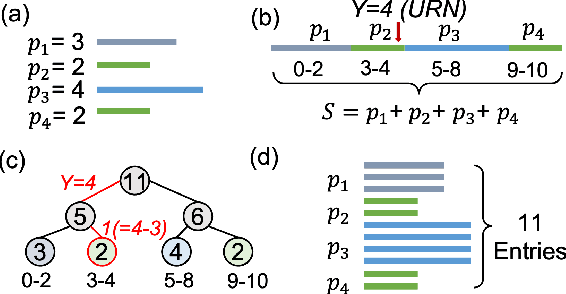
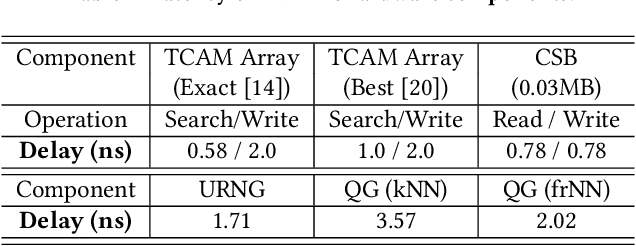
Abstract:Experience replay is an essential component in deep reinforcement learning (DRL), which stores the experiences and generates experiences for the agent to learn in real time. Recently, prioritized experience replay (PER) has been proven to be powerful and widely deployed in DRL agents. However, implementing PER on traditional CPU or GPU architectures incurs significant latency overhead due to its frequent and irregular memory accesses. This paper proposes a hardware-software co-design approach to design an associative memory (AM) based PER, AMPER, with an AM-friendly priority sampling operation. AMPER replaces the widely-used time-costly tree-traversal-based priority sampling in PER while preserving the learning performance. Further, we design an in-memory computing hardware architecture based on AM to support AMPER by leveraging parallel in-memory search operations. AMPER shows comparable learning performance while achieving 55x to 270x latency improvement when running on the proposed hardware compared to the state-of-the-art PER running on GPU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge