Maurizio Denna
Efficient and Accurate Quantized Image Super-Resolution on Mobile NPUs, Mobile AI & AIM 2022 challenge: Report
Nov 07, 2022
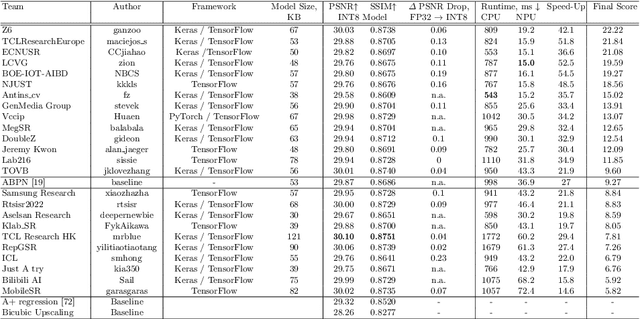
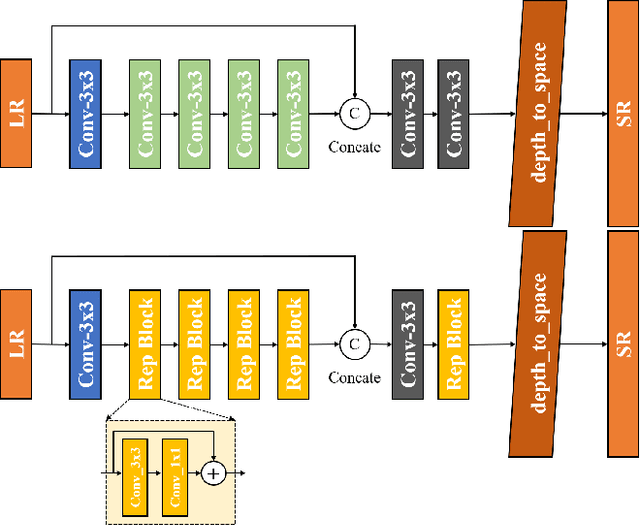
Abstract:Image super-resolution is a common task on mobile and IoT devices, where one often needs to upscale and enhance low-resolution images and video frames. While numerous solutions have been proposed for this problem in the past, they are usually not compatible with low-power mobile NPUs having many computational and memory constraints. In this Mobile AI challenge, we address this problem and propose the participants to design an efficient quantized image super-resolution solution that can demonstrate a real-time performance on mobile NPUs. The participants were provided with the DIV2K dataset and trained INT8 models to do a high-quality 3X image upscaling. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the Synaptics VS680 Smart Home board with a dedicated edge NPU capable of accelerating quantized neural networks. All proposed solutions are fully compatible with the above NPU, demonstrating an up to 60 FPS rate when reconstructing Full HD resolution images. A detailed description of all models developed in the challenge is provided in this paper.
Real-Time Quantized Image Super-Resolution on Mobile NPUs, Mobile AI 2021 Challenge: Report
May 17, 2021
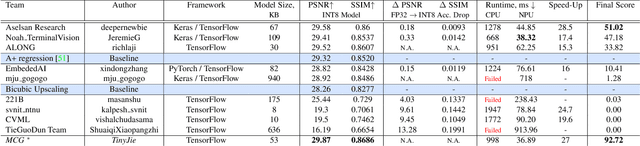
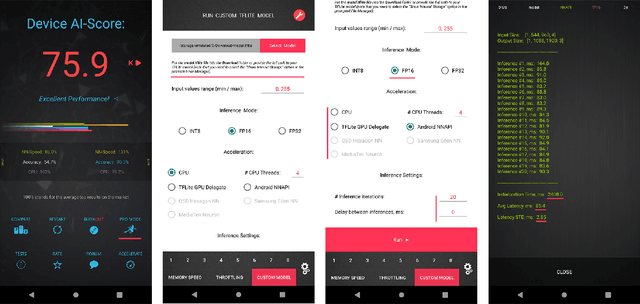
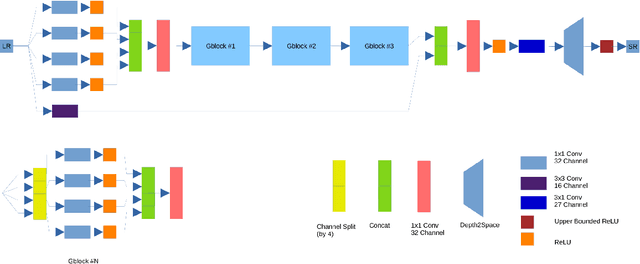
Abstract:Image super-resolution is one of the most popular computer vision problems with many important applications to mobile devices. While many solutions have been proposed for this task, they are usually not optimized even for common smartphone AI hardware, not to mention more constrained smart TV platforms that are often supporting INT8 inference only. To address this problem, we introduce the first Mobile AI challenge, where the target is to develop an end-to-end deep learning-based image super-resolution solutions that can demonstrate a real-time performance on mobile or edge NPUs. For this, the participants were provided with the DIV2K dataset and trained quantized models to do an efficient 3X image upscaling. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the Synaptics VS680 Smart Home board with a dedicated NPU capable of accelerating quantized neural networks. The proposed solutions are fully compatible with all major mobile AI accelerators and are capable of reconstructing Full HD images under 40-60 ms while achieving high fidelity results. A detailed description of all models developed in the challenge is provided in this paper.
Automated Design Space Exploration for optimised Deployment of DNN on Arm Cortex-A CPUs
Jun 09, 2020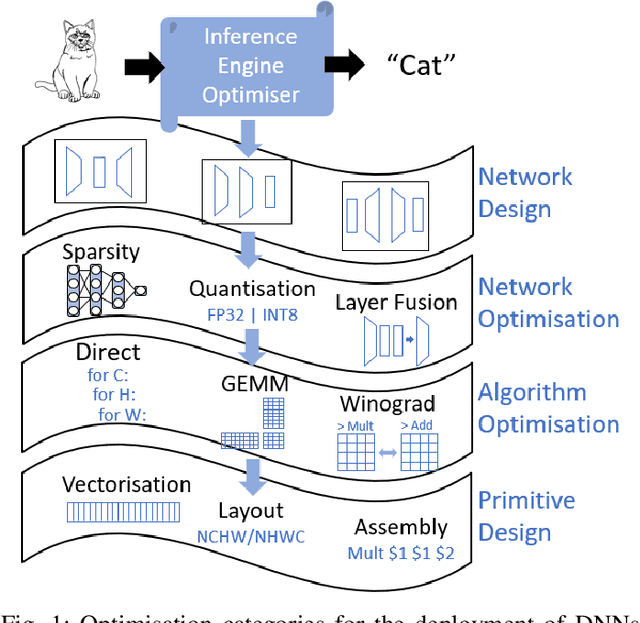
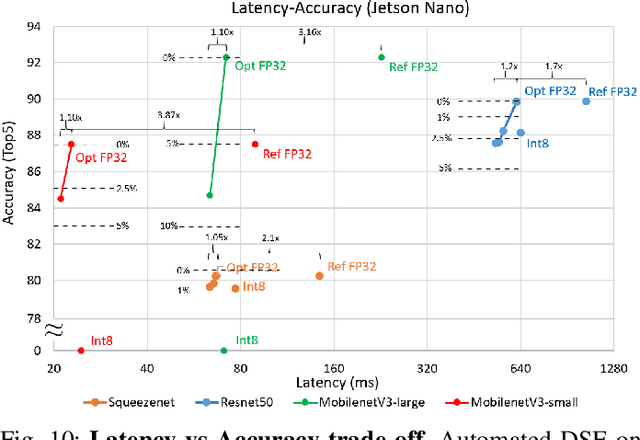
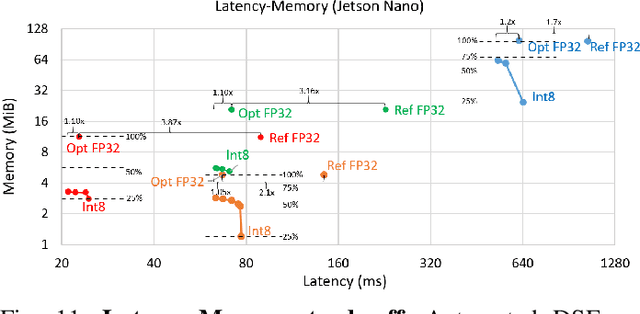
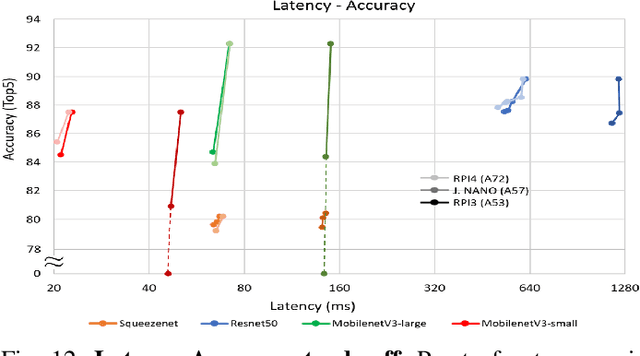
Abstract:The spread of deep learning on embedded devices has prompted the development of numerous methods to optimise the deployment of deep neural networks (DNN). Works have mainly focused on: i) efficient DNN architectures, ii) network optimisation techniques such as pruning and quantisation, iii) optimised algorithms to speed up the execution of the most computational intensive layers and, iv) dedicated hardware to accelerate the data flow and computation. However, there is a lack of research on the combination of these methods as the space of approaches becomes too large to test and obtain a globally optimised solution, which leads to suboptimal deployment in terms of latency, accuracy, and memory. In this work, we first detail and analyse the methods to improve the deployment of DNNs across the different levels of software optimisation. Building on this knowledge, we present an automated exploration framework to ease the deployment of DNNs for industrial applications by automatically exploring the design space and learning an optimised solution that speeds up the performance and reduces the memory on embedded CPU platforms. The framework relies on a Reinforcement Learning -based search that, combined with a deep learning inference framework, enables the deployment of DNN implementations to obtain empirical measurements on embedded AI applications. Thus, we present a set of results for state-of-the-art DNNs on a range of Arm Cortex-A CPU platforms achieving up to 4x improvement in performance and over 2x reduction in memory with negligible loss in accuracy with respect to the BLAS floating-point implementation.
QUENN: QUantization Engine for low-power Neural Networks
Nov 14, 2018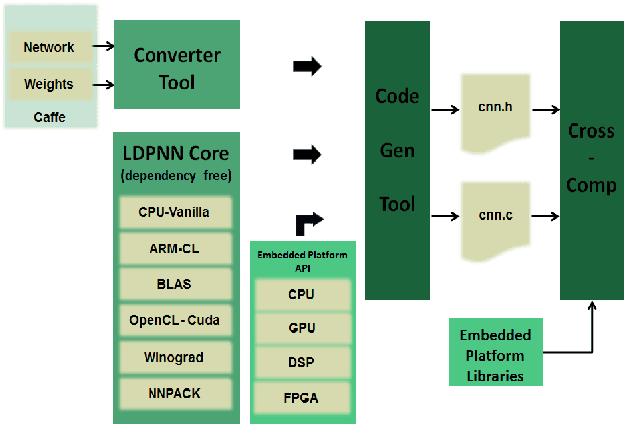
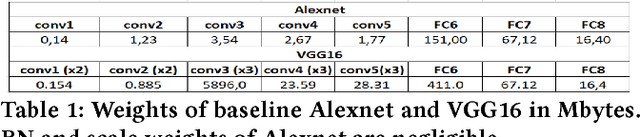
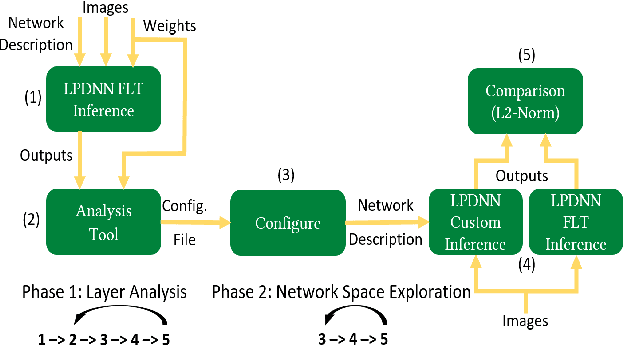
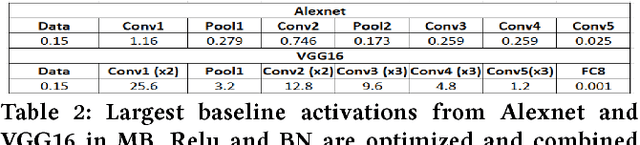
Abstract:Deep Learning is moving to edge devices, ushering in a new age of distributed Artificial Intelligence (AI). The high demand of computational resources required by deep neural networks may be alleviated by approximate computing techniques, and most notably reduced-precision arithmetic with coarsely quantized numerical representations. In this context, Bonseyes comes in as an initiative to enable stakeholders to bring AI to low-power and autonomous environments such as: Automotive, Medical Healthcare and Consumer Electronics. To achieve this, we introduce LPDNN, a framework for optimized deployment of Deep Neural Networks on heterogeneous embedded devices. In this work, we detail the quantization engine that is integrated in LPDNN. The engine depends on a fine-grained workflow which enables a Neural Network Design Exploration and a sensitivity analysis of each layer for quantization. We demonstrate the engine with a case study on Alexnet and VGG16 for three different techniques for direct quantization: standard fixed-point, dynamic fixed-point and k-means clustering, and demonstrate the potential of the latter. We argue that using a Gaussian quantizer with k-means clustering can achieve better performance than linear quantizers. Without retraining, we achieve over 55.64\% saving for weights' storage and 69.17\% for run-time memory accesses with less than 1\% drop in top5 accuracy in Imagenet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge