Xueyi Zhou
P2P: Part-to-Part Motion Cues Guide a Strong Tracking Framework for LiDAR Point Clouds
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:3D single object tracking (SOT) methods based on appearance matching has long suffered from insufficient appearance information incurred by incomplete, textureless and semantically deficient LiDAR point clouds. While motion paradigm exploits motion cues instead of appearance matching for tracking, it incurs complex multi-stage processing and segmentation module. In this paper, we first provide in-depth explorations on motion paradigm, which proves that (\textbf{i}) it is feasible to directly infer target relative motion from point clouds across consecutive frames; (\textbf{ii}) fine-grained information comparison between consecutive point clouds facilitates target motion modeling. We thereby propose to perform part-to-part motion modeling for consecutive point clouds and introduce a novel tracking framework, termed \textbf{P2P}. The novel framework fuses each corresponding part information between consecutive point clouds, effectively exploring detailed information changes and thus modeling accurate target-related motion cues. Following this framework, we present P2P-point and P2P-voxel models, incorporating implicit and explicit part-to-part motion modeling by point- and voxel-based representation, respectively. Without bells and whistles, P2P-voxel sets a new state-of-the-art performance ($\sim$\textbf{89\%}, \textbf{72\%} and \textbf{63\%} precision on KITTI, NuScenes and Waymo Open Dataset, respectively). Moreover, under the same point-based representation, P2P-point outperforms the previous motion tracker M$^2$Track by \textbf{3.3\%} and \textbf{6.7\%} on the KITTI and NuScenes, while running at a considerably high speed of \textbf{107 Fps} on a single RTX3090 GPU. The source code and pre-trained models are available at \url{https://github.com/haooozi/P2P}.
Towards Category Unification of 3D Single Object Tracking on Point Clouds
Jan 20, 2024Abstract:Category-specific models are provenly valuable methods in 3D single object tracking (SOT) regardless of Siamese or motion-centric paradigms. However, such over-specialized model designs incur redundant parameters, thus limiting the broader applicability of 3D SOT task. This paper first introduces unified models that can simultaneously track objects across all categories using a single network with shared model parameters. Specifically, we propose to explicitly encode distinct attributes associated to different object categories, enabling the model to adapt to cross-category data. We find that the attribute variances of point cloud objects primarily occur from the varying size and shape (e.g., large and square vehicles v.s. small and slender humans). Based on this observation, we design a novel point set representation learning network inheriting transformer architecture, termed AdaFormer, which adaptively encodes the dynamically varying shape and size information from cross-category data in a unified manner. We further incorporate the size and shape prior derived from the known template targets into the model's inputs and learning objective, facilitating the learning of unified representation. Equipped with such designs, we construct two category-unified models SiamCUT and MoCUT.Extensive experiments demonstrate that SiamCUT and MoCUT exhibit strong generalization and training stability. Furthermore, our category-unified models outperform the category-specific counterparts by a significant margin (e.g., on KITTI dataset, 12% and 3% performance gains on the Siamese and motion paradigms). Our code will be available.
Real-Time Video Super-Resolution on Smartphones with Deep Learning, Mobile AI 2021 Challenge: Report
May 17, 2021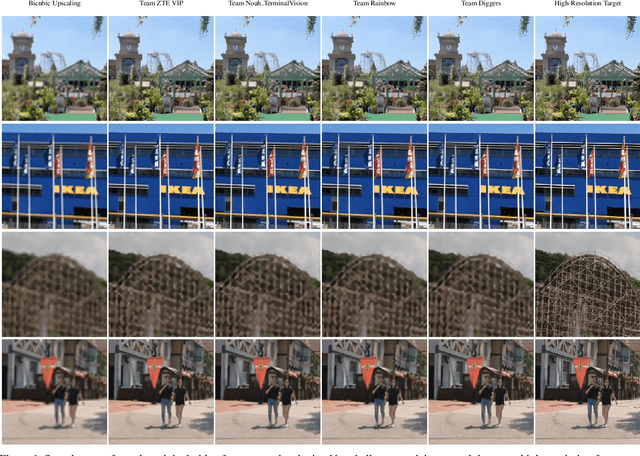
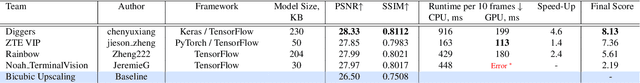
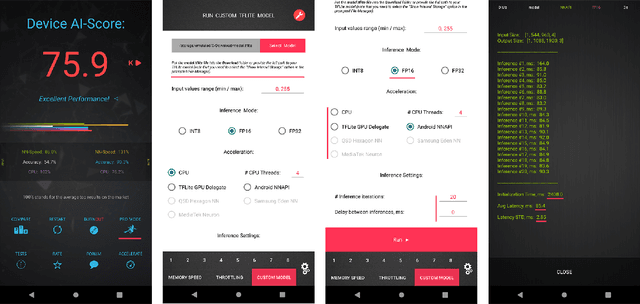
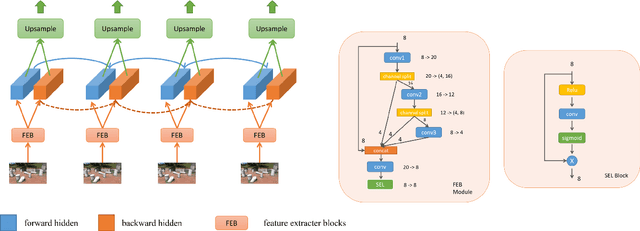
Abstract:Video super-resolution has recently become one of the most important mobile-related problems due to the rise of video communication and streaming services. While many solutions have been proposed for this task, the majority of them are too computationally expensive to run on portable devices with limited hardware resources. To address this problem, we introduce the first Mobile AI challenge, where the target is to develop an end-to-end deep learning-based video super-resolution solutions that can achieve a real-time performance on mobile GPUs. The participants were provided with the REDS dataset and trained their models to do an efficient 4X video upscaling. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the OPPO Find X2 smartphone with the Snapdragon 865 SoC capable of accelerating floating-point networks on its Adreno GPU. The proposed solutions are fully compatible with any mobile GPU and can upscale videos to HD resolution at up to 80 FPS while demonstrating high fidelity results. A detailed description of all models developed in the challenge is provided in this paper.
Real-Time Quantized Image Super-Resolution on Mobile NPUs, Mobile AI 2021 Challenge: Report
May 17, 2021
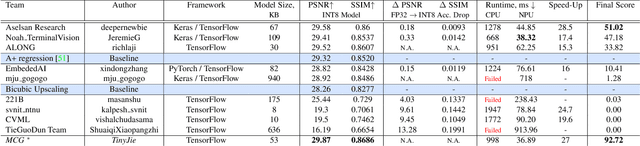
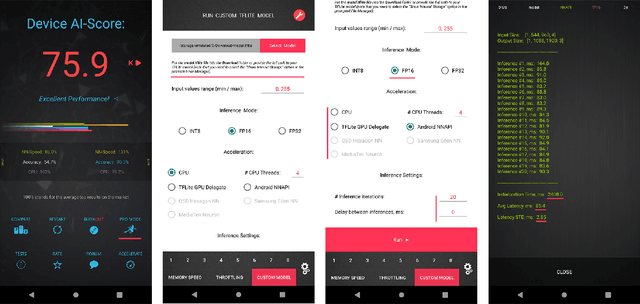
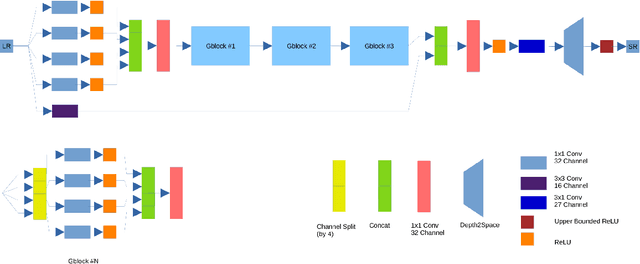
Abstract:Image super-resolution is one of the most popular computer vision problems with many important applications to mobile devices. While many solutions have been proposed for this task, they are usually not optimized even for common smartphone AI hardware, not to mention more constrained smart TV platforms that are often supporting INT8 inference only. To address this problem, we introduce the first Mobile AI challenge, where the target is to develop an end-to-end deep learning-based image super-resolution solutions that can demonstrate a real-time performance on mobile or edge NPUs. For this, the participants were provided with the DIV2K dataset and trained quantized models to do an efficient 3X image upscaling. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the Synaptics VS680 Smart Home board with a dedicated NPU capable of accelerating quantized neural networks. The proposed solutions are fully compatible with all major mobile AI accelerators and are capable of reconstructing Full HD images under 40-60 ms while achieving high fidelity results. A detailed description of all models developed in the challenge is provided in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge