Kyoung Mu Lee
StarryGazer: Leveraging Monocular Depth Estimation Models for Domain-Agnostic Single Depth Image Completion
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:The problem of depth completion involves predicting a dense depth image from a single sparse depth map and an RGB image. Unsupervised depth completion methods have been proposed for various datasets where ground truth depth data is unavailable and supervised methods cannot be applied. However, these models require auxiliary data to estimate depth values, which is far from real scenarios. Monocular depth estimation (MDE) models can produce a plausible relative depth map from a single image, but there is no work to properly combine the sparse depth map with MDE for depth completion; a simple affine transformation to the depth map will yield a high error since MDE are inaccurate at estimating depth difference between objects. We introduce StarryGazer, a domain-agnostic framework that predicts dense depth images from a single sparse depth image and an RGB image without relying on ground-truth depth by leveraging the power of large MDE models. First, we employ a pre-trained MDE model to produce relative depth images. These images are segmented and randomly rescaled to form synthetic pairs for dense pseudo-ground truth and corresponding sparse depths. A refinement network is trained with the synthetic pairs, incorporating the relative depth maps and RGB images to improve the model's accuracy and robustness. StarryGazer shows superior results over existing unsupervised methods and transformed MDE results on various datasets, demonstrating that our framework exploits the power of MDE models while appropriately fixing errors using sparse depth information.
MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning: Datasets, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Outlook
Sep 17, 2025
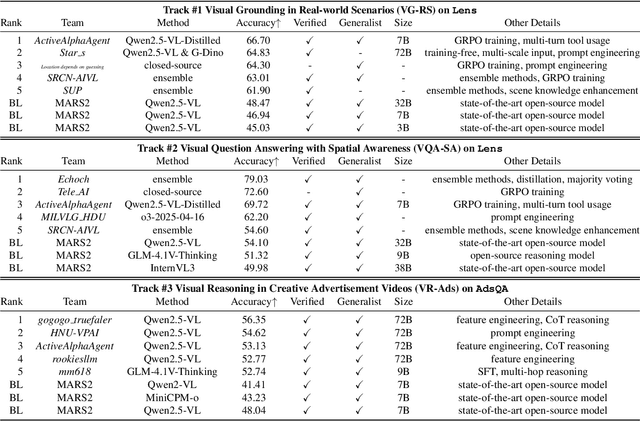

Abstract:This paper reviews the MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning. We aim to bring together different approaches in multimodal machine learning and LLMs via a large benchmark. We hope it better allows researchers to follow the state-of-the-art in this very dynamic area. Meanwhile, a growing number of testbeds have boosted the evolution of general-purpose large language models. Thus, this year's MARS2 focuses on real-world and specialized scenarios to broaden the multimodal reasoning applications of MLLMs. Our organizing team released two tailored datasets Lens and AdsQA as test sets, which support general reasoning in 12 daily scenarios and domain-specific reasoning in advertisement videos, respectively. We evaluated 40+ baselines that include both generalist MLLMs and task-specific models, and opened up three competition tracks, i.e., Visual Grounding in Real-world Scenarios (VG-RS), Visual Question Answering with Spatial Awareness (VQA-SA), and Visual Reasoning in Creative Advertisement Videos (VR-Ads). Finally, 76 teams from the renowned academic and industrial institutions have registered and 40+ valid submissions (out of 1200+) have been included in our ranking lists. Our datasets, code sets (40+ baselines and 15+ participants' methods), and rankings are publicly available on the MARS2 workshop website and our GitHub organization page https://github.com/mars2workshop/, where our updates and announcements of upcoming events will be continuously provided.
Exploiting Diffusion Prior for Task-driven Image Restoration
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Task-driven image restoration (TDIR) has recently emerged to address performance drops in high-level vision tasks caused by low-quality (LQ) inputs. Previous TDIR methods struggle to handle practical scenarios in which images are degraded by multiple complex factors, leaving minimal clues for restoration. This motivates us to leverage the diffusion prior, one of the most powerful natural image priors. However, while the diffusion prior can help generate visually plausible results, using it to restore task-relevant details remains challenging, even when combined with recent TDIR methods. To address this, we propose EDTR, which effectively harnesses the power of diffusion prior to restore task-relevant details. Specifically, we propose directly leveraging useful clues from LQ images in the diffusion process by generating from pixel-error-based pre-restored LQ images with mild noise added. Moreover, we employ a small number of denoising steps to prevent the generation of redundant details that dilute crucial task-related information. We demonstrate that our method effectively utilizes diffusion prior for TDIR, significantly enhancing task performance and visual quality across diverse tasks with multiple complex degradations.
PARTE: Part-Guided Texturing for 3D Human Reconstruction from a Single Image
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:The misaligned human texture across different human parts is one of the main limitations of existing 3D human reconstruction methods. Each human part, such as a jacket or pants, should maintain a distinct texture without blending into others. The structural coherence of human parts serves as a crucial cue to infer human textures in the invisible regions of a single image. However, most existing 3D human reconstruction methods do not explicitly exploit such part segmentation priors, leading to misaligned textures in their reconstructions. In this regard, we present PARTE, which utilizes 3D human part information as a key guide to reconstruct 3D human textures. Our framework comprises two core components. First, to infer 3D human part information from a single image, we propose a 3D part segmentation module (PartSegmenter) that initially reconstructs a textureless human surface and predicts human part labels based on the textureless surface. Second, to incorporate part information into texture reconstruction, we introduce a part-guided texturing module (PartTexturer), which acquires prior knowledge from a pre-trained image generation network on texture alignment of human parts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves state-of-the-art quality in 3D human reconstruction. The project page is available at https://hygenie1228.github.io/PARTE/.
GLOS: Sign Language Generation with Temporally Aligned Gloss-Level Conditioning
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Sign language generation (SLG), or text-to-sign generation, bridges the gap between signers and non-signers. Despite recent progress in SLG, existing methods still often suffer from incorrect lexical ordering and low semantic accuracy. This is primarily due to sentence-level condition, which encodes the entire sentence of the input text into a single feature vector as a condition for SLG. This approach fails to capture the temporal structure of sign language and lacks the granularity of word-level semantics, often leading to disordered sign sequences and ambiguous motions. To overcome these limitations, we propose GLOS, a sign language generation framework with temporally aligned gloss-level conditioning. First, we employ gloss-level conditions, which we define as sequences of gloss embeddings temporally aligned with the motion sequence. This enables the model to access both the temporal structure of sign language and word-level semantics at each timestep. As a result, this allows for fine-grained control of signs and better preservation of lexical order. Second, we introduce a condition fusion module, temporal alignment conditioning (TAC), to efficiently deliver the word-level semantic and temporal structure provided by the gloss-level condition to the corresponding motion timesteps. Our method, which is composed of gloss-level conditions and TAC, generates signs with correct lexical order and high semantic accuracy, outperforming prior methods on CSL-Daily and Phoenix-2014T.
Learning Dense Hand Contact Estimation from Imbalanced Data
May 16, 2025Abstract:Hands are essential to human interaction, and understanding contact between hands and the world can promote comprehensive understanding of their function. Recently, there have been growing number of hand interaction datasets that cover interaction with object, other hand, scene, and body. Despite the significance of the task and increasing high-quality data, how to effectively learn dense hand contact estimation remains largely underexplored. There are two major challenges for learning dense hand contact estimation. First, there exists class imbalance issue from hand contact datasets where majority of samples are not in contact. Second, hand contact datasets contain spatial imbalance issue with most of hand contact exhibited in finger tips, resulting in challenges for generalization towards contacts in other hand regions. To tackle these issues, we present a framework that learns dense HAnd COntact estimation (HACO) from imbalanced data. To resolve the class imbalance issue, we introduce balanced contact sampling, which builds and samples from multiple sampling groups that fairly represent diverse contact statistics for both contact and non-contact samples. Moreover, to address the spatial imbalance issue, we propose vertex-level class-balanced (VCB) loss, which incorporates spatially varying contact distribution by separately reweighting loss contribution of each vertex based on its contact frequency across dataset. As a result, we effectively learn to predict dense hand contact estimation with large-scale hand contact data without suffering from class and spatial imbalance issue. The codes will be released.
Auto-regressive transformation for image alignment
May 08, 2025



Abstract:Existing methods for image alignment struggle in cases involving feature-sparse regions, extreme scale and field-of-view differences, and large deformations, often resulting in suboptimal accuracy. Robustness to these challenges improves through iterative refinement of the transformation field while focusing on critical regions in multi-scale image representations. We thus propose Auto-Regressive Transformation (ART), a novel method that iteratively estimates the coarse-to-fine transformations within an auto-regressive framework. Leveraging hierarchical multi-scale features, our network refines the transformations using randomly sampled points at each scale. By incorporating guidance from the cross-attention layer, the model focuses on critical regions, ensuring accurate alignment even in challenging, feature-limited conditions. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate that ART significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, establishing it as a powerful new method for precise image alignment with broad applicability.
Find A Winning Sign: Sign Is All We Need to Win the Lottery
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:The Lottery Ticket Hypothesis (LTH) posits the existence of a sparse subnetwork (a.k.a. winning ticket) that can generalize comparably to its over-parameterized counterpart when trained from scratch. The common approach to finding a winning ticket is to preserve the original strong generalization through Iterative Pruning (IP) and transfer information useful for achieving the learned generalization by applying the resulting sparse mask to an untrained network. However, existing IP methods still struggle to generalize their observations beyond ad-hoc initialization and small-scale architectures or datasets, or they bypass these challenges by applying their mask to trained weights instead of initialized ones. In this paper, we demonstrate that the parameter sign configuration plays a crucial role in conveying useful information for generalization to any randomly initialized network. Through linear mode connectivity analysis, we observe that a sparse network trained by an existing IP method can retain its basin of attraction if its parameter signs and normalization layer parameters are preserved. To take a step closer to finding a winning ticket, we alleviate the reliance on normalization layer parameters by preventing high error barriers along the linear path between the sparse network trained by our method and its counterpart with initialized normalization layer parameters. Interestingly, across various architectures and datasets, we observe that any randomly initialized network can be optimized to exhibit low error barriers along the linear path to the sparse network trained by our method by inheriting its sparsity and parameter sign information, potentially achieving performance comparable to the original. The code is available at https://github.com/JungHunOh/AWS\_ICLR2025.git
DeClotH: Decomposable 3D Cloth and Human Body Reconstruction from a Single Image
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Most existing methods of 3D clothed human reconstruction from a single image treat the clothed human as a single object without distinguishing between cloth and human body. In this regard, we present DeClotH, which separately reconstructs 3D cloth and human body from a single image. This task remains largely unexplored due to the extreme occlusion between cloth and the human body, making it challenging to infer accurate geometries and textures. Moreover, while recent 3D human reconstruction methods have achieved impressive results using text-to-image diffusion models, directly applying such an approach to this problem often leads to incorrect guidance, particularly in reconstructing 3D cloth. To address these challenges, we propose two core designs in our framework. First, to alleviate the occlusion issue, we leverage 3D template models of cloth and human body as regularizations, which provide strong geometric priors to prevent erroneous reconstruction by the occlusion. Second, we introduce a cloth diffusion model specifically designed to provide contextual information about cloth appearance, thereby enhancing the reconstruction of 3D cloth. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach is highly effective in reconstructing both 3D cloth and the human body. More qualitative results are provided at https://hygenie1228.github.io/DeClotH/.
International AI Safety Report
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:The first International AI Safety Report comprehensively synthesizes the current evidence on the capabilities, risks, and safety of advanced AI systems. The report was mandated by the nations attending the AI Safety Summit in Bletchley, UK. Thirty nations, the UN, the OECD, and the EU each nominated a representative to the report's Expert Advisory Panel. A total of 100 AI experts contributed, representing diverse perspectives and disciplines. Led by the report's Chair, these independent experts collectively had full discretion over the report's content.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge