Yiming Cui
FPNet: Joint Wi-Fi Beamforming Matrix Feedback and Anomaly-Aware Indoor Positioning
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Channel State Information (CSI) provides a detailed description of the wireless channel and has been widely adopted for Wi-Fi sensing, particularly for high-precision indoor positioning. However, complete CSI is rarely available in real-world deployments due to hardware constraints and the high communication overhead required for feedback. Moreover, existing positioning models lack mechanisms to detect when users move outside their trained regions, leading to unreliable estimates in dynamic environments. In this paper, we present FPNet, a unified deep learning framework that jointly addresses channel feedback compression, accurate indoor positioning, and robust anomaly detection (AD). FPNet leverages the beamforming feedback matrix (BFM), a compressed CSI representation natively supported by IEEE 802.11ac/ax/be protocols, to minimize feedback overhead while preserving critical positioning features. To enhance reliability, we integrate ADBlock, a lightweight AD module trained on normal BFM samples, which identifies out-of-distribution scenarios when users exit predefined spatial regions. Experimental results using standard 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi hardware show that FPNet achieves positioning accuracy above 97% with only 100 feedback bits, boosts net throughput by up to 22.92%, and attains AD accuracy over 99% with a false alarm rate below 1.5%. These results demonstrate FPNet's ability to deliver efficient, accurate, and reliable indoor positioning on commodity Wi-Fi devices.
EchoFoley: Event-Centric Hierarchical Control for Video Grounded Creative Sound Generation
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Sound effects build an essential layer of multimodal storytelling, shaping the emotional atmosphere and the narrative semantics of videos. Despite recent advancement in video-text-to-audio (VT2A), the current formulation faces three key limitations: First, an imbalance between visual and textual conditioning that leads to visual dominance; Second, the absence of a concrete definition for fine-grained controllable generation; Third, weak instruction understanding and following, as existing datasets rely on brief categorical tags. To address these limitations, we introduce EchoFoley, a new task designed for video-grounded sound generation with both event level local control and hierarchical semantic control. Our symbolic representation for sounding events specifies when, what, and how each sound is produced within a video or instruction, enabling fine-grained controls like sound generation, insertion, and editing. To support this task, we construct EchoFoley-6k, a large-scale, expert-curated benchmark containing over 6,000 video-instruction-annotation triplets. Building upon this foundation, we propose EchoVidia a sounding-event-centric agentic generation framework with slow-fast thinking strategy. Experiments show that EchoVidia surpasses recent VT2A models by 40.7% in controllability and 12.5% in perceptual quality.
VP-AutoTest: A Virtual-Physical Fusion Autonomous Driving Testing Platform
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of autonomous vehicles has led to a surge in testing demand. Traditional testing methods, such as virtual simulation, closed-course, and public road testing, face several challenges, including unrealistic vehicle states, limited testing capabilities, and high costs. These issues have prompted increasing interest in virtual-physical fusion testing. However, despite its potential, virtual-physical fusion testing still faces challenges, such as limited element types, narrow testing scope, and fixed evaluation metrics. To address these challenges, we propose the Virtual-Physical Testing Platform for Autonomous Vehicles (VP-AutoTest), which integrates over ten types of virtual and physical elements, including vehicles, pedestrians, and roadside infrastructure, to replicate the diversity of real-world traffic participants. The platform also supports both single-vehicle interaction and multi-vehicle cooperation testing, employing adversarial testing and parallel deduction to accelerate fault detection and explore algorithmic limits, while OBU and Redis communication enable seamless vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) cooperation across all levels of cooperative automation. Furthermore, VP-AutoTest incorporates a multidimensional evaluation framework and AI-driven expert systems to conduct comprehensive performance assessment and defect diagnosis. Finally, by comparing virtual-physical fusion test results with real-world experiments, the platform performs credibility self-evaluation to ensure both the fidelity and efficiency of autonomous driving testing. Please refer to the website for the full testing functionalities on the autonomous driving public service platform OnSite:https://www.onsite.com.cn.
CoReVLA: A Dual-Stage End-to-End Autonomous Driving Framework for Long-Tail Scenarios via Collect-and-Refine
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Autonomous Driving (AD) systems have made notable progress, but their performance in long-tail, safety-critical scenarios remains limited. These rare cases contribute a disproportionate number of accidents. Vision-Language Action (VLA) models have strong reasoning abilities and offer a potential solution, but their effectiveness is limited by the lack of high-quality data and inefficient learning in such conditions. To address these challenges, we propose CoReVLA, a continual learning end-to-end autonomous driving framework that improves the performance in long-tail scenarios through a dual-stage process of data Collection and behavior Refinement. First, the model is jointly fine-tuned on a mixture of open-source driving QA datasets, allowing it to acquire a foundational understanding of driving scenarios. Next, CoReVLA is deployed within the Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE) simulation platform, where driver takeover data is collected from real-time interactions. Each takeover indicates a long-tail scenario that CoReVLA fails to handle reliably. Finally, the model is refined via Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), allowing it to learn directly from human preferences and thereby avoid reward hacking caused by manually designed rewards. Extensive open-loop and closed-loop experiments demonstrate that the proposed CoReVLA model can accurately perceive driving scenarios and make appropriate decisions. On the Bench2Drive benchmark, CoReVLA achieves a Driving Score (DS) of 72.18 and a Success Rate (SR) of 50%, outperforming state-of-the-art methods by 7.96 DS and 15% SR under long-tail, safety-critical scenarios. Furthermore, case studies demonstrate the model's ability to continually improve its performance in similar failure-prone scenarios by leveraging past takeover experiences. All codea and preprocessed datasets are available at: https://github.com/FanGShiYuu/CoReVLA
AdapCsiNet: Environment-Adaptive CSI Feedback via Scene Graph-Aided Deep Learning
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:Accurate channel state information (CSI) is critical for realizing the full potential of multiple-antenna wireless communication systems. While deep learning (DL)-based CSI feedback methods have shown promise in reducing feedback overhead, their generalization capability across varying propagation environments remains limited due to their data-driven nature. Existing solutions based on online training improve adaptability but impose significant overhead in terms of data collection and computational resources. In this work, we propose AdapCsiNet, an environment-adaptive DL-based CSI feedback framework that eliminates the need for online training. By integrating environmental information -- represented as a scene graph -- into a hypernetwork-guided CSI reconstruction process, AdapCsiNet dynamically adapts to diverse channel conditions. A two-step training strategy is introduced to ensure baseline reconstruction performance and effective environment-aware adaptation. Simulation results demonstrate that AdapCsiNet achieves up to 46.4% improvement in CSI reconstruction accuracy and matches the performance of online learning methods without incurring additional runtime overhead.
A Vehicle-Infrastructure Multi-layer Cooperative Decision-making Framework
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving has entered the testing phase, but due to the limited decision-making capabilities of individual vehicle algorithms, safety and efficiency issues have become more apparent in complex scenarios. With the advancement of connected communication technologies, autonomous vehicles equipped with connectivity can leverage vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications, offering a potential solution to the decision-making challenges from individual vehicle's perspective. We propose a multi-level vehicle-infrastructure cooperative decision-making framework for complex conflict scenarios at unsignalized intersections. First, based on vehicle states, we define a method for quantifying vehicle impacts and their propagation relationships, using accumulated impact to group vehicles through motif-based graph clustering. Next, within and between vehicle groups, a pass order negotiation process based on Large Language Models (LLM) is employed to determine the vehicle passage order, resulting in planned vehicle actions. Simulation results from ablation experiments show that our approach reduces negotiation complexity and ensures safer, more efficient vehicle passage at intersections, aligning with natural decision-making logic.
Prompt-Enabled Large AI Models for CSI Feedback
Jan 18, 2025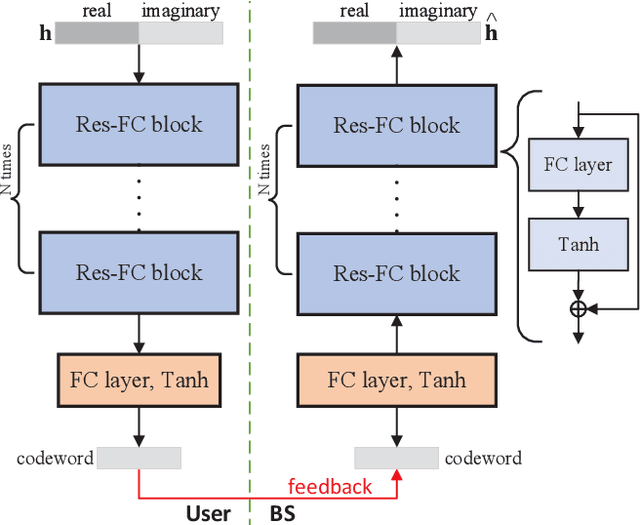
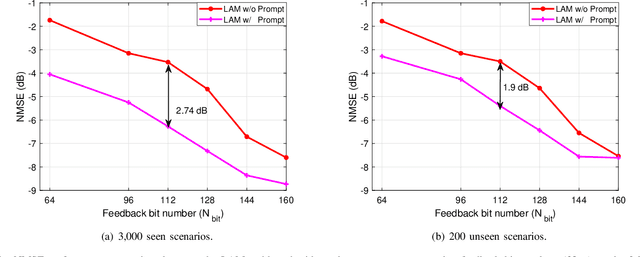
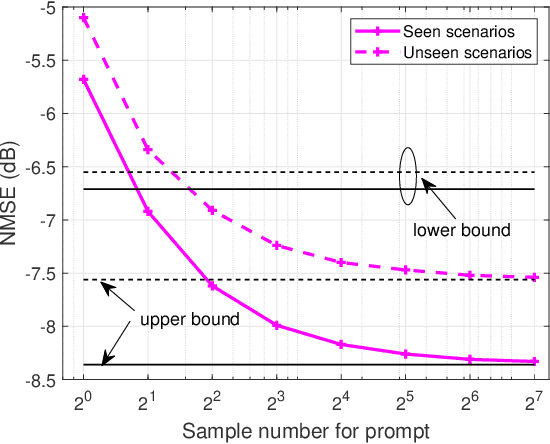
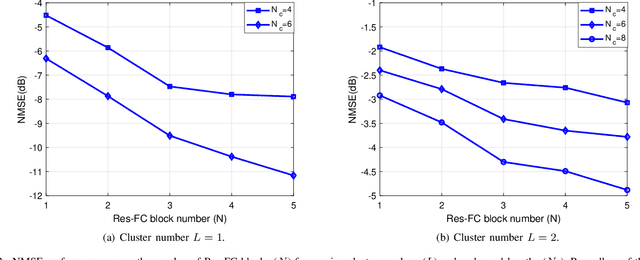
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising tool for channel state information (CSI) feedback. While recent research primarily focuses on improving feedback accuracy through novel architectures, the underlying mechanisms of AI-based CSI feedback remain unclear. This study investigates these mechanisms by analyzing performance across diverse datasets and reveals that superior feedback performance stems from the strong fitting capabilities of AI models and their ability to leverage environmental knowledge. Building on these findings, we propose a prompt-enabled large AI model (LAM) for CSI feedback. The LAM employs powerful transformer blocks and is trained on extensive datasets from various scenarios. To further enhance reconstruction quality, the channel distribution -- represented as the mean of channel magnitude in the angular domain -- is incorporated as a prompt within the decoder. Simulation results confirm that the proposed prompt-enabled LAM significantly improves feedback accuracy and generalization performance while reducing data collection requirements in new scenarios.
A Static and Dynamic Attention Framework for Multi Turn Dialogue Generation
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Recently, research on open domain dialogue systems have attracted extensive interests of academic and industrial researchers. The goal of an open domain dialogue system is to imitate humans in conversations. Previous works on single turn conversation generation have greatly promoted the research of open domain dialogue systems. However, understanding multiple single turn conversations is not equal to the understanding of multi turn dialogue due to the coherent and context dependent properties of human dialogue. Therefore, in open domain multi turn dialogue generation, it is essential to modeling the contextual semantics of the dialogue history, rather than only according to the last utterance. Previous research had verified the effectiveness of the hierarchical recurrent encoder-decoder framework on open domain multi turn dialogue generation. However, using RNN-based model to hierarchically encoding the utterances to obtain the representation of dialogue history still face the problem of a vanishing gradient. To address this issue, in this paper, we proposed a static and dynamic attention-based approach to model the dialogue history and then generate open domain multi turn dialogue responses. Experimental results on Ubuntu and Opensubtitles datasets verify the effectiveness of the proposed static and dynamic attention-based approach on automatic and human evaluation metrics in various experimental settings. Meanwhile, we also empirically verify the performance of combining the static and dynamic attentions on open domain multi turn dialogue generation.
* published as a journal paper at ACM Transactions on Information Systems 2023. 30 pages, 6 figures
Visualizing attention zones in machine reading comprehension models
Oct 28, 2024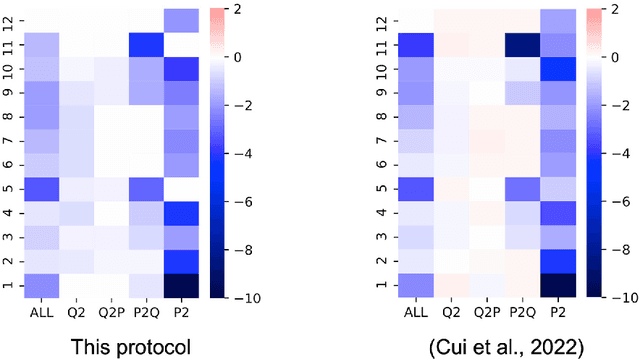
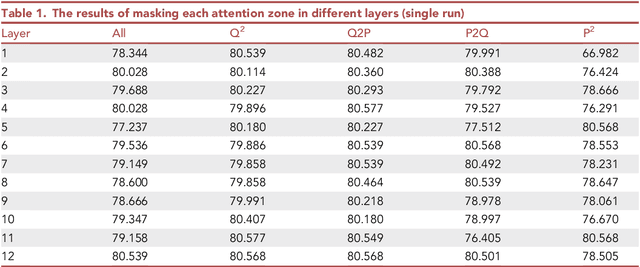
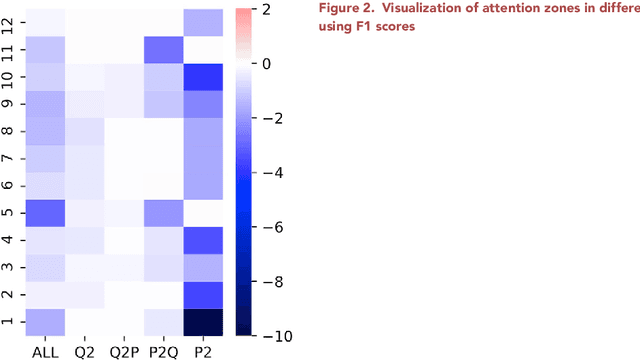
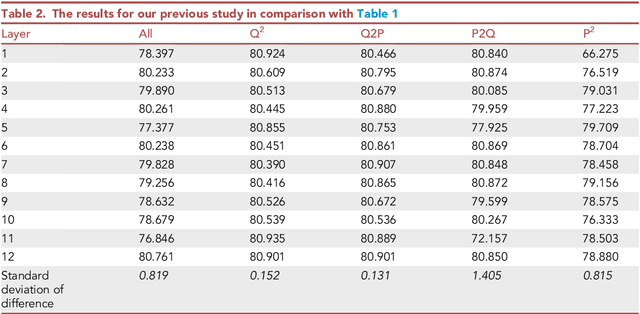
Abstract:The attention mechanism plays an important role in the machine reading comprehension (MRC) model. Here, we describe a pipeline for building an MRC model with a pretrained language model and visualizing the effect of each attention zone in different layers, which can indicate the explainability of the model. With the presented protocol and accompanying code, researchers can easily visualize the relevance of each attention zone in the MRC model. This approach can be generalized to other pretrained language models.
Efficient Deep Learning-based Cascaded Channel Feedback in RIS-Assisted Communications
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:In the realm of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted communication systems, the connection between a base station (BS) and user equipment (UE) is formed by a cascaded channel, merging the BS-RIS and RIS-UE channels. Due to the fixed positioning of the BS and RIS and the mobility of UE, these two channels generally exhibit different time-varying characteristics, which are challenging to identify and exploit for feedback overhead reduction, given the separate channel estimation difficulty. To address this challenge, this letter introduces an innovative deep learning-based framework tailored for cascaded channel feedback, ingeniously capturing the intrinsic time variation in the cascaded channel. When an entire cascaded channel has been sent to the BS, this framework advocates the feedback of an efficient representation of this variation within a subsequent period through an extraction-compression scheme. This scheme involves RIS unit-grained channel variation extraction, followed by autoencoder-based deep compression to enhance compactness. Numerical simulations confirm that this feedback framework significantly reduces both the feedback and computational burdens.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge