Aurelia Guy
Intra-agent speech permits zero-shot task acquisition
Jun 07, 2022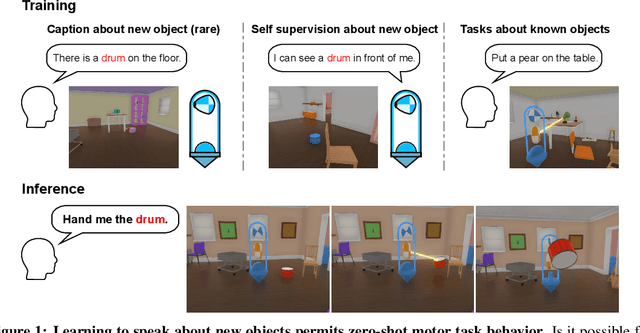
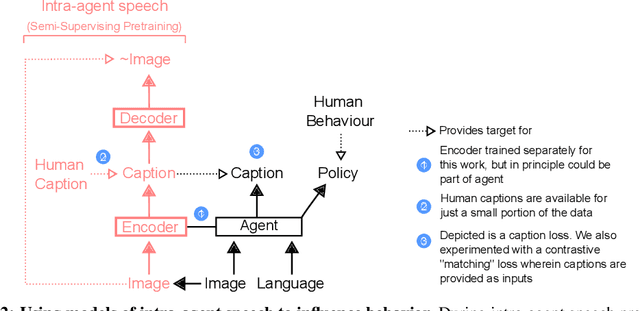

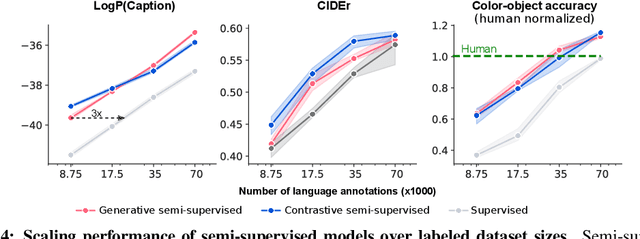
Abstract:Human language learners are exposed to a trickle of informative, context-sensitive language, but a flood of raw sensory data. Through both social language use and internal processes of rehearsal and practice, language learners are able to build high-level, semantic representations that explain their perceptions. Here, we take inspiration from such processes of "inner speech" in humans (Vygotsky, 1934) to better understand the role of intra-agent speech in embodied behavior. First, we formally pose intra-agent speech as a semi-supervised problem and develop two algorithms that enable visually grounded captioning with little labeled language data. We then experimentally compute scaling curves over different amounts of labeled data and compare the data efficiency against a supervised learning baseline. Finally, we incorporate intra-agent speech into an embodied, mobile manipulator agent operating in a 3D virtual world, and show that with as few as 150 additional image captions, intra-agent speech endows the agent with the ability to manipulate and answer questions about a new object without any related task-directed experience (zero-shot). Taken together, our experiments suggest that modelling intra-agent speech is effective in enabling embodied agents to learn new tasks efficiently and without direct interaction experience.
Training Compute-Optimal Large Language Models
Mar 29, 2022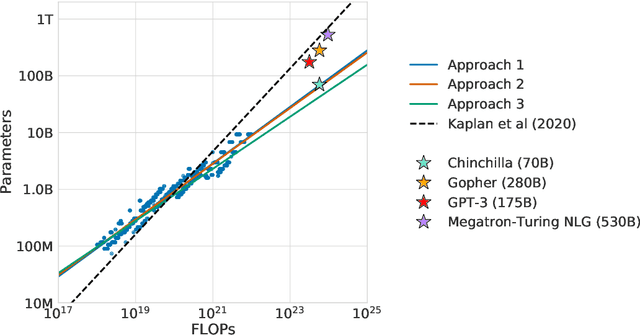
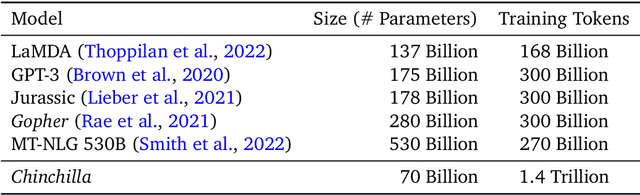

Abstract:We investigate the optimal model size and number of tokens for training a transformer language model under a given compute budget. We find that current large language models are significantly undertrained, a consequence of the recent focus on scaling language models whilst keeping the amount of training data constant. By training over \nummodels language models ranging from 70 million to over 16 billion parameters on 5 to 500 billion tokens, we find that for compute-optimal training, the model size and the number of training tokens should be scaled equally: for every doubling of model size the number of training tokens should also be doubled. We test this hypothesis by training a predicted compute-optimal model, \chinchilla, that uses the same compute budget as \gopher but with 70B parameters and 4$\times$ more more data. \chinchilla uniformly and significantly outperforms \Gopher (280B), GPT-3 (175B), Jurassic-1 (178B), and Megatron-Turing NLG (530B) on a large range of downstream evaluation tasks. This also means that \chinchilla uses substantially less compute for fine-tuning and inference, greatly facilitating downstream usage. As a highlight, \chinchilla reaches a state-of-the-art average accuracy of 67.5\% on the MMLU benchmark, greater than a 7\% improvement over \gopher.
Unified Scaling Laws for Routed Language Models
Feb 09, 2022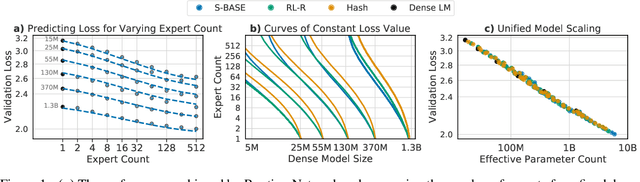

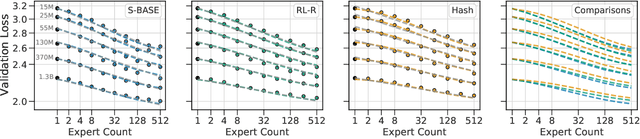
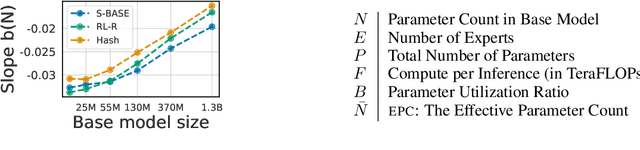
Abstract:The performance of a language model has been shown to be effectively modeled as a power-law in its parameter count. Here we study the scaling behaviors of Routing Networks: architectures that conditionally use only a subset of their parameters while processing an input. For these models, parameter count and computational requirement form two independent axes along which an increase leads to better performance. In this work we derive and justify scaling laws defined on these two variables which generalize those known for standard language models and describe the performance of a wide range of routing architectures trained via three different techniques. Afterwards we provide two applications of these laws: first deriving an Effective Parameter Count along which all models scale at the same rate, and then using the scaling coefficients to give a quantitative comparison of the three routing techniques considered. Our analysis derives from an extensive evaluation of Routing Networks across five orders of magnitude of size, including models with hundreds of experts and hundreds of billions of parameters.
Improving language models by retrieving from trillions of tokens
Jan 11, 2022
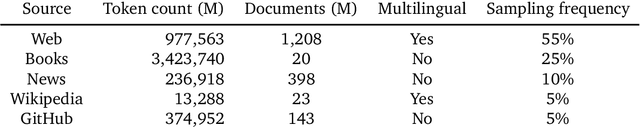

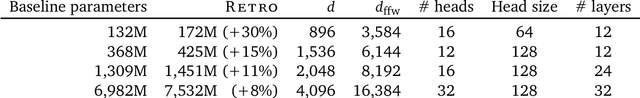
Abstract:We enhance auto-regressive language models by conditioning on document chunks retrieved from a large corpus, based on local similarity with preceding tokens. With a $2$ trillion token database, our Retrieval-Enhanced Transformer (RETRO) obtains comparable performance to GPT-3 and Jurassic-1 on the Pile, despite using 25$\times$ fewer parameters. After fine-tuning, RETRO performance translates to downstream knowledge-intensive tasks such as question answering. RETRO combines a frozen Bert retriever, a differentiable encoder and a chunked cross-attention mechanism to predict tokens based on an order of magnitude more data than what is typically consumed during training. We typically train RETRO from scratch, yet can also rapidly RETROfit pre-trained transformers with retrieval and still achieve good performance. Our work opens up new avenues for improving language models through explicit memory at unprecedented scale.
Scaling Language Models: Methods, Analysis & Insights from Training Gopher
Dec 08, 2021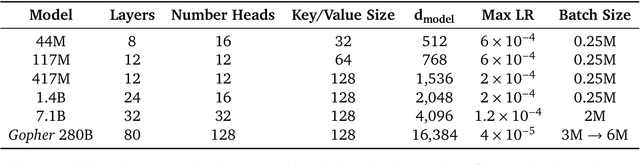
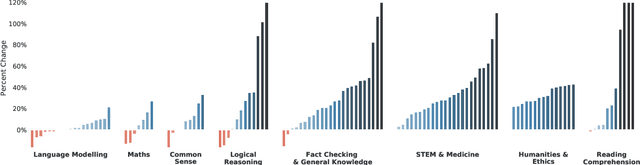
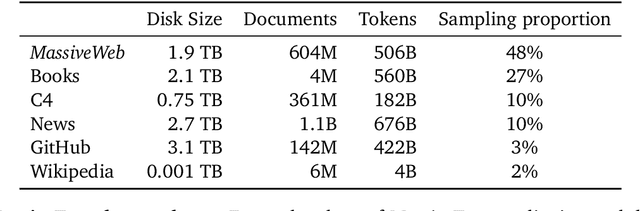
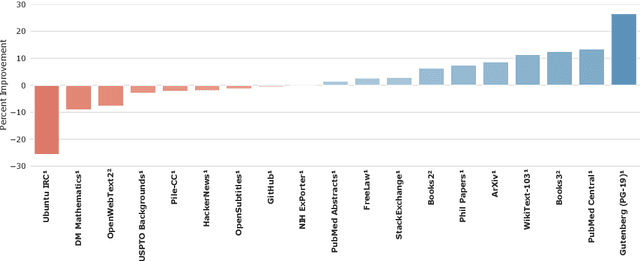
Abstract:Language modelling provides a step towards intelligent communication systems by harnessing large repositories of written human knowledge to better predict and understand the world. In this paper, we present an analysis of Transformer-based language model performance across a wide range of model scales -- from models with tens of millions of parameters up to a 280 billion parameter model called Gopher. These models are evaluated on 152 diverse tasks, achieving state-of-the-art performance across the majority. Gains from scale are largest in areas such as reading comprehension, fact-checking, and the identification of toxic language, but logical and mathematical reasoning see less benefit. We provide a holistic analysis of the training dataset and model's behaviour, covering the intersection of model scale with bias and toxicity. Finally we discuss the application of language models to AI safety and the mitigation of downstream harms.
Imitating Interactive Intelligence
Jan 21, 2021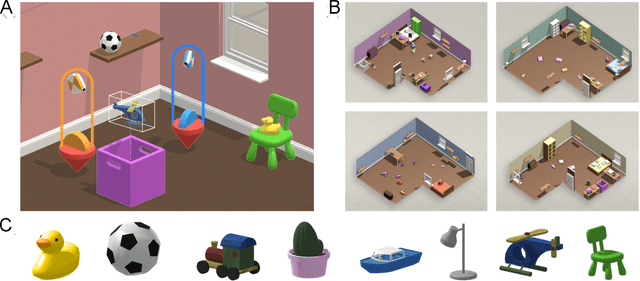
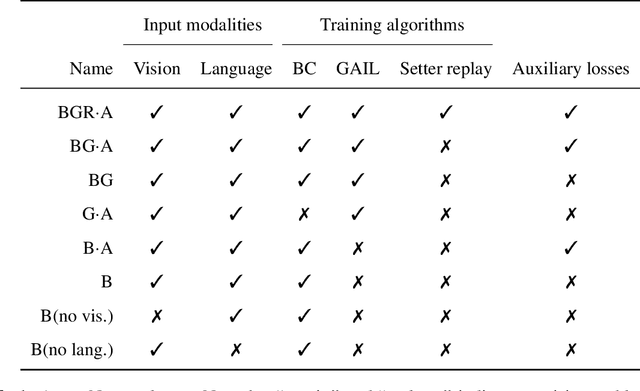
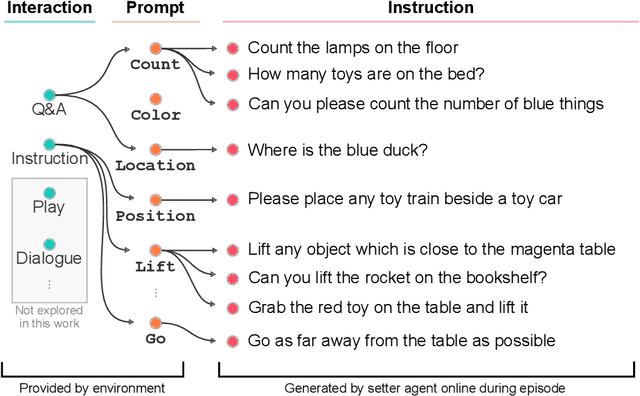
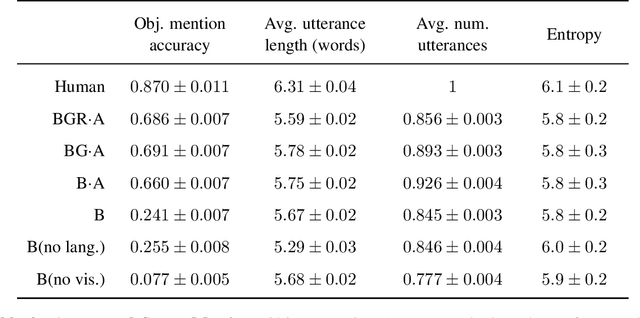
Abstract:A common vision from science fiction is that robots will one day inhabit our physical spaces, sense the world as we do, assist our physical labours, and communicate with us through natural language. Here we study how to design artificial agents that can interact naturally with humans using the simplification of a virtual environment. This setting nevertheless integrates a number of the central challenges of artificial intelligence (AI) research: complex visual perception and goal-directed physical control, grounded language comprehension and production, and multi-agent social interaction. To build agents that can robustly interact with humans, we would ideally train them while they interact with humans. However, this is presently impractical. Therefore, we approximate the role of the human with another learned agent, and use ideas from inverse reinforcement learning to reduce the disparities between human-human and agent-agent interactive behaviour. Rigorously evaluating our agents poses a great challenge, so we develop a variety of behavioural tests, including evaluation by humans who watch videos of agents or interact directly with them. These evaluations convincingly demonstrate that interactive training and auxiliary losses improve agent behaviour beyond what is achieved by supervised learning of actions alone. Further, we demonstrate that agent capabilities generalise beyond literal experiences in the dataset. Finally, we train evaluation models whose ratings of agents agree well with human judgement, thus permitting the evaluation of new agent models without additional effort. Taken together, our results in this virtual environment provide evidence that large-scale human behavioural imitation is a promising tool to create intelligent, interactive agents, and the challenge of reliably evaluating such agents is possible to surmount.
A Distraction Score for Watermarks
Aug 09, 2019



Abstract:In this work we propose a novel technique to quantify how distracting watermarks are on an image. We begin with watermark detection using a two-tower CNN model composed of a binary classification task and a semantic segmentation prediction. With this model, we demonstrate significant improvement in image precision while maintaining per-pixel accuracy, especially for our real-world dataset with sparse positive examples. We fit a nonlinear function to represent detected watermarks by a single score correlated with human perception based on their size, location, and visual obstructiveness. Finally, we validate our method in an image ranking setup, which is the main application of our watermark scoring algorithm.
Simple random search provides a competitive approach to reinforcement learning
Mar 19, 2018



Abstract:A common belief in model-free reinforcement learning is that methods based on random search in the parameter space of policies exhibit significantly worse sample complexity than those that explore the space of actions. We dispel such beliefs by introducing a random search method for training static, linear policies for continuous control problems, matching state-of-the-art sample efficiency on the benchmark MuJoCo locomotion tasks. Our method also finds a nearly optimal controller for a challenging instance of the Linear Quadratic Regulator, a classical problem in control theory, when the dynamics are not known. Computationally, our random search algorithm is at least 15 times more efficient than the fastest competing model-free methods on these benchmarks. We take advantage of this computational efficiency to evaluate the performance of our method over hundreds of random seeds and many different hyperparameter configurations for each benchmark task. Our simulations highlight a high variability in performance in these benchmark tasks, suggesting that commonly used estimations of sample efficiency do not adequately evaluate the performance of RL algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge