RGAR: Recurrence Generation-augmented Retrieval for Factual-aware Medical Question Answering
Paper and Code
Feb 19, 2025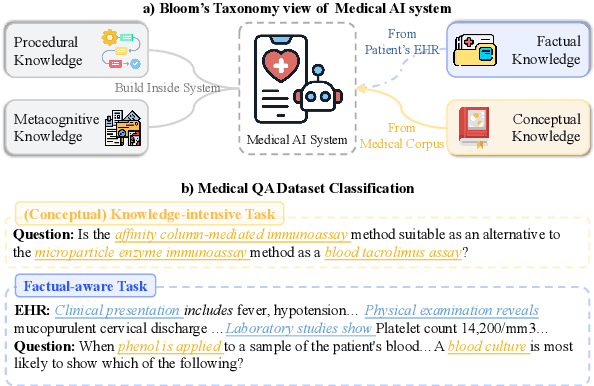
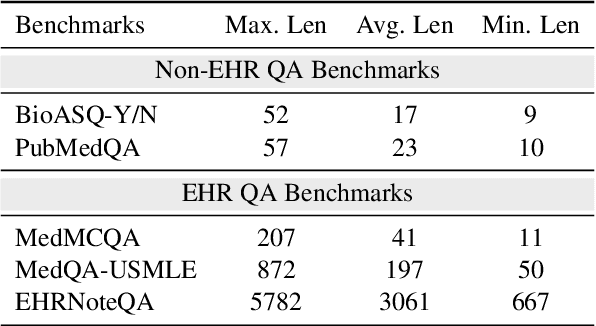
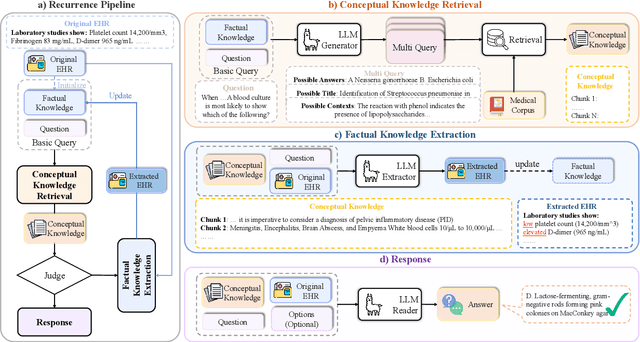
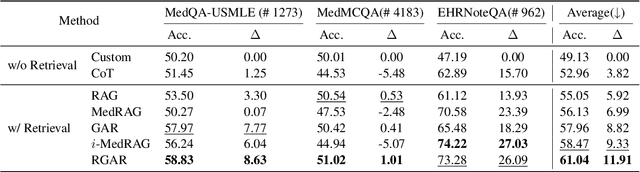
Medical question answering requires extensive access to specialized conceptual knowledge. The current paradigm, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), acquires expertise medical knowledge through large-scale corpus retrieval and uses this knowledge to guide a general-purpose large language model (LLM) for generating answers. However, existing retrieval approaches often overlook the importance of factual knowledge, which limits the relevance of retrieved conceptual knowledge and restricts its applicability in real-world scenarios, such as clinical decision-making based on Electronic Health Records (EHRs). This paper introduces RGAR, a recurrence generation-augmented retrieval framework that retrieves both relevant factual and conceptual knowledge from dual sources (i.e., EHRs and the corpus), allowing them to interact and refine each another. Through extensive evaluation across three factual-aware medical question answering benchmarks, RGAR establishes a new state-of-the-art performance among medical RAG systems. Notably, the Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct model with RGAR surpasses the considerably larger, RAG-enhanced GPT-3.5. Our findings demonstrate the benefit of extracting factual knowledge for retrieval, which consistently yields improved generation quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge