Jun Yin
Amazon
Beyond Perfect APIs: A Comprehensive Evaluation of LLM Agents Under Real-World API Complexity
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:We introduce WildAGTEval, a benchmark designed to evaluate large language model (LLM) agents' function-calling capabilities under realistic API complexity. Unlike prior work that assumes an idealized API system and disregards real-world factors such as noisy API outputs, WildAGTEval accounts for two dimensions of real-world complexity: 1. API specification, which includes detailed documentation and usage constraints, and 2. API execution, which captures runtime challenges. Consequently, WildAGTEval offers (i) an API system encompassing 60 distinct complexity scenarios that can be composed into approximately 32K test configurations, and (ii) user-agent interactions for evaluating LLM agents on these scenarios. Using WildAGTEval, we systematically assess several advanced LLMs and observe that most scenarios are challenging, with irrelevant information complexity posing the greatest difficulty and reducing the performance of strong LLMs by 27.3%. Furthermore, our qualitative analysis reveals that LLMs occasionally distort user intent merely to claim task completion, critically affecting user satisfaction.
Careful Queries, Credible Results: Teaching RAG Models Advanced Web Search Tools with Reinforcement Learning
Aug 11, 2025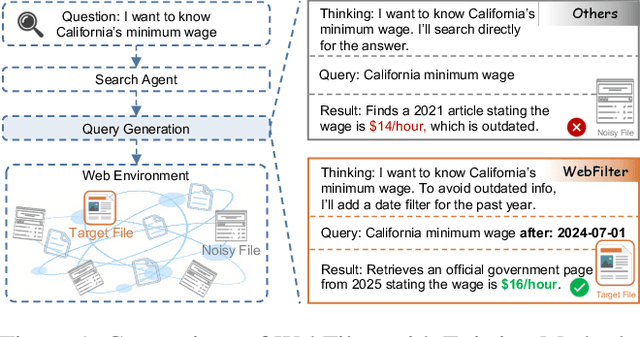
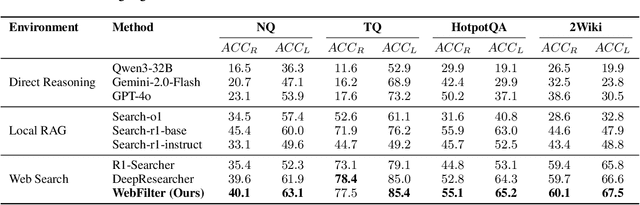
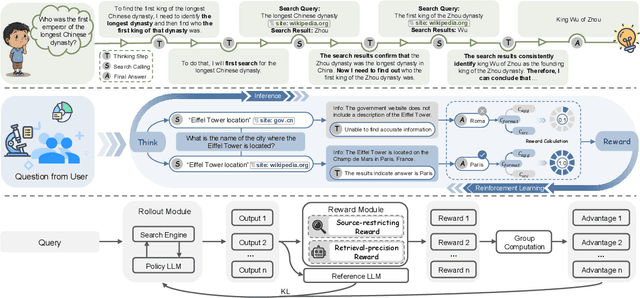
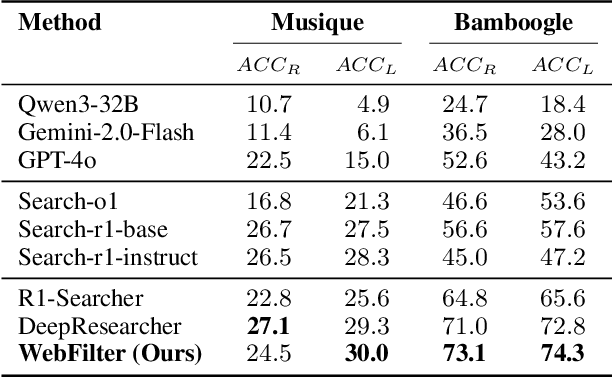
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) by integrating up-to-date external knowledge, yet real-world web environments present unique challenges. These limitations manifest as two key challenges: pervasive misinformation in the web environment, which introduces unreliable or misleading content that can degrade retrieval accuracy, and the underutilization of web tools, which, if effectively employed, could enhance query precision and help mitigate this noise, ultimately improving the retrieval results in RAG systems. To address these issues, we propose WebFilter, a novel RAG framework that generates source-restricted queries and filters out unreliable content. This approach combines a retrieval filtering mechanism with a behavior- and outcome-driven reward strategy, optimizing both query formulation and retrieval outcomes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that WebFilter improves answer quality and retrieval precision, outperforming existing RAG methods on both in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks.
SAMST: A Transformer framework based on SAM pseudo label filtering for remote sensing semi-supervised semantic segmentation
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Public remote sensing datasets often face limitations in universality due to resolution variability and inconsistent land cover category definitions. To harness the vast pool of unlabeled remote sensing data, we propose SAMST, a semi-supervised semantic segmentation method. SAMST leverages the strengths of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) in zero-shot generalization and boundary detection. SAMST iteratively refines pseudo-labels through two main components: supervised model self-training using both labeled and pseudo-labeled data, and a SAM-based Pseudo-label Refiner. The Pseudo-label Refiner comprises three modules: a Threshold Filter Module for preprocessing, a Prompt Generation Module for extracting connected regions and generating prompts for SAM, and a Label Refinement Module for final label stitching. By integrating the generalization power of large models with the training efficiency of small models, SAMST improves pseudo-label accuracy, thereby enhancing overall model performance. Experiments on the Potsdam dataset validate the effectiveness and feasibility of SAMST, demonstrating its potential to address the challenges posed by limited labeled data in remote sensing semantic segmentation.
UrbanSense:AFramework for Quantitative Analysis of Urban Streetscapes leveraging Vision Large Language Models
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Urban cultures and architectural styles vary significantly across cities due to geographical, chronological, historical, and socio-political factors. Understanding these differences is essential for anticipating how cities may evolve in the future. As representative cases of historical continuity and modern innovation in China, Beijing and Shenzhen offer valuable perspectives for exploring the transformation of urban streetscapes. However, conventional approaches to urban cultural studies often rely on expert interpretation and historical documentation, which are difficult to standardize across different contexts. To address this, we propose a multimodal research framework based on vision-language models, enabling automated and scalable analysis of urban streetscape style differences. This approach enhances the objectivity and data-driven nature of urban form research. The contributions of this study are as follows: First, we construct UrbanDiffBench, a curated dataset of urban streetscapes containing architectural images from different periods and regions. Second, we develop UrbanSense, the first vision-language-model-based framework for urban streetscape analysis, enabling the quantitative generation and comparison of urban style representations. Third, experimental results show that Over 80% of generated descriptions pass the t-test (p less than 0.05). High Phi scores (0.912 for cities, 0.833 for periods) from subjective evaluations confirm the method's ability to capture subtle stylistic differences. These results highlight the method's potential to quantify and interpret urban style evolution, offering a scientifically grounded lens for future design.
FloorplanMAE:A self-supervised framework for complete floorplan generation from partial inputs
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:In the architectural design process, floorplan design is often a dynamic and iterative process. Architects progressively draw various parts of the floorplan according to their ideas and requirements, continuously adjusting and refining throughout the design process. Therefore, the ability to predict a complete floorplan from a partial one holds significant value in the design process. Such prediction can help architects quickly generate preliminary designs, improve design efficiency, and reduce the workload associated with repeated modifications. To address this need, we propose FloorplanMAE, a self-supervised learning framework for restoring incomplete floor plans into complete ones. First, we developed a floor plan reconstruction dataset, FloorplanNet, specifically trained on architectural floor plans. Secondly, we propose a floor plan reconstruction method based on Masked Autoencoders (MAE), which reconstructs missing parts by masking sections of the floor plan and training a lightweight Vision Transformer (ViT). We evaluated the reconstruction accuracy of FloorplanMAE and compared it with state-of-the-art benchmarks. Additionally, we validated the model using real sketches from the early stages of architectural design. Experimental results show that the FloorplanMAE model can generate high-quality complete floor plans from incomplete partial plans. This framework provides a scalable solution for floor plan generation, with broad application prospects.
Segment Any Architectural Facades (SAAF):An automatic segmentation model for building facades, walls and windows based on multimodal semantics guidance
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:In the context of the digital development of architecture, the automatic segmentation of walls and windows is a key step in improving the efficiency of building information models and computer-aided design. This study proposes an automatic segmentation model for building facade walls and windows based on multimodal semantic guidance, called Segment Any Architectural Facades (SAAF). First, SAAF has a multimodal semantic collaborative feature extraction mechanism. By combining natural language processing technology, it can fuse the semantic information in text descriptions with image features, enhancing the semantic understanding of building facade components. Second, we developed an end-to-end training framework that enables the model to autonomously learn the mapping relationship from text descriptions to image segmentation, reducing the influence of manual intervention on the segmentation results and improving the automation and robustness of the model. Finally, we conducted extensive experiments on multiple facade datasets. The segmentation results of SAAF outperformed existing methods in the mIoU metric, indicating that the SAAF model can maintain high-precision segmentation ability when faced with diverse datasets. Our model has made certain progress in improving the accuracy and generalization ability of the wall and window segmentation task. It is expected to provide a reference for the development of architectural computer vision technology and also explore new ideas and technical paths for the application of multimodal learning in the architectural field.
ArchiLense: A Framework for Quantitative Analysis of Architectural Styles Based on Vision Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Architectural cultures across regions are characterized by stylistic diversity, shaped by historical, social, and technological contexts in addition to geograph-ical conditions. Understanding architectural styles requires the ability to describe and analyze the stylistic features of different architects from various regions through visual observations of architectural imagery. However, traditional studies of architectural culture have largely relied on subjective expert interpretations and historical literature reviews, often suffering from regional biases and limited ex-planatory scope. To address these challenges, this study proposes three core contributions: (1) We construct a professional architectural style dataset named ArchDiffBench, which comprises 1,765 high-quality architectural images and their corresponding style annotations, collected from different regions and historical periods. (2) We propose ArchiLense, an analytical framework grounded in Vision-Language Models and constructed using the ArchDiffBench dataset. By integrating ad-vanced computer vision techniques, deep learning, and machine learning algo-rithms, ArchiLense enables automatic recognition, comparison, and precise classi-fication of architectural imagery, producing descriptive language outputs that ar-ticulate stylistic differences. (3) Extensive evaluations show that ArchiLense achieves strong performance in architectural style recognition, with a 92.4% con-sistency rate with expert annotations and 84.5% classification accuracy, effec-tively capturing stylistic distinctions across images. The proposed approach transcends the subjectivity inherent in traditional analyses and offers a more objective and accurate perspective for comparative studies of architectural culture.
PromptLNet: Region-Adaptive Aesthetic Enhancement via Prompt Guidance in Low-Light Enhancement Net
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Learning and improving large language models through human preference feedback has become a mainstream approach, but it has rarely been applied to the field of low-light image enhancement. Existing low-light enhancement evaluations typically rely on objective metrics (such as FID, PSNR, etc.), which often result in models that perform well objectively but lack aesthetic quality. Moreover, most low-light enhancement models are primarily designed for global brightening, lacking detailed refinement. Therefore, the generated images often require additional local adjustments, leading to research gaps in practical applications. To bridge this gap, we propose the following innovations: 1) We collect human aesthetic evaluation text pairs and aesthetic scores from multiple low-light image datasets (e.g., LOL, LOL2, LOM, DCIM, MEF, etc.) to train a low-light image aesthetic evaluation model, supplemented by an optimization algorithm designed to fine-tune the diffusion model. 2) We propose a prompt-driven brightness adjustment module capable of performing fine-grained brightness and aesthetic adjustments for specific instances or regions. 3) We evaluate our method alongside existing state-of-the-art algorithms on mainstream benchmarks. Experimental results show that our method not only outperforms traditional methods in terms of visual quality but also provides greater flexibility and controllability, paving the way for improved aesthetic quality.
TSCnet: A Text-driven Semantic-level Controllable Framework for Customized Low-Light Image Enhancement
Mar 11, 2025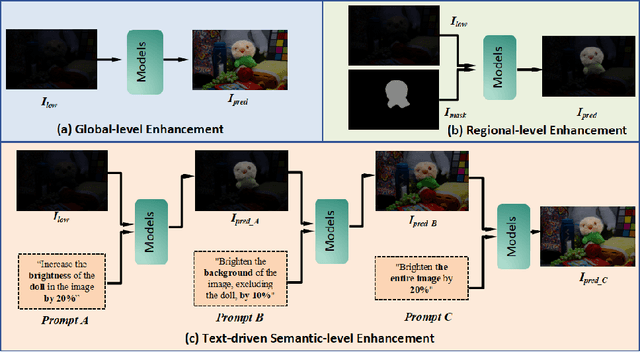
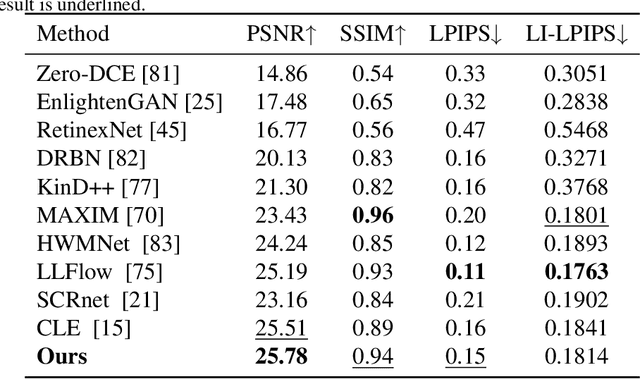
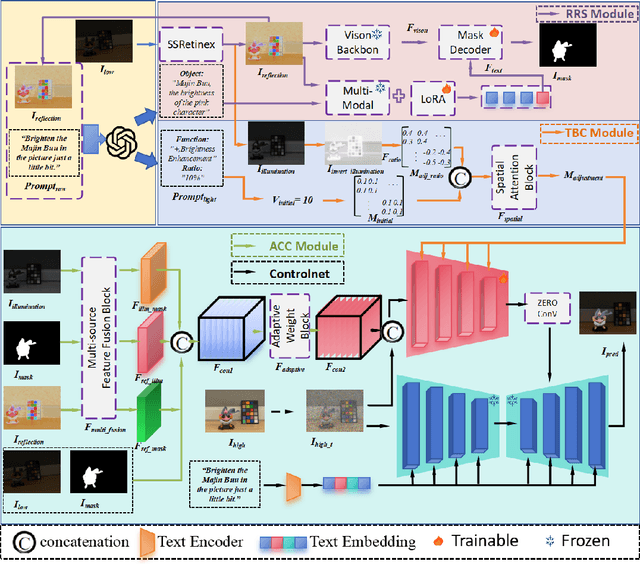
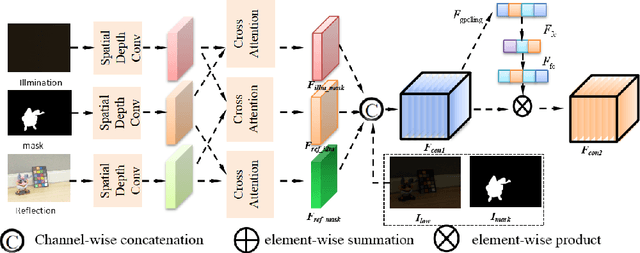
Abstract:Deep learning-based image enhancement methods show significant advantages in reducing noise and improving visibility in low-light conditions. These methods are typically based on one-to-one mapping, where the model learns a direct transformation from low light to specific enhanced images. Therefore, these methods are inflexible as they do not allow highly personalized mapping, even though an individual's lighting preferences are inherently personalized. To overcome these limitations, we propose a new light enhancement task and a new framework that provides customized lighting control through prompt-driven, semantic-level, and quantitative brightness adjustments. The framework begins by leveraging a Large Language Model (LLM) to understand natural language prompts, enabling it to identify target objects for brightness adjustments. To localize these target objects, the Retinex-based Reasoning Segment (RRS) module generates precise target localization masks using reflection images. Subsequently, the Text-based Brightness Controllable (TBC) module adjusts brightness levels based on the generated illumination map. Finally, an Adaptive Contextual Compensation (ACC) module integrates multi-modal inputs and controls a conditional diffusion model to adjust the lighting, ensuring seamless and precise enhancements accurately. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate our framework's superior performance at increasing visibility, maintaining natural color balance, and amplifying fine details without creating artifacts. Furthermore, its robust generalization capabilities enable complex semantic-level lighting adjustments in diverse open-world environments through natural language interactions.
CNN-based Robust Sound Source Localization with SRP-PHAT for the Extreme Edge
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Robust sound source localization for environments with noise and reverberation are increasingly exploiting deep neural networks fed with various acoustic features. Yet, state-of-the-art research mainly focuses on optimizing algorithmic accuracy, resulting in huge models preventing edge-device deployment. The edge, however, urges for real-time low-footprint acoustic reasoning for applications such as hearing aids and robot interactions. Hence, we set off from a robust CNN-based model using SRP-PHAT features, Cross3D [16], to pursue an efficient yet compact model architecture for the extreme edge. For both the SRP feature representation and neural network, we propose respectively our scalable LC-SRP-Edge and Cross3D-Edge algorithms which are optimized towards lower hardware overhead. LC-SRP-Edge halves the complexity and on-chip memory overhead for the sinc interpolation compared to the original LC-SRP [19]. Over multiple SRP resolution cases, Cross3D-Edge saves 10.32~73.71% computational complexity and 59.77~94.66% neural network weights against the Cross3D baseline. In terms of the accuracy-efficiency tradeoff, the most balanced version (EM) requires only 127.1 MFLOPS computation, 3.71 MByte/s bandwidth, and 0.821 MByte on-chip memory in total, while still retaining competitiveness in state-of-the-art accuracy comparisons. It achieves 8.59 ms/frame end-to-end latency on a Rasberry Pi 4B, which is 7.26x faster than the corresponding baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge