Xueyan Zhang
UORA: Uniform Orthogonal Reinitialization Adaptation in Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces Uniform Orthogonal Reinitialization Adaptation (UORA), a novel parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approach for Large Language Models (LLMs). UORA achieves state-of-the-art performance and parameter efficiency by leveraging a low-rank approximation method to reduce the number of trainable parameters. Unlike existing methods such as LoRA and VeRA, UORA employs an interpolation-based reparametrization mechanism that selectively reinitializes rows and columns in frozen projection matrices, guided by the vector magnitude heuristic. This results in substantially fewer trainable parameters compared to LoRA and outperforms VeRA in computation and storage efficiency. Comprehensive experiments across various benchmarks demonstrate UORA's superiority in achieving competitive fine-tuning performance with negligible computational overhead. We demonstrate its performance on GLUE and E2E benchmarks and its effectiveness in instruction-tuning large language models and image classification models. Our contributions establish a new paradigm for scalable and resource-efficient fine-tuning of LLMs.
* 20 pages, 2 figures, 15 tables
Can Language Model Understand Word Semantics as A Chatbot? An Empirical Study of Language Model Internal External Mismatch
Sep 21, 2024

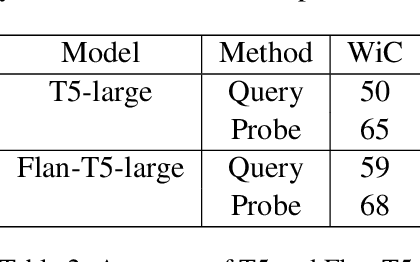

Abstract:Current common interactions with language models is through full inference. This approach may not necessarily align with the model's internal knowledge. Studies show discrepancies between prompts and internal representations. Most focus on sentence understanding. We study the discrepancy of word semantics understanding in internal and external mismatch across Encoder-only, Decoder-only, and Encoder-Decoder pre-trained language models.
Exploring the Limitations of Large Language Models in Compositional Relation Reasoning
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:We present a comprehensive evaluation of large language models(LLMs)' ability to reason about composition relations through a benchmark encompassing 1,500 test cases in English, designed to cover six distinct types of composition relations: Positional, Comparative, Personal, Mathematical, Identity, and Other. Acknowledging the significance of multilingual capabilities, we expanded our assessment to include translations of these cases into Chinese, Japanese, French, and Korean. Our Multilingual Composition Relation (MCR) benchmark aims at investigating the robustness and adaptability of LLMs in handling composition relation reasoning across diverse linguistic contexts.
Leveraging SAM for Single-Source Domain Generalization in Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Domain Generalization (DG) aims to reduce domain shifts between domains to achieve promising performance on the unseen target domain, which has been widely practiced in medical image segmentation. Single-source domain generalization (SDG) is the most challenging setting that trains on only one source domain. Although existing methods have made considerable progress on SDG of medical image segmentation, the performances are still far from the applicable standards when faced with a relatively large domain shift. In this paper, we leverage the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to SDG to greatly improve the ability of generalization. Specifically, we introduce a parallel framework, the source images are sent into the SAM module and normal segmentation module respectively. To reduce the calculation resources, we apply a merging strategy before sending images to the SAM module. We extract the bounding boxes from the segmentation module and send the refined version as prompts to the SAM module. We evaluate our model on a classic DG dataset and achieve competitive results compared to other state-of-the-art DG methods. Furthermore, We conducted a series of ablation experiments to prove the effectiveness of the proposed method. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/SARIHUST/SAMMed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge