Xiaodong Zhang
ROMAN: Reward-Orchestrated Multi-Head Attention Network for Autonomous Driving System Testing
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Automated Driving System (ADS) acts as the brain of autonomous vehicles, responsible for their safety and efficiency. Safe deployment requires thorough testing in diverse real-world scenarios and compliance with traffic laws like speed limits, signal obedience, and right-of-way rules. Violations like running red lights or speeding pose severe safety risks. However, current testing approaches face significant challenges: limited ability to generate complex and high-risk law-breaking scenarios, and failing to account for complex interactions involving multiple vehicles and critical situations. To address these challenges, we propose ROMAN, a novel scenario generation approach for ADS testing that combines a multi-head attention network with a traffic law weighting mechanism. ROMAN is designed to generate high-risk violation scenarios to enable more thorough and targeted ADS evaluation. The multi-head attention mechanism models interactions among vehicles, traffic signals, and other factors. The traffic law weighting mechanism implements a workflow that leverages an LLM-based risk weighting module to evaluate violations based on the two dimensions of severity and occurrence. We have evaluated ROMAN by testing the Baidu Apollo ADS within the CARLA simulation platform and conducting extensive experiments to measure its performance. Experimental results demonstrate that ROMAN surpassed state-of-the-art tools ABLE and LawBreaker by achieving 7.91% higher average violation count than ABLE and 55.96% higher than LawBreaker, while also maintaining greater scenario diversity. In addition, only ROMAN successfully generated violation scenarios for every clause of the input traffic laws, enabling it to identify more high-risk violations than existing approaches.
STARS: Shared-specific Translation and Alignment for missing-modality Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Multimodal remote sensing technology significantly enhances the understanding of surface semantics by integrating heterogeneous data such as optical images, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), and Digital Surface Models (DSM). However, in practical applications, the missing of modality data (e.g., optical or DSM) is a common and severe challenge, which leads to performance decline in traditional multimodal fusion models. Existing methods for addressing missing modalities still face limitations, including feature collapse and overly generalized recovered features. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{STARS} (\textbf{S}hared-specific \textbf{T}ranslation and \textbf{A}lignment for missing-modality \textbf{R}emote \textbf{S}ensing), a robust semantic segmentation framework for incomplete multimodal inputs. STARS is built on two key designs. First, we introduce an asymmetric alignment mechanism with bidirectional translation and stop-gradient, which effectively prevents feature collapse and reduces sensitivity to hyperparameters. Second, we propose a Pixel-level Semantic sampling Alignment (PSA) strategy that combines class-balanced pixel sampling with cross-modality semantic alignment loss, to mitigate alignment failures caused by severe class imbalance and improve minority-class recognition.
ComLQ: Benchmarking Complex Logical Queries in Information Retrieval
Nov 15, 2025

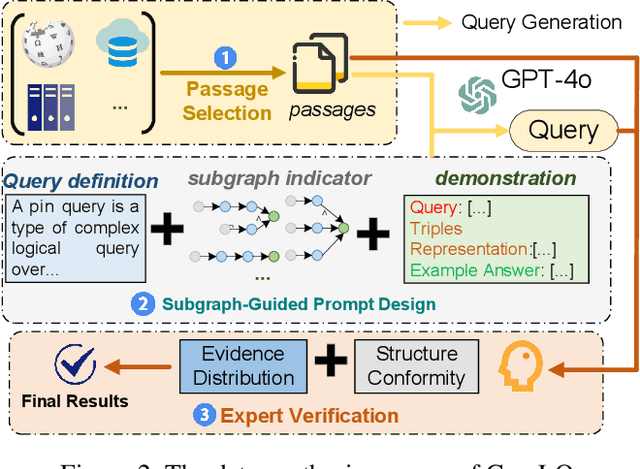
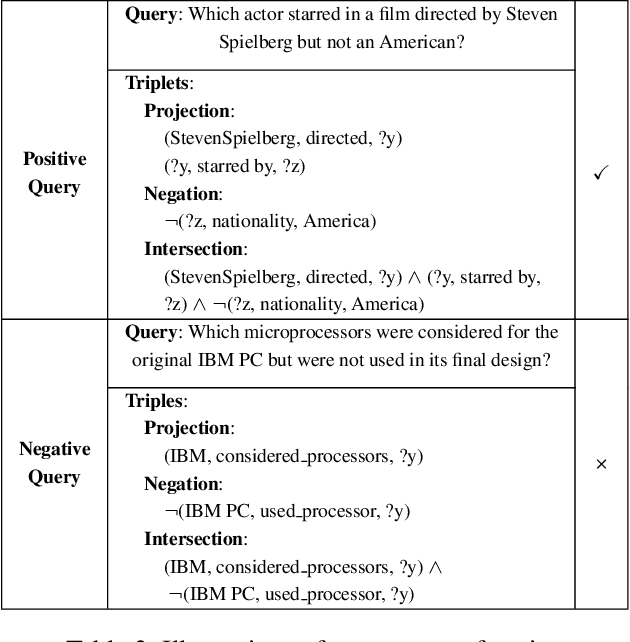
Abstract:Information retrieval (IR) systems play a critical role in navigating information overload across various applications. Existing IR benchmarks primarily focus on simple queries that are semantically analogous to single- and multi-hop relations, overlooking \emph{complex logical queries} involving first-order logic operations such as conjunction ($\land$), disjunction ($\lor$), and negation ($\lnot$). Thus, these benchmarks can not be used to sufficiently evaluate the performance of IR models on complex queries in real-world scenarios. To address this problem, we propose a novel method leveraging large language models (LLMs) to construct a new IR dataset \textbf{ComLQ} for \textbf{Com}plex \textbf{L}ogical \textbf{Q}ueries, which comprises 2,909 queries and 11,251 candidate passages. A key challenge in constructing the dataset lies in capturing the underlying logical structures within unstructured text. Therefore, by designing the subgraph-guided prompt with the subgraph indicator, an LLM (such as GPT-4o) is guided to generate queries with specific logical structures based on selected passages. All query-passage pairs in ComLQ are ensured \emph{structure conformity} and \emph{evidence distribution} through expert annotation. To better evaluate whether retrievers can handle queries with negation, we further propose a new evaluation metric, \textbf{Log-Scaled Negation Consistency} (\textbf{LSNC@$K$}). As a supplement to standard relevance-based metrics (such as nDCG and mAP), LSNC@$K$ measures whether top-$K$ retrieved passages violate negation conditions in queries. Our experimental results under zero-shot settings demonstrate existing retrieval models' limited performance on complex logical queries, especially on queries with negation, exposing their inferior capabilities of modeling exclusion.
AMF-MedIT: An Efficient Align-Modulation-Fusion Framework for Medical Image-Tabular Data
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Multimodal medical analysis combining image and tabular data has gained increasing attention. However, effective fusion remains challenging due to cross-modal discrepancies in feature dimensions and modality contributions, as well as the noise from high-dimensional tabular inputs. To address these problems, we present AMF-MedIT, an efficient Align-Modulation-Fusion framework for medical image and tabular data integration, particularly under data-scarce conditions. To harmonize dimension discrepancies and dynamically adjust modality contributions, we propose the Adaptive Modulation and Fusion (AMF) module, a novel modulation-based fusion paradigm with a streamlined architecture. We first derive the modulation objectives and introduce a modality confidence ratio, enabling the incorporation of prior knowledge into the fusion process. Then, the feature masks, density and leakage losses are proposed to achieve the modulation objectives. Additionally, we introduce FT-Mamba, a powerful tabular encoder leveraging a selective mechanism to handle noisy medical tabular data efficiently. Furthermore, interpretability studies are conducted to explore how different tabular encoders supervise the imaging modality during contrastive pretraining for the first time. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AMF-MedIT achieves a superior balance between multimodal performance and data efficiency while showing strong adaptability to incomplete tabular data. Interpretability analysis also highlights FT-Mamba's capabilities in extracting distinct tabular features and guiding the image encoder toward more accurate and flexible attention patterns.
MSSDF: Modality-Shared Self-supervised Distillation for High-Resolution Multi-modal Remote Sensing Image Learning
Jun 11, 2025
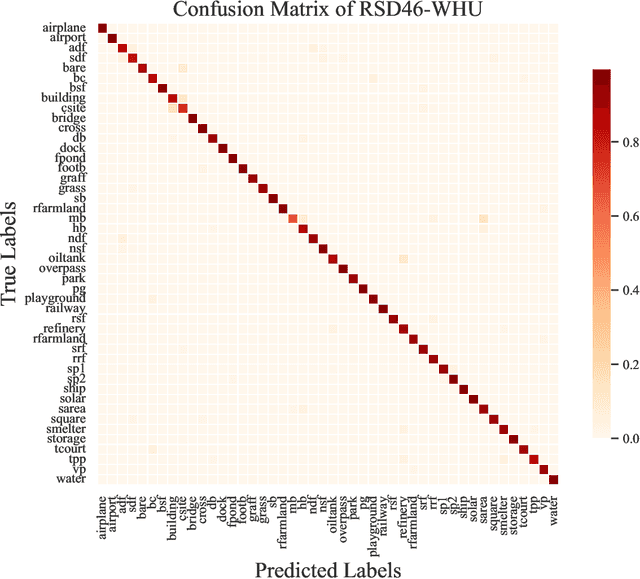
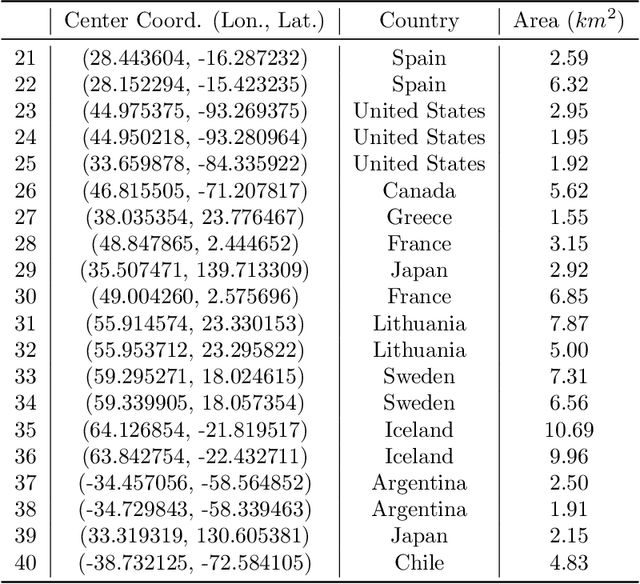
Abstract:Remote sensing image interpretation plays a critical role in environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster assessment. However, acquiring high-quality labeled data is often costly and time-consuming. To address this challenge, we proposes a multi-modal self-supervised learning framework that leverages high-resolution RGB images, multi-spectral data, and digital surface models (DSM) for pre-training. By designing an information-aware adaptive masking strategy, cross-modal masking mechanism, and multi-task self-supervised objectives, the framework effectively captures both the correlations across different modalities and the unique feature structures within each modality. We evaluated the proposed method on multiple downstream tasks, covering typical remote sensing applications such as scene classification, semantic segmentation, change detection, object detection, and depth estimation. Experiments are conducted on 15 remote sensing datasets, encompassing 26 tasks. The results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing pretraining approaches in most tasks. Specifically, on the Potsdam and Vaihingen semantic segmentation tasks, our method achieved mIoU scores of 78.30\% and 76.50\%, with only 50\% train-set. For the US3D depth estimation task, the RMSE error is reduced to 0.182, and for the binary change detection task in SECOND dataset, our method achieved mIoU scores of 47.51\%, surpassing the second CS-MAE by 3 percentage points. Our pretrain code, checkpoints, and HR-Pairs dataset can be found in https://github.com/CVEO/MSSDF.
Logical Consistency is Vital: Neural-Symbolic Information Retrieval for Negative-Constraint Queries
May 29, 2025

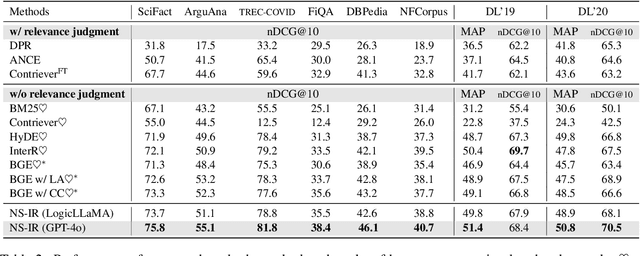
Abstract:Information retrieval plays a crucial role in resource localization. Current dense retrievers retrieve the relevant documents within a corpus via embedding similarities, which compute similarities between dense vectors mainly depending on word co-occurrence between queries and documents, but overlook the real query intents. Thus, they often retrieve numerous irrelevant documents. Particularly in the scenarios of complex queries such as \emph{negative-constraint queries}, their retrieval performance could be catastrophic. To address the issue, we propose a neuro-symbolic information retrieval method, namely \textbf{NS-IR}, that leverages first-order logic (FOL) to optimize the embeddings of naive natural language by considering the \emph{logical consistency} between queries and documents. Specifically, we introduce two novel techniques, \emph{logic alignment} and \emph{connective constraint}, to rerank candidate documents, thereby enhancing retrieval relevance. Furthermore, we construct a new dataset \textbf{NegConstraint} including negative-constraint queries to evaluate our NS-IR's performance on such complex IR scenarios. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that NS-IR not only achieves superior zero-shot retrieval performance on web search and low-resource retrieval tasks, but also performs better on negative-constraint queries. Our scource code and dataset are available at https://github.com/xgl-git/NS-IR-main.
On-Demand Scenario Generation for Testing Automated Driving Systems
May 20, 2025Abstract:The safety and reliability of Automated Driving Systems (ADS) are paramount, necessitating rigorous testing methodologies to uncover potential failures before deployment. Traditional testing approaches often prioritize either natural scenario sampling or safety-critical scenario generation, resulting in overly simplistic or unrealistic hazardous tests. In practice, the demand for natural scenarios (e.g., when evaluating the ADS's reliability in real-world conditions), critical scenarios (e.g., when evaluating safety in critical situations), or somewhere in between (e.g., when testing the ADS in regions with less civilized drivers) varies depending on the testing objectives. To address this issue, we propose the On-demand Scenario Generation (OSG) Framework, which generates diverse scenarios with varying risk levels. Achieving the goal of OSG is challenging due to the complexity of quantifying the criticalness and naturalness stemming from intricate vehicle-environment interactions, as well as the need to maintain scenario diversity across various risk levels. OSG learns from real-world traffic datasets and employs a Risk Intensity Regulator to quantitatively control the risk level. It also leverages an improved heuristic search method to ensure scenario diversity. We evaluate OSG on the Carla simulators using various ADSs. We verify OSG's ability to generate scenarios with different risk levels and demonstrate its necessity by comparing accident types across risk levels. With the help of OSG, we are now able to systematically and objectively compare the performance of different ADSs based on different risk levels.
BrainSegDMlF: A Dynamic Fusion-enhanced SAM for Brain Lesion Segmentation
May 09, 2025Abstract:The segmentation of substantial brain lesions is a significant and challenging task in the field of medical image segmentation. Substantial brain lesions in brain imaging exhibit high heterogeneity, with indistinct boundaries between lesion regions and normal brain tissue. Small lesions in single slices are difficult to identify, making the accurate and reproducible segmentation of abnormal regions, as well as their feature description, highly complex. Existing methods have the following limitations: 1) They rely solely on single-modal information for learning, neglecting the multi-modal information commonly used in diagnosis. This hampers the ability to comprehensively acquire brain lesion information from multiple perspectives and prevents the effective integration and utilization of multi-modal data inputs, thereby limiting a holistic understanding of lesions. 2) They are constrained by the amount of data available, leading to low sensitivity to small lesions and difficulty in detecting subtle pathological changes. 3) Current SAM-based models rely on external prompts, which cannot achieve automatic segmentation and, to some extent, affect diagnostic efficiency.To address these issues, we have developed a large-scale fully automated segmentation model specifically designed for brain lesion segmentation, named BrainSegDMLF. This model has the following features: 1) Dynamic Modal Interactive Fusion (DMIF) module that processes and integrates multi-modal data during the encoding process, providing the SAM encoder with more comprehensive modal information. 2) Layer-by-Layer Upsampling Decoder, enabling the model to extract rich low-level and high-level features even with limited data, thereby detecting the presence of small lesions. 3) Automatic segmentation masks, allowing the model to generate lesion masks automatically without requiring manual prompts.
Variational Autoencoder Framework for Hyperspectral Retrievals (Hyper-VAE) of Phytoplankton Absorption and Chlorophyll a in Coastal Waters for NASA's EMIT and PACE Missions
Apr 18, 2025



Abstract:Phytoplankton absorb and scatter light in unique ways, subtly altering the color of water, changes that are often minor for human eyes to detect but can be captured by sensitive ocean color instruments onboard satellites from space. Hyperspectral sensors, paired with advanced algorithms, are expected to significantly enhance the characterization of phytoplankton community composition, especially in coastal waters where ocean color remote sensing applications have historically encountered significant challenges. This study presents novel machine learning-based solutions for NASA's hyperspectral missions, including EMIT and PACE, tackling high-fidelity retrievals of phytoplankton absorption coefficient and chlorophyll a from their hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance. Given that a single Rrs spectrum may correspond to varied combinations of inherent optical properties and associated concentrations, the Variational Autoencoder (VAE) is used as a backbone in this study to handle such multi-distribution prediction problems. We first time tailor the VAE model with innovative designs to achieve hyperspectral retrievals of aphy and of Chl-a from hyperspectral Rrs in optically complex estuarine-coastal waters. Validation with extensive experimental observation demonstrates superior performance of the VAE models with high precision and low bias. The in-depth analysis of VAE's advanced model structures and learning designs highlights the improvement and advantages of VAE-based solutions over the mixture density network (MDN) approach, particularly on high-dimensional data, such as PACE. Our study provides strong evidence that current EMIT and PACE hyperspectral data as well as the upcoming Surface Biology Geology mission will open new pathways toward a better understanding of phytoplankton community dynamics in aquatic ecosystems when integrated with AI technologies.
Integrated trucks assignment and scheduling problem with mixed service mode docks: A Q-learning based adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Mixed service mode docks enhance efficiency by flexibly handling both loading and unloading trucks in warehouses. However, existing research often predetermines the number and location of these docks prior to planning truck assignment and sequencing. This paper proposes a new model integrating dock mode decision, truck assignment, and scheduling, thus enabling adaptive dock mode arrangements. Specifically, we introduce a Q-learning-based adaptive large neighborhood search (Q-ALNS) algorithm to address the integrated problem. The algorithm adjusts dock modes via perturbation operators, while truck assignment and scheduling are solved using destroy and repair local search operators. Q-learning adaptively selects these operators based on their performance history and future gains, employing the epsilon-greedy strategy. Extensive experimental results and statistical analysis indicate that the Q-ALNS benefits from efficient operator combinations and its adaptive mechanism, consistently outperforming benchmark algorithms in terms of optimality gap and Pareto front discovery. In comparison to the predetermined service mode, our adaptive strategy results in lower average tardiness and makespan, highlighting its superior adaptability to varying demands.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge