Mikko Valkama
Phase-Only Positioning in Distributed MIMO Under Phase Impairments: AP Selection Using Deep Learning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Carrier phase positioning (CPP) can enable cm-level accuracy in next-generation wireless systems, while recent literature shows that accuracy remains high using phase-only measurements in distributed MIMO (D-MIMO). However, the impact of phase synchronization errors on such systems remains insufficiently explored. To address this gap, we first show that the proposed hyperbola intersection method achieves highly accurate positioning even in the presence of phase synchronization errors, when trained on appropriate data reflecting such impairments. We then introduce a deep learning (DL)-based D-MIMO antenna point (AP) selection framework that ensures high-precision localization under phase synchronization errors. Simulation results show that the proposed framework improves positioning accuracy compared to prior-art methods, while reducing inference complexity by approximately 19.7%.
Multi-band Carrier Phase Positioning toward 6G: Performance Bounds and Efficient Estimators
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:In addition to satellite systems, carrier phase positioning (CPP) is gaining attraction also in terrestrial mobile networks, particularly in 5G New Radio evolution toward 6G. One key challenge is to resolve the integer ambiguity problem, as the carrier phase provides only relative position information. This work introduces and studies a multi-band CPP scenario with intra- and inter-band carrier aggregation (CA) opportunities across FR1, mmWave-FR2, and emerging 6G FR3 bands. Specifically, we derive multi-band CPP performance bounds, showcasing the superiority of multi-band CPP for high-precision localization in current and future mobile networks, while noting also practical imperfections such as clock offsets between the user equipment (UE) and the network as well as mutual clock imperfections between the network nodes. A wide collection of numerical results is provided, covering the impacts of the available carrier bandwidth, number of aggregated carriers, transmit power, and the number of network nodes or base stations. The offered results highlight that only two carriers suffice to substantially facilitate resolving the integer ambiguity problem while also largely enhancing the robustness of positioning against imperfections imposed by the network-side clocks and multi-path propagation. In addition, we also propose a two-stage practical estimator that achieves the derived bounds under all realistic bandwidth and transmit power conditions. Furthermore, we show that with an additional search-based refinement step, the proposed estimator becomes particularly suitable for narrowband Internet of Things applications operating efficiently even under narrow carrier bandwidths. Finally, both the derived bounds and the proposed estimators are extended to scenarios where the bands assigned to each base station are nonuniform or fully disjoint, enhancing the practical deployment flexibility.
POLO: Phase-Only Localization in Uplink Distributed MIMO Systems
Dec 10, 2025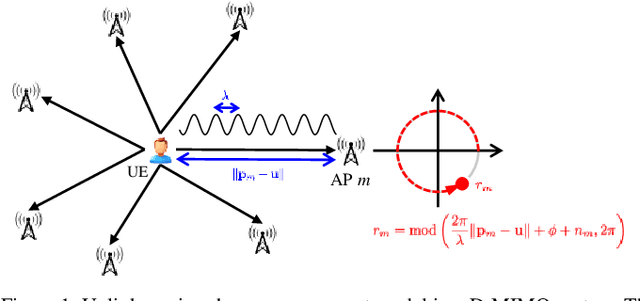

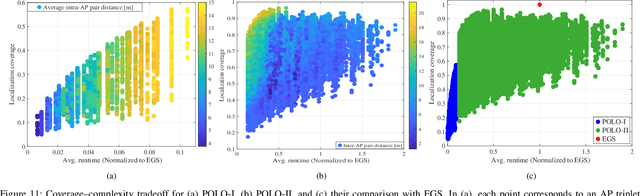
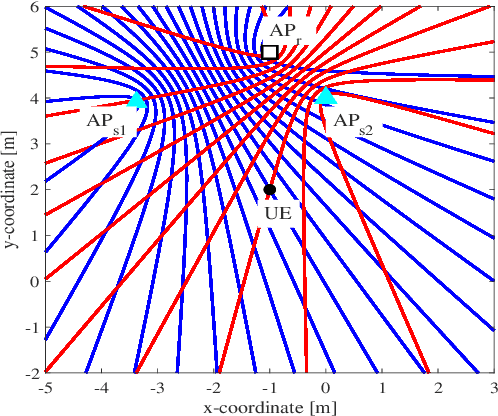
Abstract:We propose a low-complexity localization framework for uplink distributed MIMO (D-MIMO) systems, targeting the challenge of minimizing the highly spiky maximum-likelihood (ML) cost function that arises in sparsely deployed phasecoherent access points (APs) with narrowband transmission. In such systems, ML-based localization typically relies on dense grid search, incurring prohibitive computational complexity. To address this, we introduce phase-only localization (POLO), an approach that leverages differential carrier-phase measurements from selected APs to generate a compact set of candidate user positions. The ML cost function is then evaluated only at these candidates, reducing complexity significantly. A key challenge is to devise an AP selection mechanism that reduces the number of candidate points while maintaining reliable coverage. We propose two variants: POLO-I, which selects three APs to provide closed-form candidate positions with low computational cost, and POLO-II, which selects four APs using an alternative strategy that enhances coverage at marginally higher runtime. Comprehensive analytical and simulation results show that POLO achieves a favorable coverage-complexity trade-off, reducing cost by orders of magnitude relative to exhaustive grid search with only marginal loss in coverage. By characterizing this tradeoff under diverse AP configurations, we also provide practical guidelines for selecting between POLO-I and POLO-II depending on latency and coverage requirements.
UNILocPro: Unified Localization Integrating Model-Based Geometry and Channel Charting
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a unified localization framework (called UNILocPro) that integrates model-based localization and channel charting (CC) for mixed line-of-sight (LoS)/non-line-of-sight (NLoS) scenarios. Specifically, based on LoS/NLoS identification, an adaptive activation between the model-based and CC-based methods is conducted. Aiming for unsupervised learning, information obtained from the model-based method is utilized to train the CC model, where a pairwise distance loss (involving a new dissimilarity metric design), a triplet loss (if timestamps are available), a LoS-based loss, and an optimal transport (OT)-based loss are jointly employed such that the global geometry can be well preserved. To reduce the training complexity of UNILocPro, we propose a low-complexity implementation (called UNILoc), where the CC model is trained with self-generated labels produced by a single pre-training OT transformation, which avoids iterative Sinkhorn updates involved in the OT-based loss computation. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed unified frameworks achieve significantly improved positioning accuracy compared to both model-based and CC-based methods. Notably, UNILocPro with timestamps attains performance on par with fully-supervised fingerprinting despite operating without labelled training data. It is also shown that the low-complexity UNILoc can substantially reduce training complexity with only marginal performance degradation.
Sensing with Mobile Devices through Radio SLAM: Models, Methods, Opportunities, and Challenges
Sep 09, 2025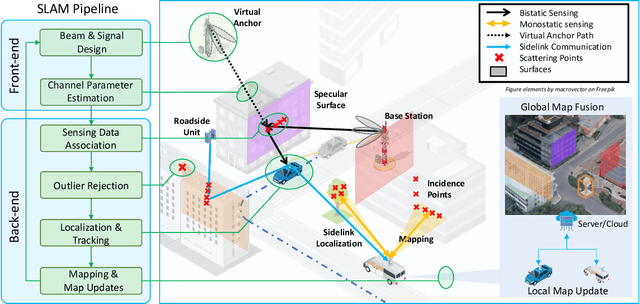
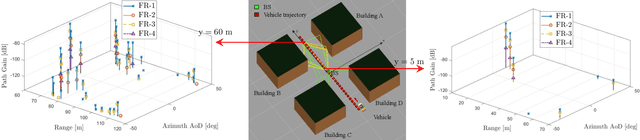
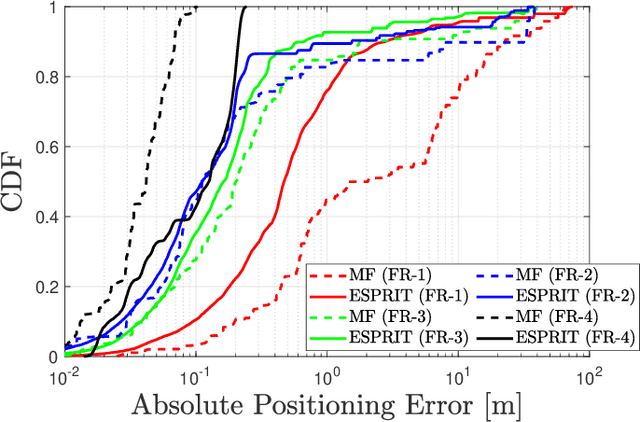
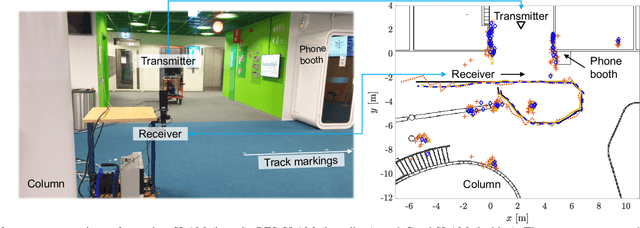
Abstract:The integration of sensing and communication (ISAC) is a cornerstone of 6G, enabling simultaneous environmental awareness and communication. This paper explores radio SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) as a key ISAC approach, using radio signals for mapping and localization. We analyze radio SLAM across different frequency bands, discussing trade-offs in coverage, resolution, and hardware requirements. We also highlight opportunities for integration with sensing, positioning, and cooperative networks. The findings pave the way for standardized solutions in 6G applications such as autonomous systems and industrial robotics.
Failure Tolerant Phase-Only Indoor Positioning via Deep Learning
Aug 20, 2025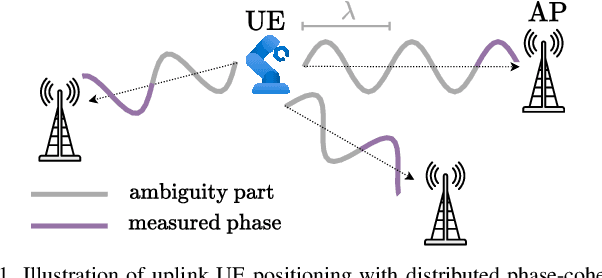
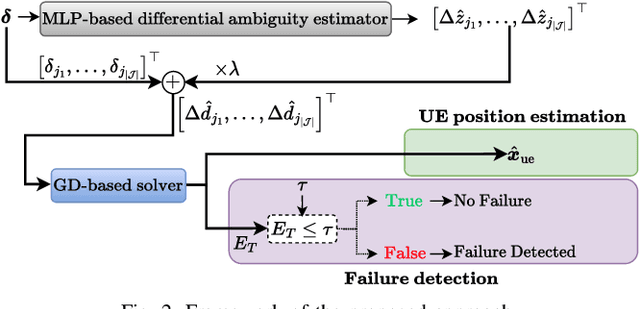
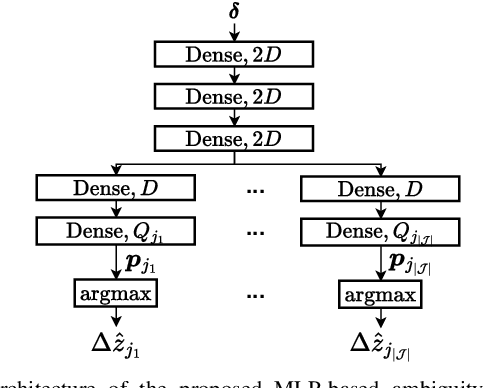
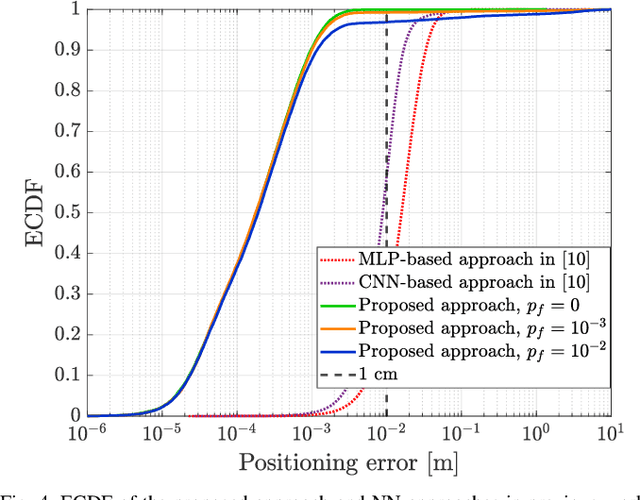
Abstract:High-precision localization turns into a crucial added value and asset for next-generation wireless systems. Carrier phase positioning (CPP) enables sub-meter to centimeter-level accuracy and is gaining interest in 5G-Advanced standardization. While CPP typically complements time-of-arrival (ToA) measurements, recent literature has introduced a phase-only positioning approach in a distributed antenna/MIMO system context with minimal bandwidth requirements, using deep learning (DL) when operating under ideal hardware assumptions. In more practical scenarios, however, antenna failures can largely degrade the performance. In this paper, we address the challenging phase-only positioning task, and propose a new DL-based localization approach harnessing the so-called hyperbola intersection principle, clearly outperforming the previous methods. Additionally, we consider and propose a processing and learning mechanism that is robust to antenna element failures. Our results show that the proposed DL model achieves robust and accurate positioning despite antenna impairments, demonstrating the viability of data-driven, impairment-tolerant phase-only positioning mechanisms. Comprehensive set of numerical results demonstrates large improvements in localization accuracy against the prior art methods.
Phase-Only Positioning: Overcoming Integer Ambiguity Challenge through Deep Learning
Jun 09, 2025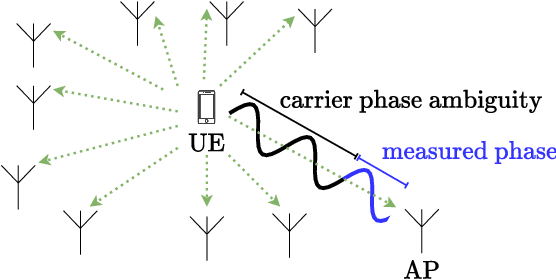
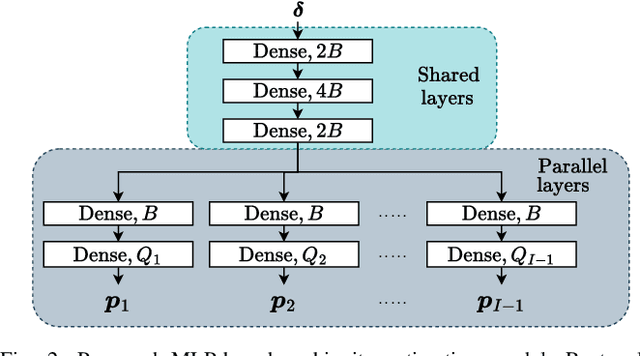
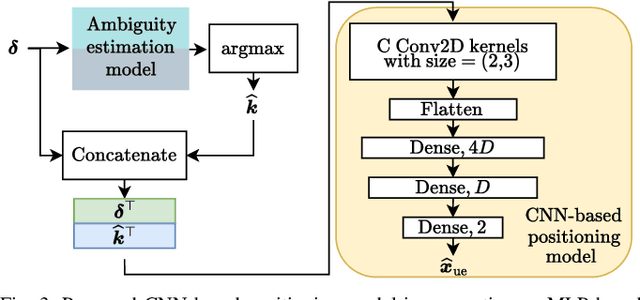
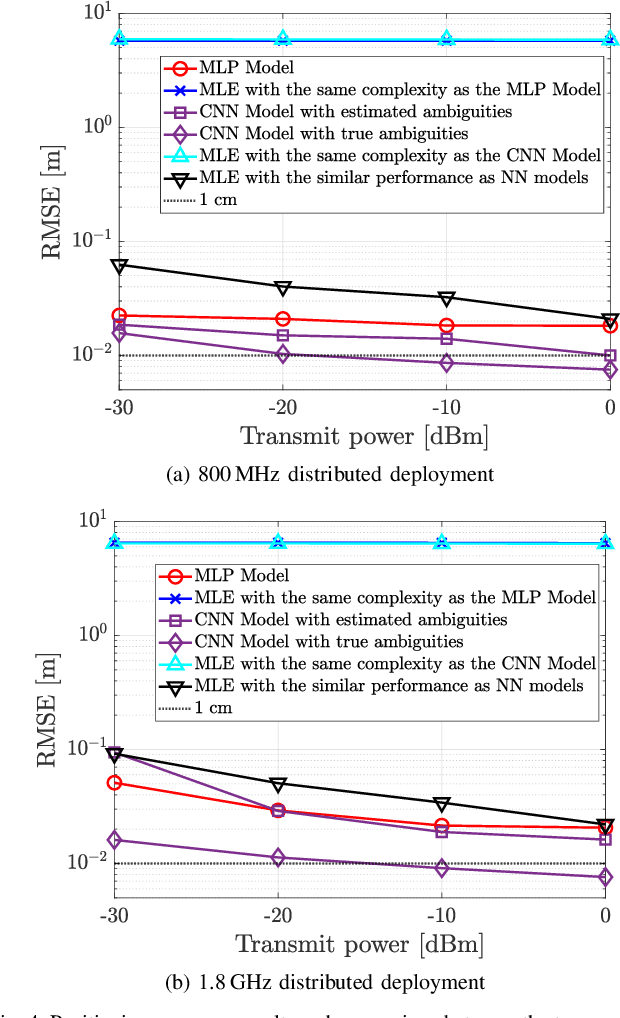
Abstract:This paper investigates uplink carrier phase positioning (CPP) in cell-free (CF) or distributed antenna system context, assuming a challenging case where only phase measurements are utilized as observations. In general, CPP can achieve sub-meter to centimeter-level accuracy but is challenged by the integer ambiguity problem. In this work, we propose two deep learning approaches for phase-only positioning, overcoming the integer ambiguity challenge. The first one directly uses phase measurements, while the second one first estimates integer ambiguities and then integrates them with phase measurements for improved accuracy. Our numerical results demonstrate that an inference complexity reduction of two to three orders of magnitude is achieved, compared to maximum likelihood baseline solution, depending on the approach and parameter configuration. This emphasizes the potential of the developed deep learning solutions for efficient and precise positioning in future CF 6G systems.
Pilot-Based End-to-End Radio Positioning and Mapping for ISAC: Beyond Point-Based Landmarks
May 12, 2025



Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication enables simultaneous communication and sensing tasks, including precise radio positioning and mapping, essential for future 6G networks. Current methods typically model environmental landmarks as isolated incidence points or small reflection areas, lacking detailed attributes essential for advanced environmental interpretation. This paper addresses these limitations by developing an end-to-end cooperative uplink framework involving multiple base stations and users. Our method uniquely estimates extended landmark objects and incorporates obstruction-based outlier removal to mitigate multi-bounce signal effects. Validation using realistic ray-tracing data demonstrates substantial improvements in the richness of the estimated environmental map.
UNILoc: Unified Localization Combining Model-Based Geometry and Unsupervised Learning
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Accurate mobile device localization is critical for emerging 5G/6G applications such as autonomous vehicles and augmented reality. In this paper, we propose a unified localization method that integrates model-based and machine learning (ML)-based methods to reap their respective advantages by exploiting available map information. In order to avoid supervised learning, we generate training labels automatically via optimal transport (OT) by fusing geometric estimates with building layouts. Ray-tracing based simulations are carried out to demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves positioning accuracy for both line-of-sight (LoS) users (compared to ML-based methods) and non-line-of-sight (NLoS) users (compared to model-based methods). Remarkably, the unified method is able to achieve competitive overall performance with the fully-supervised fingerprinting, while eliminating the need for cumbersome labeled data measurement and collection.
Detection with Uncertainty in Target Direction for Dual Functional Radar and Communication Systems
Dec 10, 2024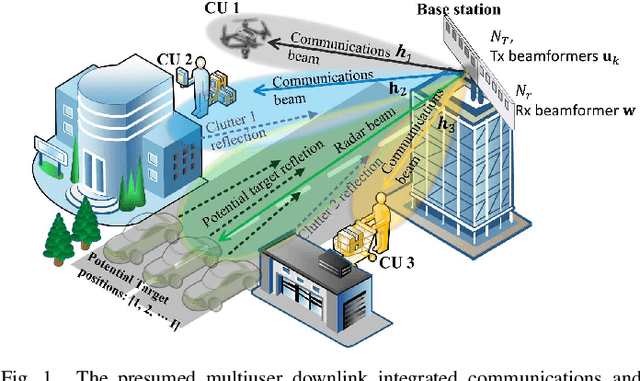
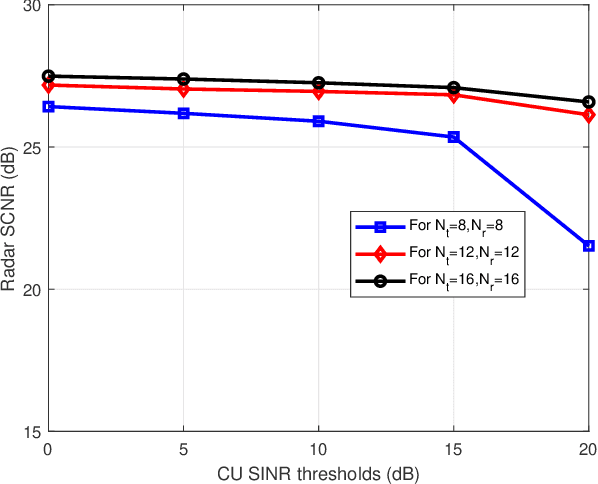
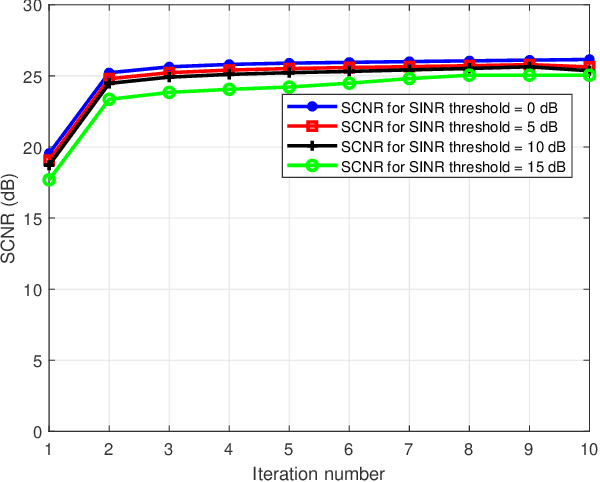
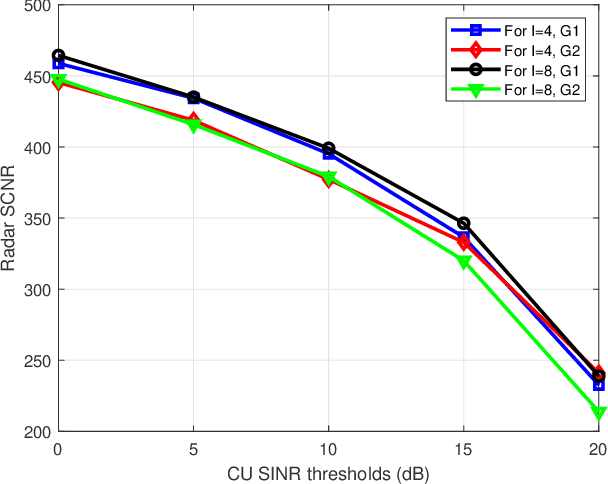
Abstract:Dual functional radar and communication (DFRC) systems are a viable approach to extend the services of future communication systems. Most studies designing DFRC systems assume that the target direction is known. In our paper, we address a critical scenario where this information is not exactly known. For such a system, a signal-to-clutter-plus-noise ratio (SCNR) maximization problem is formulated. Quality-of-service constraints for communication users (CUs) are also incorporated as constraints on their received signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratios (SINRs). To tackle the nonconvexity, an iterative alternating optimization approach is developed where, at each iteration, the optimization is alternatively performed with respect to transmit and receive beamformers. Specifically, a penalty-based approach is used to obtain an efficient sub-optimal solution for the resulting subproblem with regard to transmit beamformers. Next, a globally optimal solution is obtained for receive beamformers with the help of the Dinkleback approach. The convergence of the proposed algorithm is also proved by proving the nondecreasing nature of the objective function with iterations. The numerical results illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Specifically, it is observed that the proposed algorithm converges within almost 3 iterations, and the SCNR performance is almost unchanged with the number of possible target directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge