Elena Simona Lohan
Phase-Only Positioning in Distributed MIMO Under Phase Impairments: AP Selection Using Deep Learning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Carrier phase positioning (CPP) can enable cm-level accuracy in next-generation wireless systems, while recent literature shows that accuracy remains high using phase-only measurements in distributed MIMO (D-MIMO). However, the impact of phase synchronization errors on such systems remains insufficiently explored. To address this gap, we first show that the proposed hyperbola intersection method achieves highly accurate positioning even in the presence of phase synchronization errors, when trained on appropriate data reflecting such impairments. We then introduce a deep learning (DL)-based D-MIMO antenna point (AP) selection framework that ensures high-precision localization under phase synchronization errors. Simulation results show that the proposed framework improves positioning accuracy compared to prior-art methods, while reducing inference complexity by approximately 19.7%.
Trends and Challenges in Next-Generation GNSS Interference Management
Oct 31, 2025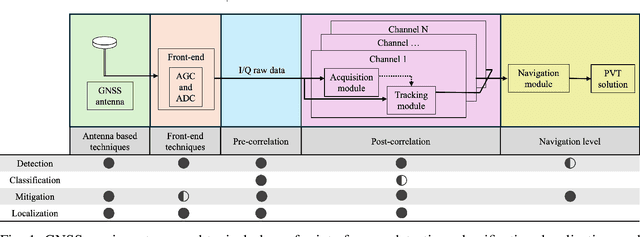
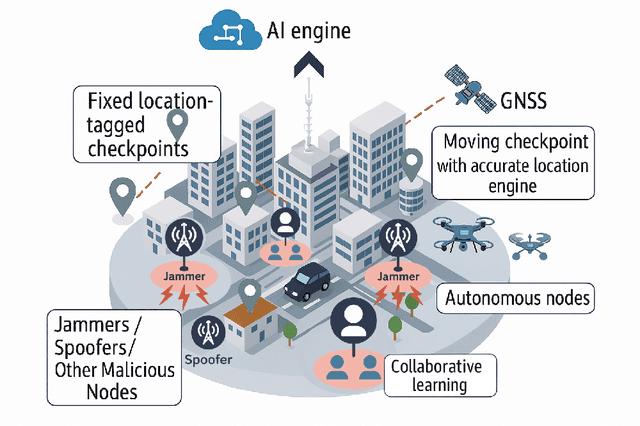
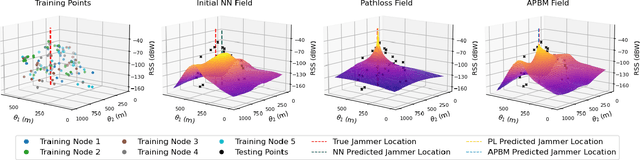
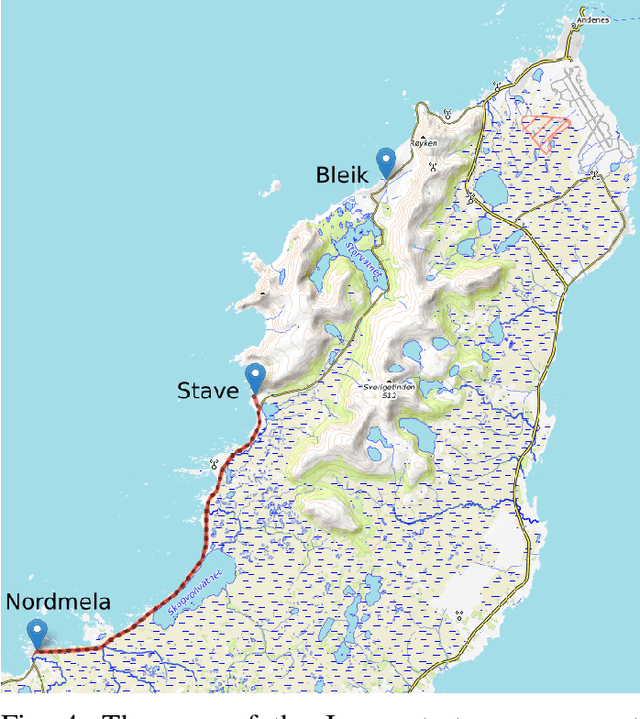
Abstract:The global navigation satellite system (GNSS) continues to evolve in order to meet the demands of emerging applications such as autonomous driving and smart environmental monitoring. However, these advancements are accompanied by a rise in interference threats, which can significantly compromise the reliability and safety of GNSS. Such interference problems are typically addressed through signal-processing techniques that rely on physics-based mathematical models. Unfortunately, solutions of this nature can often fail to fully capture the complex forms of interference. To address this, artificial intelligence (AI)-inspired solutions are expected to play a key role in future interference management solutions, thanks to their ability to exploit data in addition to physics-based models. This magazine paper discusses the main challenges and tasks required to secure GNSS and present a research vision on how AI can be leveraged towards achieving more robust GNSS-based positioning.
Failure Tolerant Phase-Only Indoor Positioning via Deep Learning
Aug 20, 2025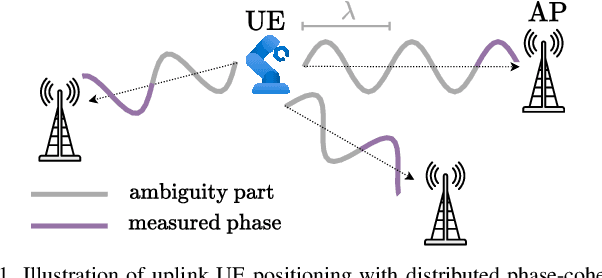
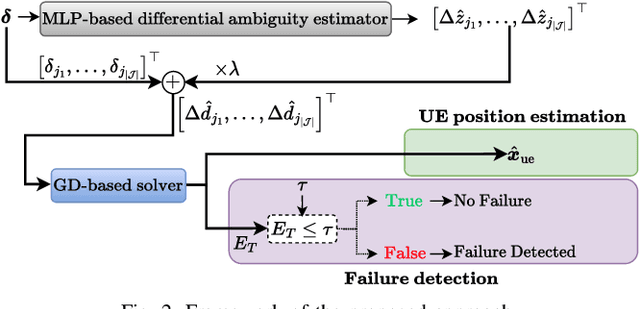
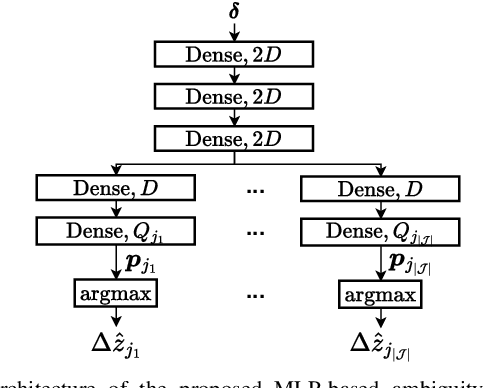
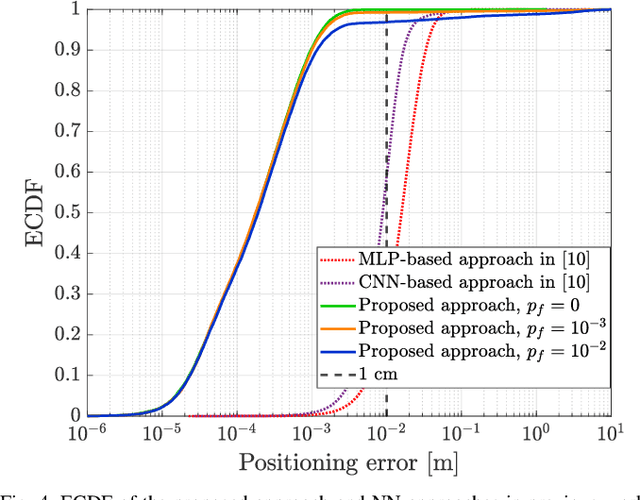
Abstract:High-precision localization turns into a crucial added value and asset for next-generation wireless systems. Carrier phase positioning (CPP) enables sub-meter to centimeter-level accuracy and is gaining interest in 5G-Advanced standardization. While CPP typically complements time-of-arrival (ToA) measurements, recent literature has introduced a phase-only positioning approach in a distributed antenna/MIMO system context with minimal bandwidth requirements, using deep learning (DL) when operating under ideal hardware assumptions. In more practical scenarios, however, antenna failures can largely degrade the performance. In this paper, we address the challenging phase-only positioning task, and propose a new DL-based localization approach harnessing the so-called hyperbola intersection principle, clearly outperforming the previous methods. Additionally, we consider and propose a processing and learning mechanism that is robust to antenna element failures. Our results show that the proposed DL model achieves robust and accurate positioning despite antenna impairments, demonstrating the viability of data-driven, impairment-tolerant phase-only positioning mechanisms. Comprehensive set of numerical results demonstrates large improvements in localization accuracy against the prior art methods.
Phase-Only Positioning: Overcoming Integer Ambiguity Challenge through Deep Learning
Jun 09, 2025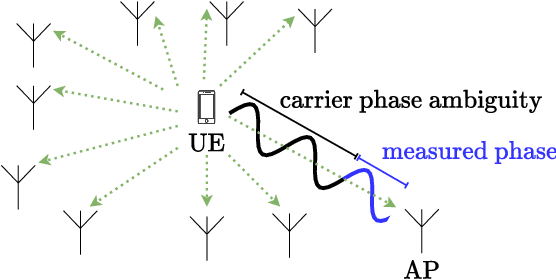
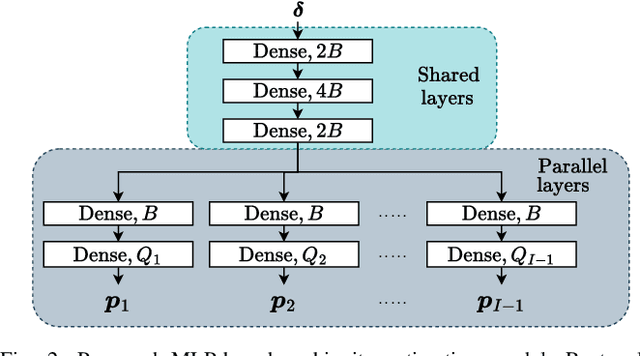
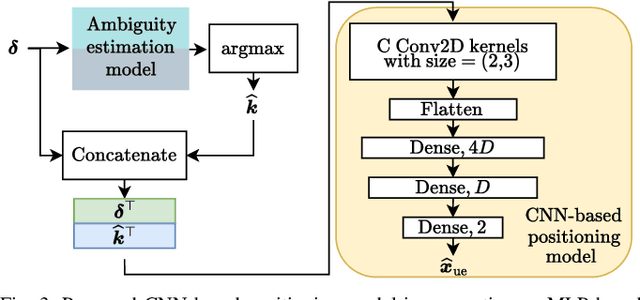
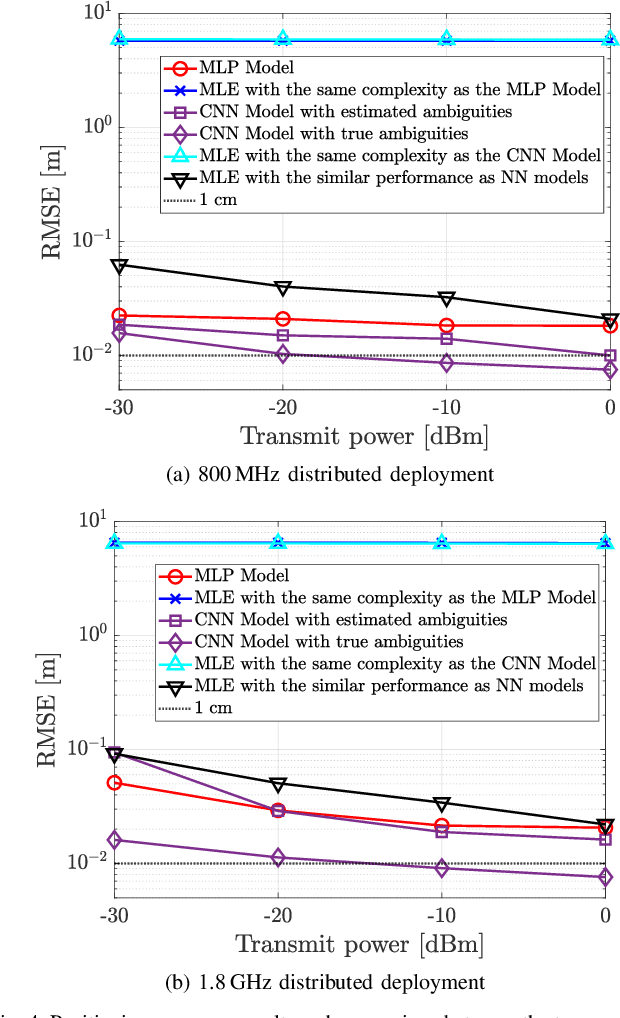
Abstract:This paper investigates uplink carrier phase positioning (CPP) in cell-free (CF) or distributed antenna system context, assuming a challenging case where only phase measurements are utilized as observations. In general, CPP can achieve sub-meter to centimeter-level accuracy but is challenged by the integer ambiguity problem. In this work, we propose two deep learning approaches for phase-only positioning, overcoming the integer ambiguity challenge. The first one directly uses phase measurements, while the second one first estimates integer ambiguities and then integrates them with phase measurements for improved accuracy. Our numerical results demonstrate that an inference complexity reduction of two to three orders of magnitude is achieved, compared to maximum likelihood baseline solution, depending on the approach and parameter configuration. This emphasizes the potential of the developed deep learning solutions for efficient and precise positioning in future CF 6G systems.
A Collaborative Approach Using Neural Networks for BLE-RSS Lateration-Based Indoor Positioning
May 21, 2022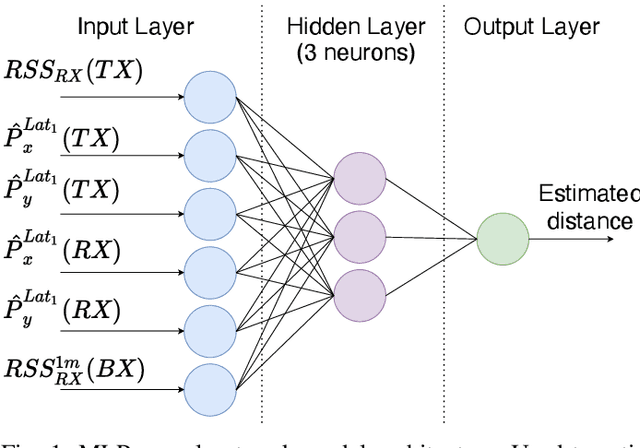
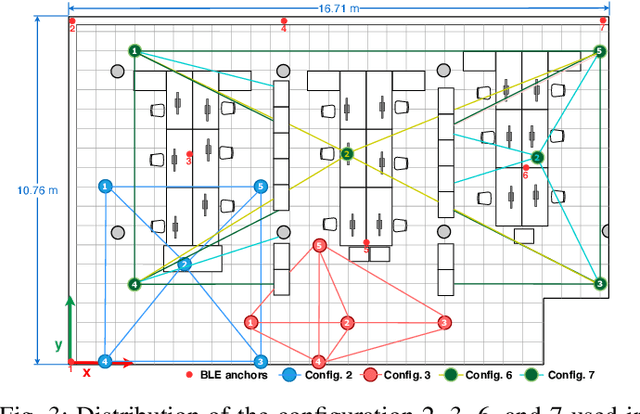
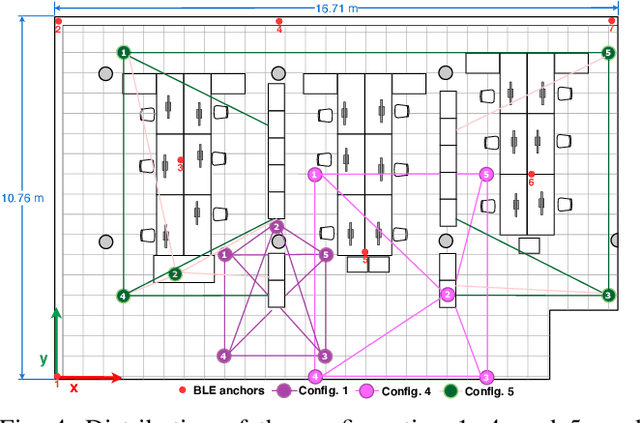
Abstract:In daily life, mobile and wearable devices with high computing power, together with anchors deployed in indoor environments, form a common solution for the increasing demands for indoor location-based services. Within the technologies and methods currently in use for indoor localization, the approaches that rely on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) anchors, Received Signal Strength (RSS), and lateration are among the most popular, mainly because of their cheap and easy deployment and accessible infrastructure by a variety of devices. Nevertheless, such BLE- and RSS-based indoor positioning systems are prone to inaccuracies, mostly due to signal fluctuations, poor quantity of anchors deployed in the environment, and/or inappropriate anchor distributions, as well as mobile device hardware variability. In this paper, we address these issues by using a collaborative indoor positioning approach, which exploits neighboring devices as additional anchors in an extended positioning network. The collaborating devices' information (i.e., estimated positions and BLE-RSS) is processed using a multilayer perceptron (MLP) neural network by taking into account the device specificity in order to estimate the relative distances. After this, the lateration is applied to collaboratively estimate the device position. Finally, the stand-alone and collaborative position estimates are combined, providing the final position estimate for each device. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed collaborative approach outperforms the stand-alone lateration method in terms of positioning accuracy.
Data Cleansing for Indoor Positioning Wi-Fi Fingerprinting Datasets
May 04, 2022



Abstract:Wearable and IoT devices requiring positioning and localisation services grow in number exponentially every year. This rapid growth also produces millions of data entries that need to be pre-processed prior to being used in any indoor positioning system to ensure the data quality and provide a high Quality of Service (QoS) to the end-user. In this paper, we offer a novel and straightforward data cleansing algorithm for WLAN fingerprinting radio maps. This algorithm is based on the correlation among fingerprints using the Received Signal Strength (RSS) values and the Access Points (APs)'s identifier. We use those to compute the correlation among all samples in the dataset and remove fingerprints with low level of correlation from the dataset. We evaluated the proposed method on 14 independent publicly-available datasets. As a result, an average of 14% of fingerprints were removed from the datasets. The 2D positioning error was reduced by 2.7% and 3D positioning error by 5.3% with a slight increase in the floor hit rate by 1.2% on average. Consequently, the average speed of position prediction was also increased by 14%.
Towards Accelerated Localization Performance Across Indoor Positioning Datasets
Apr 22, 2022



Abstract:The localization speed and accuracy in the indoor scenario can greatly impact the Quality of Experience of the user. While many individual machine learning models can achieve comparable positioning performance, their prediction mechanisms offer different complexity to the system. In this work, we propose a fingerprinting positioning method for multi-building and multi-floor deployments, composed of a cascade of three models for building classification, floor classification, and 2D localization regression. We conduct an exhaustive search for the optimally performing one in each step of the cascade while validating on 14 different openly available datasets. As a result, we bring forward the best-performing combination of models in terms of overall positioning accuracy and processing speed and evaluate on independent sets of samples. We reduce the mean prediction time by 71% while achieving comparable positioning performance across all considered datasets. Moreover, in case of voluminous training dataset, the prediction time is reduced down to 1% of the benchmark's.
Improved Sensing and Positioning via 5G and mmWave radar for Airport Surveillance
Feb 28, 2022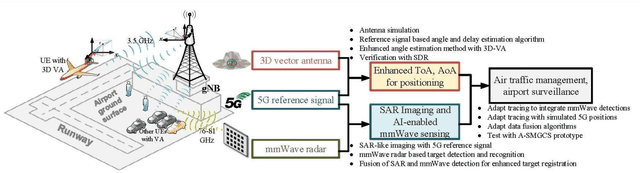
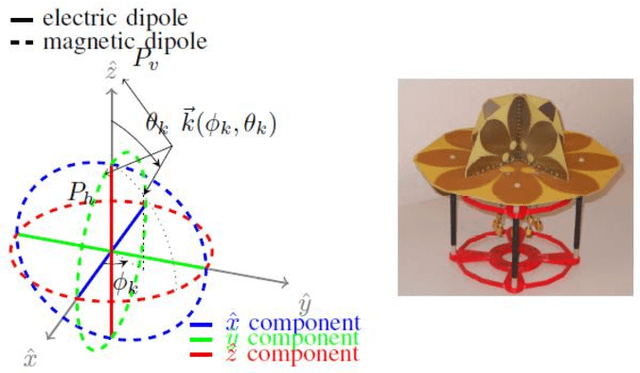
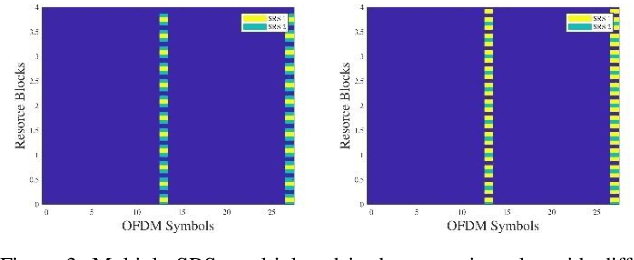
Abstract:This paper explores an integrated approach for improved sensing and positioning with applications in air traffic management (ATM) and in the Advanced Surface Movement Guidance and Control System (A-SMGCS). The integrated approach includes the synergy of 3D Vector Antenna with the novel time-of-arrival and angle-of-arrival estimate methods for accurate positioning, combining the sensing on the sub-6GHz and mmWave spectrum for the enhanced non-cooperative surveillance. For the positioning scope, both uplink and downlink 5G reference signals are investigated and their performance is evaluated. For the non-cooperative sensing scope, a novel 5G-signal-based imaging function is proposed and verified with realistic airport radio-propagation modelling and the AI-based targets tracking-and-motion recognition are investigated. The 5G-based imaging and mmWave radar based detection can be potentially fused to enhance surveillance in the airport. The work is being done within the European-funded project NewSense and it delves into the 5G, Vector Antennas, and mmWave capabilities for future ATM solutions.
Towards Ubiquitous Indoor Positioning: Comparing Systems across Heterogeneous Datasets
Sep 20, 2021



Abstract:The evaluation of Indoor Positioning Systems (IPS) mostly relies on local deployments in the researchers' or partners' facilities. The complexity of preparing comprehensive experiments, collecting data, and considering multiple scenarios usually limits the evaluation area and, therefore, the assessment of the proposed systems. The requirements and features of controlled experiments cannot be generalized since the use of the same sensors or anchors density cannot be guaranteed. The dawn of datasets is pushing IPS evaluation to a similar level as machine-learning models, where new proposals are evaluated over many heterogeneous datasets. This paper proposes a way to evaluate IPSs in multiple scenarios, that is validated with three use cases. The results prove that the proposed aggregation of the evaluation metric values is a useful tool for high-level comparison of IPSs.
Converging Radar and Communications in the Superposition Transmission
Aug 24, 2021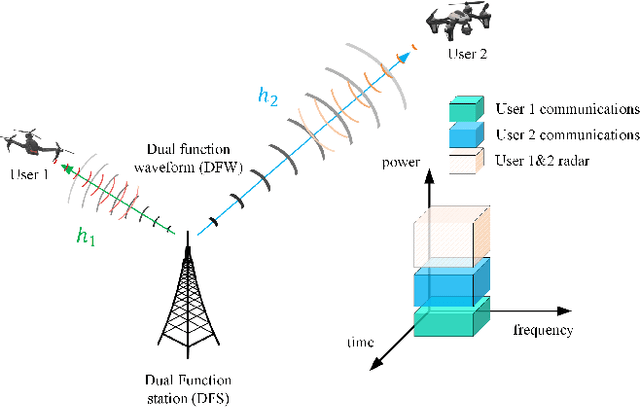
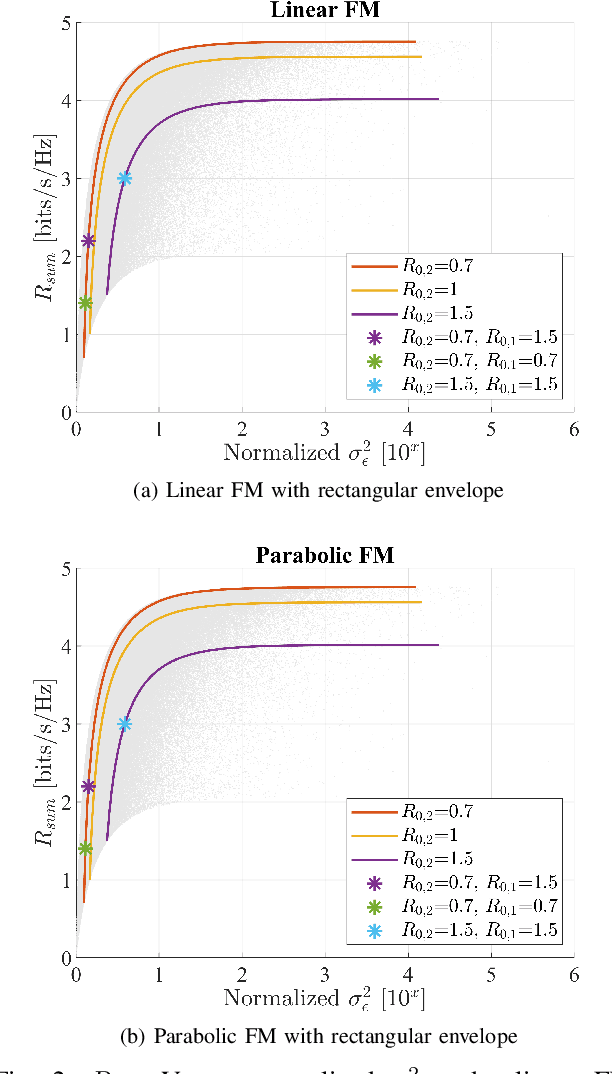
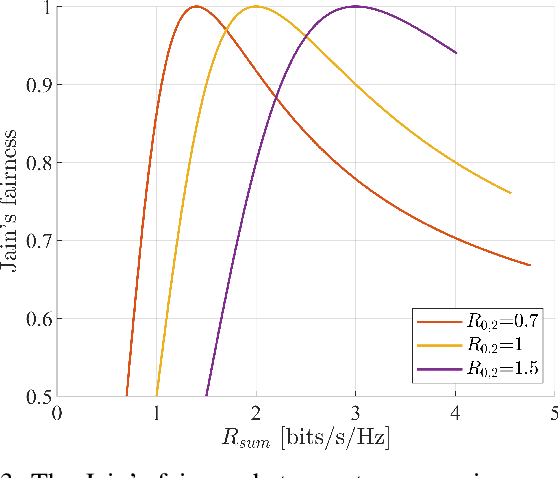
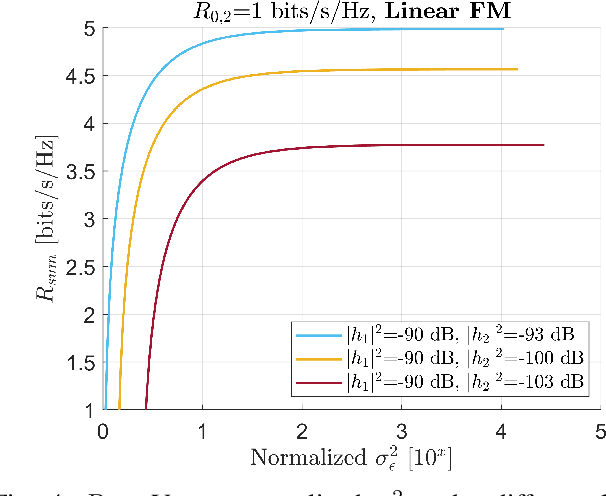
Abstract:This paper proposes a superposition transmission scheme for the future Radio Frequency (RF) convergence applications. The scheme is discussed under the assumption of a mono-static broadcasting channel topology. Under communications quality-of-service (QoS) constraints, the joint performance region of communications sum rate and radar estimation error variance is studied. Two radar signal waveforms, namely linear FM and parabolic FM, are used to investigate how signal shapes may influence the estimation accuracy. Both waveforms are generated with rectangular envelope. In the end, a numerical analysis is applied, which concludes that a moderate communications QoS promises a good communications fairness while with the limited radar performance degradation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge