Charlie Jianzhong Zhang
Integrated Monostatic Sensing and Full-Duplex Multiuser Communication for mmWave Systems
May 15, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a hybrid precoding/combining framework for communication-centric integrated sensing and full-duplex (FD) communication operating at mmWave bands. The designed precoders and combiners enable multiuser (MU) FD communication while simultaneously supporting monostatic sensing in a frequency-selective setting. The joint design of precoders and combiners involves the mitigation of self-interference (SI) caused by simultaneous transmission and reception at the FD base station (BS). Additionally, MU interference needs to be handled by the precoder/combiner design. The resulting optimization problem involves non-convex constraints since hybrid analog/digital architectures utilize networks of phase shifters. To solve the proposed problem, we separate the optimization of each precoder/combiner, and design each one of them while fixing the others. The precoders at the FD BS are designed by reformulating the communication and sensing constraints as signal-to-leakage-plus-noise ratio (SLNR) maximization problems that consider SI and MU interference as leakage. Furthermore, we design the frequency-flat analog combiner such that the residual SI at the FD BS is minimized under communication and sensing gain constraints. Finally, we design an interference-aware digital combining stage that separates MU signals and target reflections. The communication performance and sensing results show that the proposed framework efficiently supports both functionalities simultaneously.
Learned Pulse Shaping Design for PAPR Reduction in DFT-s-OFDM
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:High peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) is one of the main factors limiting cell coverage for cellular systems, especially in the uplink direction. Discrete Fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency-domain multiplexing (DFT-s-OFDM) with spectrally-extended frequency-domain spectrum shaping (FDSS) is one of the efficient techniques deployed to lower the PAPR of the uplink waveforms. In this work, we propose a machine learning-based framework to determine the FDSS filter, optimizing a tradeoff between the symbol error rate (SER), the PAPR, and the spectral flatness requirements. Our end-to-end optimization framework considers multiple important design constraints, including the Nyquist zero-ISI (inter-symbol interference) condition. The numerical results show that learned FDSS filters lower the PAPR compared to conventional baselines, with minimal SER degradation. Tuning the parameters of the optimization also helps us understand the fundamental limitations and characteristics of the FDSS filters for PAPR reduction.
Multidimensional Orthogonal Matching Pursuit-based RIS-aided Joint Localization and Channel Estimation at mmWave
Mar 24, 2022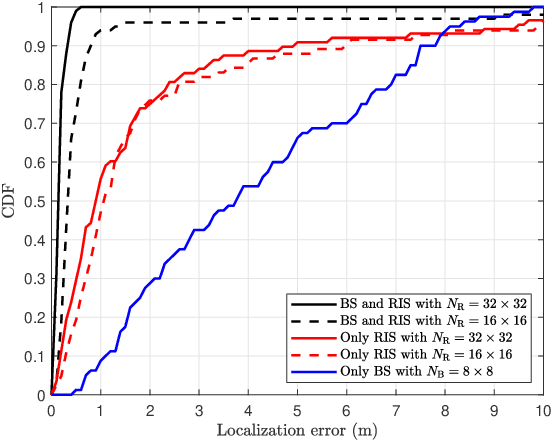
Abstract:RIS-aided millimeter wave wireless systems benefit from robustness to blockage and enhanced coverage. In this paper, we study the ability of RIS to also provide enhanced localization capabilities as a by-product of communication. We consider sparse reconstruction algorithms to obtain high resolution channel estimates that are mapped to position information. In RIS-aided mmWave systems, the complexity of sparse recovery becomes a bottleneck, given the large number of elements of the RIS and the large communication arrays. We propose to exploit a multidimensional orthogonal matching pursuit strategy for compressive channel estimation in a RIS-aided millimeter wave system. We show how this algorithm, based on computing the projections on a set of independent dictionaries instead of a single large dictionary, enables high accuracy channel estimation at reduced complexity. We also combine this strategy with a localization approach which does not rely on the absolute time of arrival of the LoS path. Localization results in a realistic 3D indoor scenario show that RIS-aided wireless system can also benefit from a significant improvement in localization accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge