Marios Kountouris
EURECOM
Multi-Sensor Scheduling for Remote State Estimation over Wireless MIMO Fading Channels with Semantic Over-the-Air Aggregation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this work, we study multi-sensor scheduling for remote state estimation over wireless multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) fading channels using a novel semantic over-the-air (SemOTA) aggregation approach. We first revisit Kalman filtering with conventional over-the-air (OTA) aggregation and highlight its transmit power limitations. To balance power efficiency and estimation performance, we formulate the scheduling task as a finite-horizon dynamic programming (DP) problem. By analyzing the structure of the optimal Q-function, we show that the resulting scheduling policy exhibits a semantic structure that adapts online to the estimation error covariance and channel variations. To obtain a practical solution, we derive a tractable upper bound on the Q-function via a positive semidefinite (PSD) cone decomposition, which enables an efficient approximate scheduling policy and a low-complexity remote estimation algorithm. Numerical results confirm that the proposed scheme outperforms existing methods in both estimation accuracy and power efficiency.
Optimizing Energy and Data Collection in UAV-aided IoT Networks using Attention-based Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Due to their adaptability and mobility, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are becoming increasingly essential for wireless network services, particularly for data harvesting tasks. In this context, Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based approaches have gained significant attention for addressing UAV path planning tasks in large and complex environments, bridging the gap with real-world deployments. However, many existing algorithms suffer from limited training data, which hampers their performance in highly dynamic environments. Moreover, they often overlook the inherently multi-objective nature of the task, treating it in an overly simplistic manner. To address these limitations, we propose an attention-based Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning (MORL) architecture that explicitly handles the trade-off between data collection and energy consumption in urban environments, even without prior knowledge of wireless channel conditions. Our method develops a single model capable of adapting to varying trade-off preferences and dynamic scenario parameters without the need for fine-tuning or retraining. Extensive simulations show that our approach achieves substantial improvements in performance, model compactness, sample efficiency, and most importantly, generalization to previously unseen scenarios, outperforming existing RL solutions.
Affine Frequency Division Multiplexing: From Communication to Sensing
Nov 06, 2025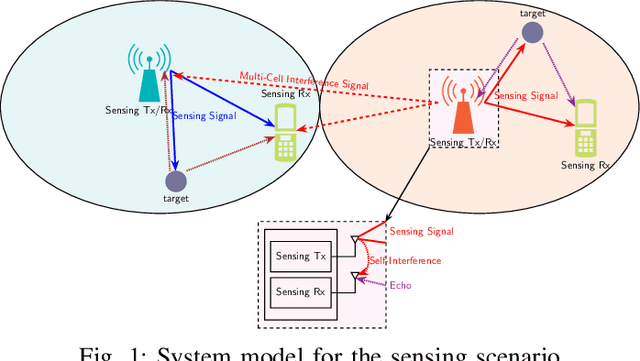
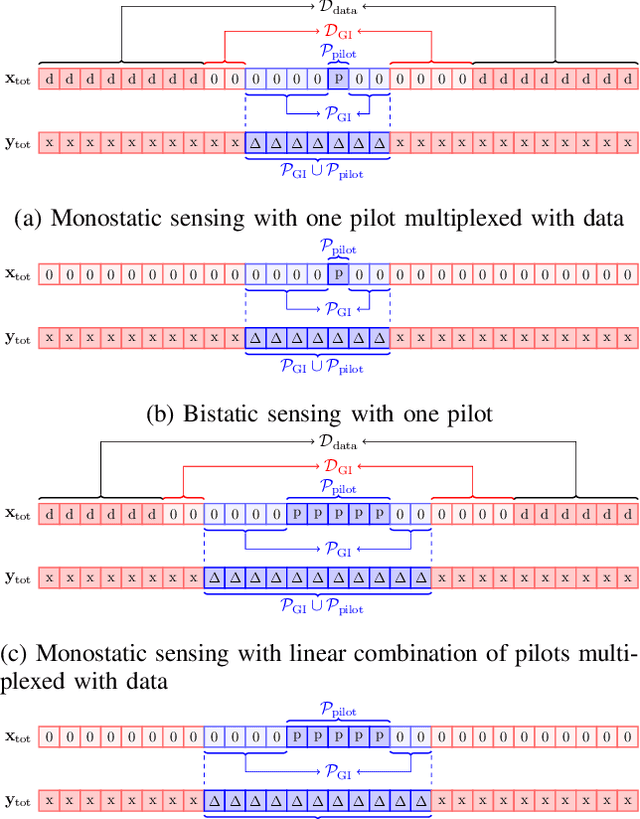
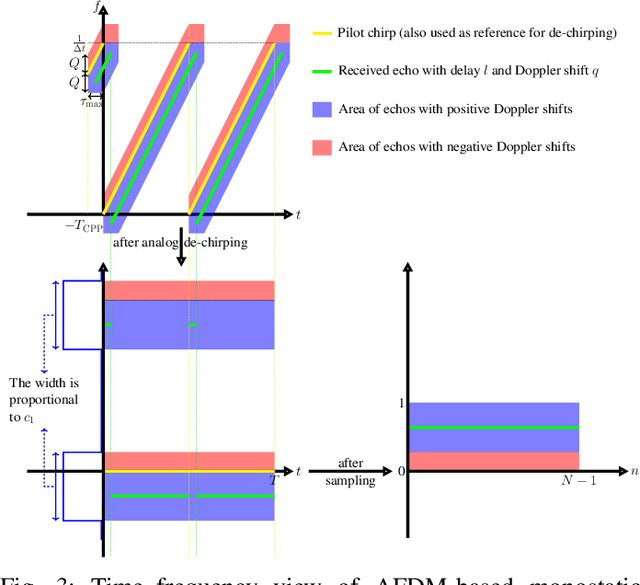
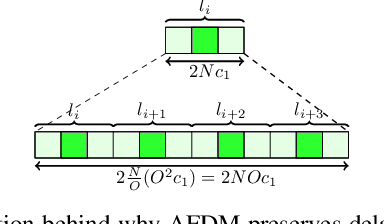
Abstract:Affine Frequency Division Multiplexing (AFDM) has been proposed as an effective waveform for achieving the full diversity of doubly-dispersive (delay-Doppler) channels. While this property is closely related to range and velocity estimation in sensing, this article focuses on other AFDM features that are particularly relevant for addressing two challenges in integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems: (1) maintaining receiver complexity and energy consumption at acceptable levels while supporting the large bandwidths required for high delay/range resolution, and (2) mitigating interference in multiradar environments. In monostatic sensing, where direct transmitter-receiver leakage is a major impairment, we show that AFDM-based ISAC receivers can address the first challenge through their compatibility with low-complexity self-interference cancellation (SIC) schemes and reduced sampling rates via analog dechirping. In bistatic sensing, where such analog solutions may not be feasible, we demonstrate that AFDM supports sub-Nyquist sampling without requiring hardware modifications while preserving delay resolution. Finally, we show that the second challenge can be addressed by leveraging the resource-assignment flexibility of the discrete affine Fourier transform (DAFT) underlying the AFDM waveform.
From OFDM to AFDM: Enabling Adaptive Integrated Sensing and Communication in High-Mobility Scenarios
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is a key feature of next-generation wireless networks, enabling a wide range of emerging applications such as vehicle-to-everything (V2X) and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which operate in high-mobility scenarios. Notably, the wireless channels within these applications typically exhibit severe delay and Doppler spreads. The latter causes serious communication performance degradation in the Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) waveform that is widely adopted in current wireless networks. To address this challenge, the recently proposed Doppler-resilient affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM) waveform, which uses flexible chirp signals as subcarriers, shows great potential for achieving adaptive ISAC in high-mobility scenarios. This article provides a comprehensive overview of AFDM-ISAC. We begin by presenting the fundamentals of AFDM-ISAC, highlighting its inherent frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW)-like characteristics. Then, we explore its ISAC performance limits by analyzing its diversity order, ambiguity function (AF), and Cramer-Rao Bound (CRB). Finally, we present several effective sensing algorithms and opportunities for AFDM-ISAC, with the aim of sparking new ideas in this emerging field.
Variational Inference for Quantum HyperNetworks
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Binary Neural Networks (BiNNs), which employ single-bit precision weights, have emerged as a promising solution to reduce memory usage and power consumption while maintaining competitive performance in large-scale systems. However, training BiNNs remains a significant challenge due to the limitations of conventional training algorithms. Quantum HyperNetworks offer a novel paradigm for enhancing the optimization of BiNN by leveraging quantum computing. Specifically, a Variational Quantum Algorithm is employed to generate binary weights through quantum circuit measurements, while key quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement facilitate the exploration of a broader solution space. In this work, we establish a connection between this approach and Bayesian inference by deriving the Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO), when direct access to the output distribution is available (i.e., in simulations), and introducing a surrogate ELBO based on the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) metric for scenarios involving implicit distributions, as commonly encountered in practice. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed methods outperform standard Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE), improving trainability and generalization.
Optimization for Semantic-Aware Resource Allocation under CPT-based Utilities
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:The problem of resource allocation in goal-oriented semantic communication with semantic-aware utilities and subjective risk perception is studied here. By linking information importance to risk aversion, we model agent behavior using Cumulative Prospect Theory (CPT), which incorporates risk-sensitive utility functions and nonlinear transformations of distributions, reflecting subjective perceptions of gains and losses. The objective is to maximize the aggregate utility across multiple CPT-modeled agents, which leads to a nonconvex, nonsmooth optimization problem. To efficiently solve this challenging problem, we propose a new algorithmic framework that combines successive convex approximation (SCA) with the projected subgradient method and Lagrangian relaxation, Our approach enables tractable optimization while preserving solution quality, offering both theoretical rigor and practical effectiveness in semantics-aware resource allocation.
Goal-Oriented Semantic Resource Allocation with Cumulative Prospect Theoretic Agents
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:We introduce a resource allocation framework for goal-oriented semantic networks, where participating agents assess system quality through subjective (e.g., context-dependent) perceptions. To accommodate this, our model accounts for agents whose preferences deviate from traditional expected utility theory (EUT), specifically incorporating cumulative prospect theory (CPT) preferences. We develop a comprehensive analytical framework that captures human-centric aspects of decision-making and risky choices under uncertainty, such as risk perception, loss aversion, and perceptual distortions in probability metrics. By identifying essential modifications in traditional resource allocation design principles required for agents with CPT preferences, we showcase the framework's relevance through its application to the problem of power allocation in multi-channel wireless communication systems.
A Conformal Predictive Measure for Assessing Catastrophic Forgetting
May 15, 2025


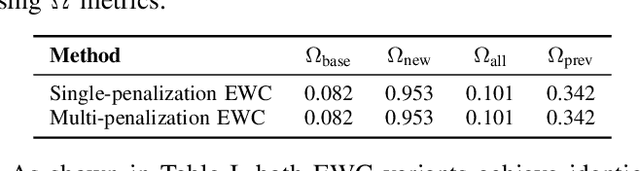
Abstract:This work introduces a novel methodology for assessing catastrophic forgetting (CF) in continual learning. We propose a new conformal prediction (CP)-based metric, termed the Conformal Prediction Confidence Factor (CPCF), to quantify and evaluate CF effectively. Our framework leverages adaptive CP to estimate forgetting by monitoring the model's confidence on previously learned tasks. This approach provides a dynamic and practical solution for monitoring and measuring CF of previous tasks as new ones are introduced, offering greater suitability for real-world applications. Experimental results on four benchmark datasets demonstrate a strong correlation between CPCF and the accuracy of previous tasks, validating the reliability and interpretability of the proposed metric. Our results highlight the potential of CPCF as a robust and effective tool for assessing and understanding CF in dynamic learning environments.
Pull-Based Query Scheduling for Goal-Oriented Semantic Communication
Mar 09, 2025



Abstract:This paper addresses query scheduling for goal-oriented semantic communication in pull-based status update systems. We consider a system where multiple sensing agents (SAs) observe a source characterized by various attributes and provide updates to multiple actuation agents (AAs), which act upon the received information to fulfill their heterogeneous goals at the endpoint. A hub serves as an intermediary, querying the SAs for updates on observed attributes and maintaining a knowledge base, which is then broadcast to the AAs. The AAs leverage the knowledge to perform their actions effectively. To quantify the semantic value of updates, we introduce a grade of effectiveness (GoE) metric. Furthermore, we integrate cumulative perspective theory (CPT) into the long-term effectiveness analysis to account for risk awareness and loss aversion in the system. Leveraging this framework, we compute effect-aware scheduling policies aimed at maximizing the expected discounted sum of CPT-based total GoE provided by the transmitted updates while complying with a given query cost constraint. To achieve this, we propose a model-based solution based on dynamic programming and model-free solutions employing state-of-the-art deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms. Our findings demonstrate that effect-aware scheduling significantly enhances the effectiveness of communicated updates compared to benchmark scheduling methods, particularly in settings with stringent cost constraints where optimal query scheduling is vital for system performance and overall effectiveness.
Large-Scale AI in Telecom: Charting the Roadmap for Innovation, Scalability, and Enhanced Digital Experiences
Mar 06, 2025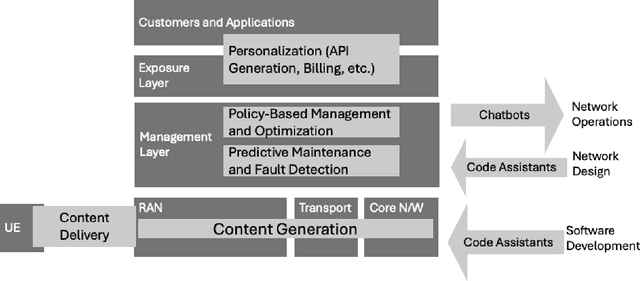
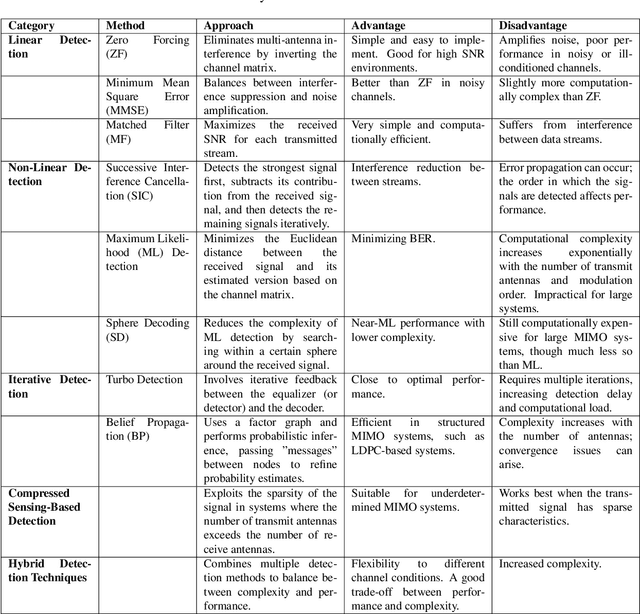
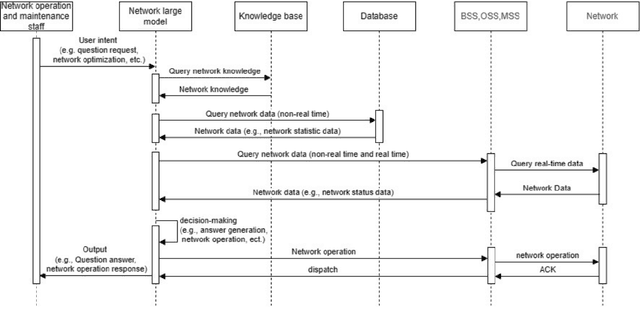
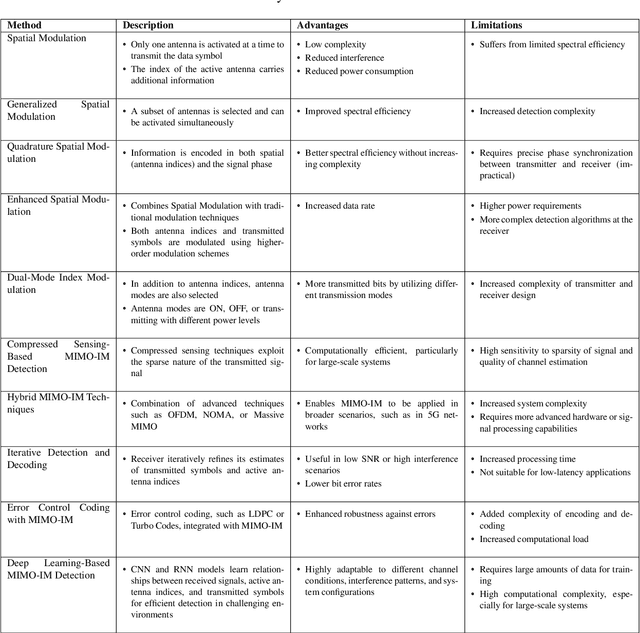
Abstract:This white paper discusses the role of large-scale AI in the telecommunications industry, with a specific focus on the potential of generative AI to revolutionize network functions and user experiences, especially in the context of 6G systems. It highlights the development and deployment of Large Telecom Models (LTMs), which are tailored AI models designed to address the complex challenges faced by modern telecom networks. The paper covers a wide range of topics, from the architecture and deployment strategies of LTMs to their applications in network management, resource allocation, and optimization. It also explores the regulatory, ethical, and standardization considerations for LTMs, offering insights into their future integration into telecom infrastructure. The goal is to provide a comprehensive roadmap for the adoption of LTMs to enhance scalability, performance, and user-centric innovation in telecom networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge