Ioannis Pitsiorlas
A Conformal Predictive Measure for Assessing Catastrophic Forgetting
May 15, 2025


Abstract:This work introduces a novel methodology for assessing catastrophic forgetting (CF) in continual learning. We propose a new conformal prediction (CP)-based metric, termed the Conformal Prediction Confidence Factor (CPCF), to quantify and evaluate CF effectively. Our framework leverages adaptive CP to estimate forgetting by monitoring the model's confidence on previously learned tasks. This approach provides a dynamic and practical solution for monitoring and measuring CF of previous tasks as new ones are introduced, offering greater suitability for real-world applications. Experimental results on four benchmark datasets demonstrate a strong correlation between CPCF and the accuracy of previous tasks, validating the reliability and interpretability of the proposed metric. Our results highlight the potential of CPCF as a robust and effective tool for assessing and understanding CF in dynamic learning environments.
Large-Scale AI in Telecom: Charting the Roadmap for Innovation, Scalability, and Enhanced Digital Experiences
Mar 06, 2025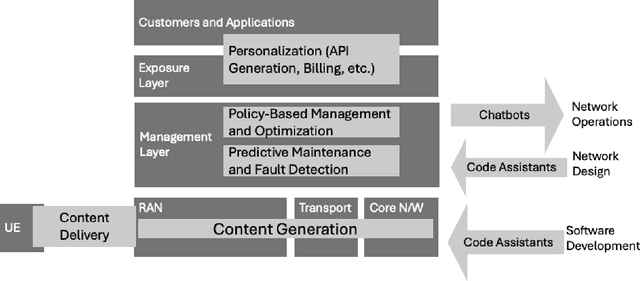
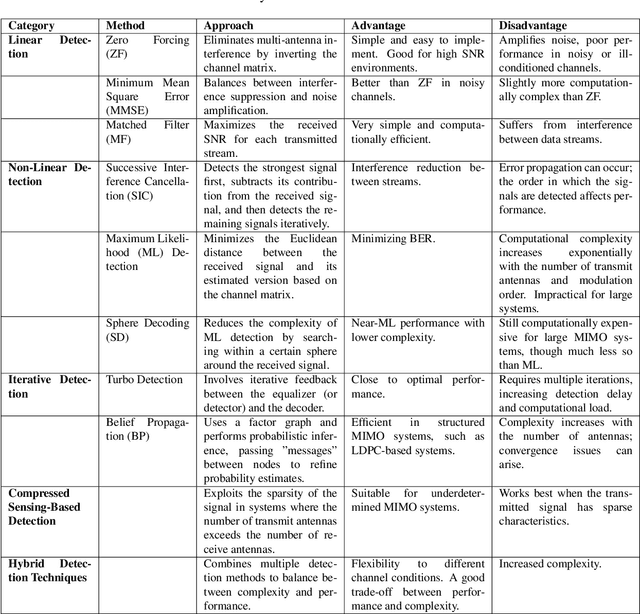
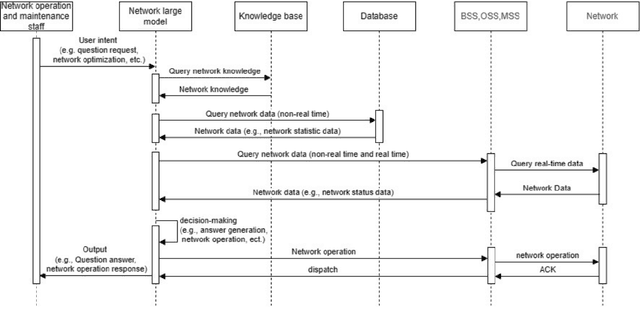
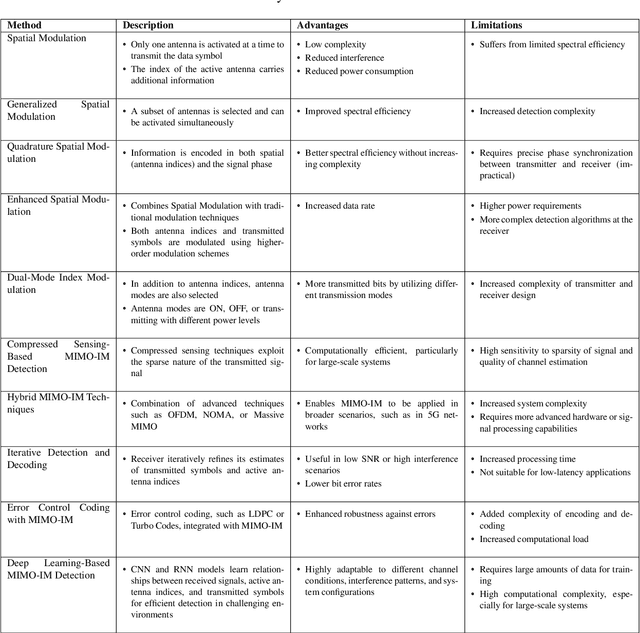
Abstract:This white paper discusses the role of large-scale AI in the telecommunications industry, with a specific focus on the potential of generative AI to revolutionize network functions and user experiences, especially in the context of 6G systems. It highlights the development and deployment of Large Telecom Models (LTMs), which are tailored AI models designed to address the complex challenges faced by modern telecom networks. The paper covers a wide range of topics, from the architecture and deployment strategies of LTMs to their applications in network management, resource allocation, and optimization. It also explores the regulatory, ethical, and standardization considerations for LTMs, offering insights into their future integration into telecom infrastructure. The goal is to provide a comprehensive roadmap for the adoption of LTMs to enhance scalability, performance, and user-centric innovation in telecom networks.
SMILE-UHURA Challenge -- Small Vessel Segmentation at Mesoscopic Scale from Ultra-High Resolution 7T Magnetic Resonance Angiograms
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:The human brain receives nutrients and oxygen through an intricate network of blood vessels. Pathology affecting small vessels, at the mesoscopic scale, represents a critical vulnerability within the cerebral blood supply and can lead to severe conditions, such as Cerebral Small Vessel Diseases. The advent of 7 Tesla MRI systems has enabled the acquisition of higher spatial resolution images, making it possible to visualise such vessels in the brain. However, the lack of publicly available annotated datasets has impeded the development of robust, machine learning-driven segmentation algorithms. To address this, the SMILE-UHURA challenge was organised. This challenge, held in conjunction with the ISBI 2023, in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, aimed to provide a platform for researchers working on related topics. The SMILE-UHURA challenge addresses the gap in publicly available annotated datasets by providing an annotated dataset of Time-of-Flight angiography acquired with 7T MRI. This dataset was created through a combination of automated pre-segmentation and extensive manual refinement. In this manuscript, sixteen submitted methods and two baseline methods are compared both quantitatively and qualitatively on two different datasets: held-out test MRAs from the same dataset as the training data (with labels kept secret) and a separate 7T ToF MRA dataset where both input volumes and labels are kept secret. The results demonstrate that most of the submitted deep learning methods, trained on the provided training dataset, achieved reliable segmentation performance. Dice scores reached up to 0.838 $\pm$ 0.066 and 0.716 $\pm$ 0.125 on the respective datasets, with an average performance of up to 0.804 $\pm$ 0.15.
A Latent Space Metric for Enhancing Prediction Confidence in Earth Observation Data
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:This study presents a new approach for estimating confidence in machine learning model predictions, specifically in regression tasks utilizing Earth Observation (EO) data, with a particular focus on mosquito abundance (MA) estimation. We take advantage of a Variational AutoEncoder architecture, to derive a confidence metric by the latent space representations of EO datasets. This methodology is pivotal in establishing a correlation between the Euclidean distance in latent representations and the Absolute Error (AE) in individual MA predictions. Our research focuses on EO datasets from the Veneto region in Italy and the Upper Rhine Valley in Germany, targeting areas significantly affected by mosquito populations. A key finding is a notable correlation of 0.46 between the AE of MA predictions and the proposed confidence metric. This correlation signifies a robust, new metric for quantifying the reliability and enhancing the trustworthiness of the AI model's predictions in the context of both EO data analysis and mosquito abundance studies.
JoB-VS: Joint Brain-Vessel Segmentation in TOF-MRA Images
Apr 16, 2023



Abstract:We propose the first joint-task learning framework for brain and vessel segmentation (JoB-VS) from Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance images. Unlike state-of-the-art vessel segmentation methods, our approach avoids the pre-processing step of implementing a model to extract the brain from the volumetric input data. Skipping this additional step makes our method an end-to-end vessel segmentation framework. JoB-VS uses a lattice architecture that favors the segmentation of structures of different scales (e.g., the brain and vessels). Its segmentation head allows the simultaneous prediction of the brain and vessel mask. Moreover, we generate data augmentation with adversarial examples, which our results demonstrate to enhance the performance. JoB-VS achieves 70.03% mean AP and 69.09% F1-score in the OASIS-3 dataset and is capable of generalizing the segmentation in the IXI dataset. These results show the adequacy of JoB-VS for the challenging task of vessel segmentation in complete TOF-MRA images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge