Yaqiang Wu
AERO: Autonomous Evolutionary Reasoning Optimization via Endogenous Dual-Loop Feedback
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved significant success in complex reasoning but remain bottlenecked by reliance on expert-annotated data and external verifiers. While existing self-evolution paradigms aim to bypass these constraints, they often fail to identify the optimal learning zone and risk reinforcing collective hallucinations and incorrect priors through flawed internal feedback. To address these challenges, we propose \underline{A}utonomous \underline{E}volutionary \underline{R}easoning \underline{O}ptimization (AERO), an unsupervised framework that achieves autonomous reasoning evolution by internalizing self-questioning, answering, and criticism within a synergistic dual-loop system. Inspired by the \textit{Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)} theory, AERO utilizes entropy-based positioning to target the ``solvability gap'' and employs Independent Counterfactual Correction for robust verification. Furthermore, we introduce a Staggered Training Strategy to synchronize capability growth across functional roles and prevent curriculum collapse. Extensive evaluations across nine benchmarks spanning three domains demonstrate that AERO achieves average performance improvements of 4.57\% on Qwen3-4B-Base and 5.10\% on Qwen3-8B-Base, outperforming competitive baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/mira-ai-lab/AERO.
SketchVL: Policy Optimization via Fine-Grained Credit Assignment for Chart Understanding and More
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Charts are high-density visual carriers of complex data and medium for information extraction and analysis. Due to the need for precise and complex visual reasoning, automated chart understanding poses a significant challenge to existing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Many MLLMs trained with reinforcement learning (RL) face the challenge of credit assignment. Their advantage estimation, typically performed at the trajectory level, cannot distinguish between correct and incorrect reasoning steps within a single generated response. To address this limitation, we introduce SketchVL, a novel MLLM that optimized with FinePO, a new RL algorithm designed for fine-grained credit assignment within each trajectory. SketchVL's methodology involves drawing its intermediate reasoning steps as markers on the image and feeding the annotated image back to itself, creating a robust, multi-step reasoning process. During training, the FinePO algorithm leverages a Fine-grained Process Reward Model (FinePRM) to score each drawing action within a trajectory, thereby precisely assigning credit for each step. This mechanism allows FinePO to more strongly reward correct tokens when a trajectory is globally successful, and more heavily penalize incorrect tokens when the trajectory is globally suboptimal, thus achieving fine-grained reinforcement signals. Experiments show that SketchVL learns to align its step-level behavior with the FinePRM, achieving an average performance gain of 7.23\% over its base model across chart datasets, natural image datasets, and mathematics, providing a promising new direction for training powerful reasoning models.
ChartSketcher: Reasoning with Multimodal Feedback and Reflection for Chart Understanding
May 25, 2025Abstract:Charts are high-density visualization carriers for complex data, serving as a crucial medium for information extraction and analysis. Automated chart understanding poses significant challenges to existing multimodal large language models (MLLMs) due to the need for precise and complex visual reasoning. Current step-by-step reasoning models primarily focus on text-based logical reasoning for chart understanding. However, they struggle to refine or correct their reasoning when errors stem from flawed visual understanding, as they lack the ability to leverage multimodal interaction for deeper comprehension. Inspired by human cognitive behavior, we propose ChartSketcher, a multimodal feedback-driven step-by-step reasoning method designed to address these limitations. ChartSketcher is a chart understanding model that employs Sketch-CoT, enabling MLLMs to annotate intermediate reasoning steps directly onto charts using a programmatic sketching library, iteratively feeding these visual annotations back into the reasoning process. This mechanism enables the model to visually ground its reasoning and refine its understanding over multiple steps. We employ a two-stage training strategy: a cold start phase to learn sketch-based reasoning patterns, followed by off-policy reinforcement learning to enhance reflection and generalization. Experiments demonstrate that ChartSketcher achieves promising performance on chart understanding benchmarks and general vision tasks, providing an interactive and interpretable approach to chart comprehension.
Unleashing the Potential of Model Bias for Generalized Category Discovery
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Generalized Category Discovery is a significant and complex task that aims to identify both known and undefined novel categories from a set of unlabeled data, leveraging another labeled dataset containing only known categories. The primary challenges stem from model bias induced by pre-training on only known categories and the lack of precise supervision for novel ones, leading to category bias towards known categories and category confusion among different novel categories, which hinders models' ability to identify novel categories effectively. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework named Self-Debiasing Calibration (SDC). Unlike prior methods that regard model bias towards known categories as an obstacle to novel category identification, SDC provides a novel insight into unleashing the potential of the bias to facilitate novel category learning. Specifically, the output of the biased model serves two key purposes. First, it provides an accurate modeling of category bias, which can be utilized to measure the degree of bias and debias the output of the current training model. Second, it offers valuable insights for distinguishing different novel categories by transferring knowledge between similar categories. Based on these insights, SDC dynamically adjusts the output logits of the current training model using the output of the biased model. This approach produces less biased logits to effectively address the issue of category bias towards known categories, and generates more accurate pseudo labels for unlabeled data, thereby mitigating category confusion for novel categories. Experiments on three benchmark datasets show that SDC outperforms SOTA methods, especially in the identification of novel categories. Our code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/Lackel/SDC}.
Knowledge Acquisition Disentanglement for Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering with Large Language Models
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering (KVQA) requires both image and world knowledge to answer questions. Current methods first retrieve knowledge from the image and external knowledge base with the original complex question, then generate answers with Large Language Models (LLMs). However, since the original question contains complex elements that require knowledge from different sources, acquiring different kinds of knowledge in a coupled manner may confuse models and hinder them from retrieving precise knowledge. Furthermore, the ``forward-only'' answering process fails to explicitly capture the knowledge needs of LLMs, which can further hurt answering quality. To cope with the above limitations, we propose DKA: Disentangled Knowledge Acquisition from LLM feedback, a training-free framework that disentangles knowledge acquisition to avoid confusion and uses LLM's feedback to specify the required knowledge. Specifically, DKA requires LLMs to specify what knowledge they need to answer the question and decompose the original complex question into two simple sub-questions: Image-based sub-question and Knowledge-based sub-question. Then we use the two sub-questions to retrieve knowledge from the image and knowledge base, respectively. In this way, two knowledge acquisition models can focus on the content that corresponds to them and avoid disturbance of irrelevant elements in the original complex question, which can help to provide more precise knowledge and better align the knowledge needs of LLMs to yield correct answers. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that DKA significantly outperforms SOTA models. To facilitate future research, our data and code are available at \url{https://github.com/Lackel/DKA}.
Transfer and Alignment Network for Generalized Category Discovery
Dec 27, 2023



Abstract:Generalized Category Discovery is a crucial real-world task. Despite the improved performance on known categories, current methods perform poorly on novel categories. We attribute the poor performance to two reasons: biased knowledge transfer between labeled and unlabeled data and noisy representation learning on the unlabeled data. To mitigate these two issues, we propose a Transfer and Alignment Network (TAN), which incorporates two knowledge transfer mechanisms to calibrate the biased knowledge and two feature alignment mechanisms to learn discriminative features. Specifically, we model different categories with prototypes and transfer the prototypes in labeled data to correct model bias towards known categories. On the one hand, we pull instances with known categories in unlabeled data closer to these prototypes to form more compact clusters and avoid boundary overlap between known and novel categories. On the other hand, we use these prototypes to calibrate noisy prototypes estimated from unlabeled data based on category similarities, which allows for more accurate estimation of prototypes for novel categories that can be used as reliable learning targets later. After knowledge transfer, we further propose two feature alignment mechanisms to acquire both instance- and category-level knowledge from unlabeled data by aligning instance features with both augmented features and the calibrated prototypes, which can boost model performance on both known and novel categories with less noise. Experiments on three benchmark datasets show that our model outperforms SOTA methods, especially on novel categories. Theoretical analysis is provided for an in-depth understanding of our model in general. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/Lackel/TAN.
Generalized Category Discovery with Large Language Models in the Loop
Dec 18, 2023
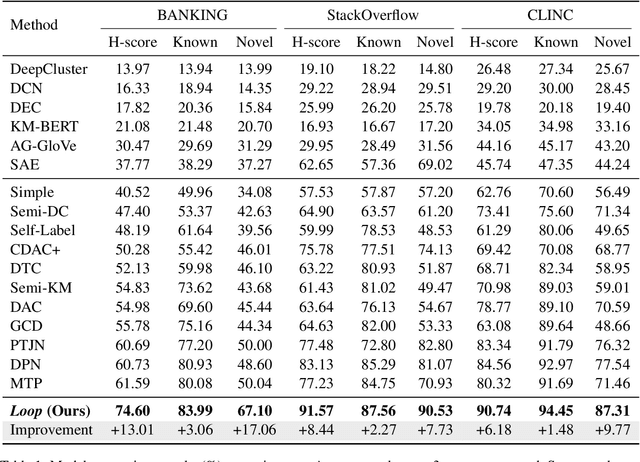

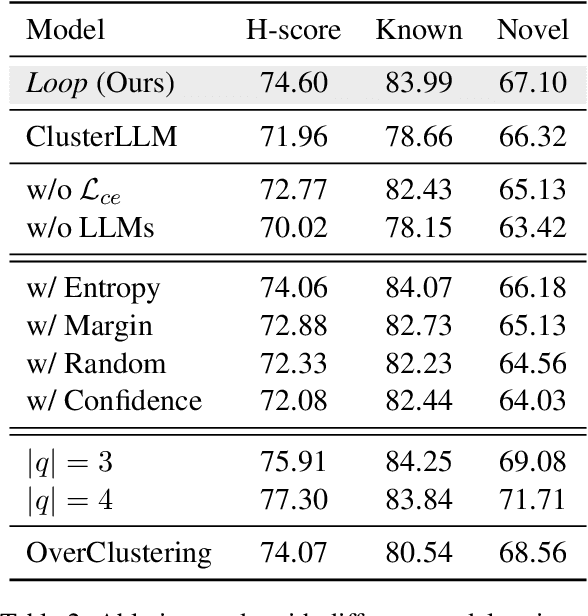
Abstract:Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) is a crucial task that aims to recognize both known and novel categories from a set of unlabeled data by utilizing a few labeled data with only known categories. Due to the lack of supervision and category information, current methods usually perform poorly on novel categories and struggle to reveal semantic meanings of the discovered clusters, which limits their applications in the real world. To mitigate above issues, we propose Loop, an end-to-end active-learning framework that introduces Large Language Models (LLMs) into the training loop, which can boost model performance and generate category names without relying on any human efforts. Specifically, we first propose Local Inconsistent Sampling (LIS) to select samples that have a higher probability of falling to wrong clusters, based on neighborhood prediction consistency and entropy of cluster assignment probabilities. Then we propose a Scalable Query strategy to allow LLMs to choose true neighbors of the selected samples from multiple candidate samples. Based on the feedback from LLMs, we perform Refined Neighborhood Contrastive Learning (RNCL) to pull samples and their neighbors closer to learn clustering-friendly representations. Finally, we select representative samples from clusters corresponding to novel categories to allow LLMs to generate category names for them. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets show that Loop outperforms SOTA models by a large margin and generates accurate category names for the discovered clusters. We will release our code and data after publication.
GPTR: Gestalt-Perception Transformer for Diagram Object Detection
Dec 29, 2022


Abstract:Diagram object detection is the key basis of practical applications such as textbook question answering. Because the diagram mainly consists of simple lines and color blocks, its visual features are sparser than those of natural images. In addition, diagrams usually express diverse knowledge, in which there are many low-frequency object categories in diagrams. These lead to the fact that traditional data-driven detection model is not suitable for diagrams. In this work, we propose a gestalt-perception transformer model for diagram object detection, which is based on an encoder-decoder architecture. Gestalt perception contains a series of laws to explain human perception, that the human visual system tends to perceive patches in an image that are similar, close or connected without abrupt directional changes as a perceptual whole object. Inspired by these thoughts, we build a gestalt-perception graph in transformer encoder, which is composed of diagram patches as nodes and the relationships between patches as edges. This graph aims to group these patches into objects via laws of similarity, proximity, and smoothness implied in these edges, so that the meaningful objects can be effectively detected. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed GPTR achieves the best results in the diagram object detection task. Our model also obtains comparable results over the competitors in natural image object detection.
MatchVIE: Exploiting Match Relevancy between Entities for Visual Information Extraction
Jun 24, 2021


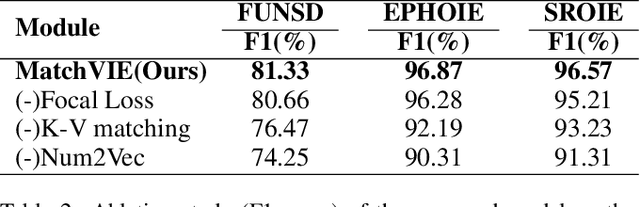
Abstract:Visual Information Extraction (VIE) task aims to extract key information from multifarious document images (e.g., invoices and purchase receipts). Most previous methods treat the VIE task simply as a sequence labeling problem or classification problem, which requires models to carefully identify each kind of semantics by introducing multimodal features, such as font, color, layout. But simply introducing multimodal features couldn't work well when faced with numeric semantic categories or some ambiguous texts. To address this issue, in this paper we propose a novel key-value matching model based on a graph neural network for VIE (MatchVIE). Through key-value matching based on relevancy evaluation, the proposed MatchVIE can bypass the recognitions to various semantics, and simply focuses on the strong relevancy between entities. Besides, we introduce a simple but effective operation, Num2Vec, to tackle the instability of encoded values, which helps model converge more smoothly. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed MatchVIE can significantly outperform previous methods. Notably, to the best of our knowledge, MatchVIE may be the first attempt to tackle the VIE task by modeling the relevancy between keys and values and it is a good complement to the existing methods.
Towards an efficient framework for Data Extraction from Chart Images
May 05, 2021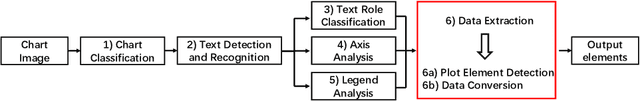
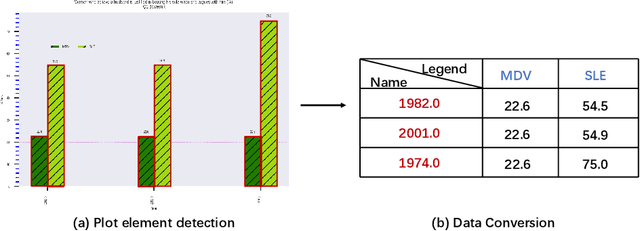
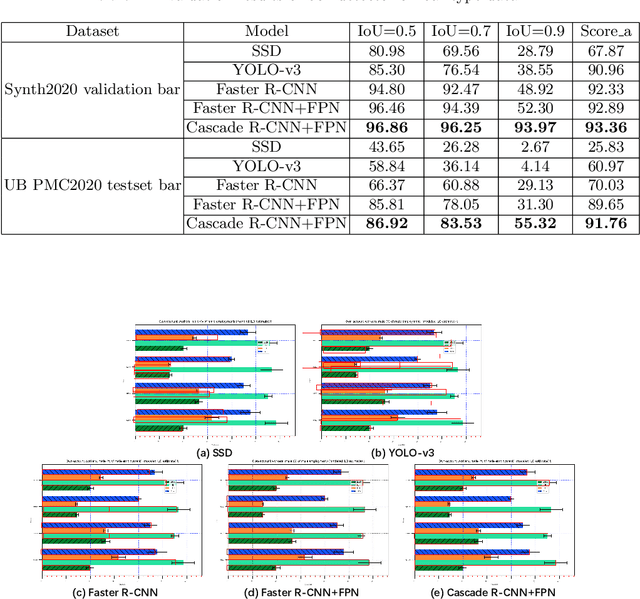
Abstract:In this paper, we fill the research gap by adopting state-of-the-art computer vision techniques for the data extraction stage in a data mining system. As shown in Fig.1, this stage contains two subtasks, namely, plot element detection and data conversion. For building a robust box detector, we comprehensively compare different deep learning-based methods and find a suitable method to detect box with high precision. For building a robust point detector, a fully convolutional network with feature fusion module is adopted, which can distinguish close points compared to traditional methods. The proposed system can effectively handle various chart data without making heuristic assumptions. For data conversion, we translate the detected element into data with semantic value. A network is proposed to measure feature similarities between legends and detected elements in the legend matching phase. Furthermore, we provide a baseline on the competition of Harvesting raw tables from Infographics. Some key factors have been found to improve the performance of each stage. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge