Yongjie Xiao
SCOP: Evaluating the Comprehension Process of Large Language Models from a Cognitive View
Jun 05, 2025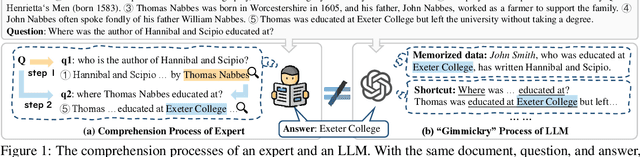

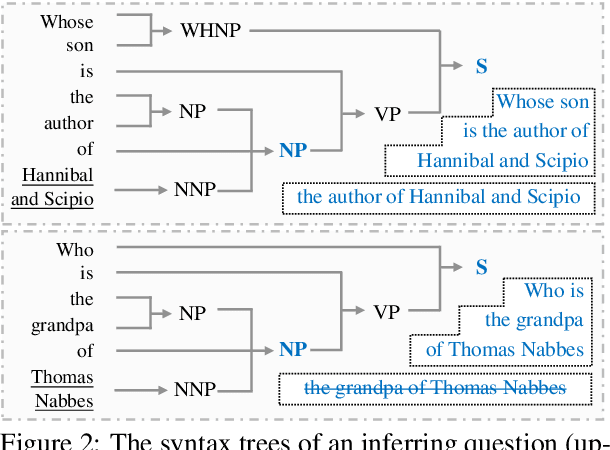

Abstract:Despite the great potential of large language models(LLMs) in machine comprehension, it is still disturbing to fully count on them in real-world scenarios. This is probably because there is no rational explanation for whether the comprehension process of LLMs is aligned with that of experts. In this paper, we propose SCOP to carefully examine how LLMs perform during the comprehension process from a cognitive view. Specifically, it is equipped with a systematical definition of five requisite skills during the comprehension process, a strict framework to construct testing data for these skills, and a detailed analysis of advanced open-sourced and closed-sourced LLMs using the testing data. With SCOP, we find that it is still challenging for LLMs to perform an expert-level comprehension process. Even so, we notice that LLMs share some similarities with experts, e.g., performing better at comprehending local information than global information. Further analysis reveals that LLMs can be somewhat unreliable -- they might reach correct answers through flawed comprehension processes. Based on SCOP, we suggest that one direction for improving LLMs is to focus more on the comprehension process, ensuring all comprehension skills are thoroughly developed during training.
Deep Rib Fracture Instance Segmentation and Classification from CT on the RibFrac Challenge
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:Rib fractures are a common and potentially severe injury that can be challenging and labor-intensive to detect in CT scans. While there have been efforts to address this field, the lack of large-scale annotated datasets and evaluation benchmarks has hindered the development and validation of deep learning algorithms. To address this issue, the RibFrac Challenge was introduced, providing a benchmark dataset of over 5,000 rib fractures from 660 CT scans, with voxel-level instance mask annotations and diagnosis labels for four clinical categories (buckle, nondisplaced, displaced, or segmental). The challenge includes two tracks: a detection (instance segmentation) track evaluated by an FROC-style metric and a classification track evaluated by an F1-style metric. During the MICCAI 2020 challenge period, 243 results were evaluated, and seven teams were invited to participate in the challenge summary. The analysis revealed that several top rib fracture detection solutions achieved performance comparable or even better than human experts. Nevertheless, the current rib fracture classification solutions are hardly clinically applicable, which can be an interesting area in the future. As an active benchmark and research resource, the data and online evaluation of the RibFrac Challenge are available at the challenge website. As an independent contribution, we have also extended our previous internal baseline by incorporating recent advancements in large-scale pretrained networks and point-based rib segmentation techniques. The resulting FracNet+ demonstrates competitive performance in rib fracture detection, which lays a foundation for further research and development in AI-assisted rib fracture detection and diagnosis.
Rethinking annotation granularity for overcoming deep shortcut learning: A retrospective study on chest radiographs
Apr 21, 2021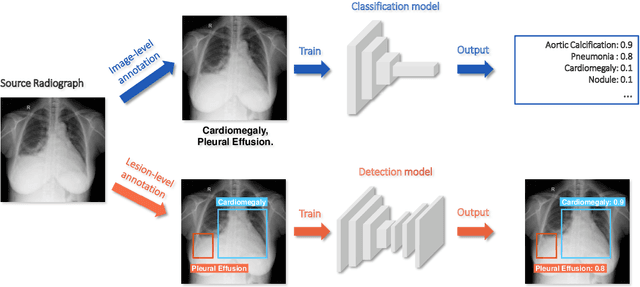
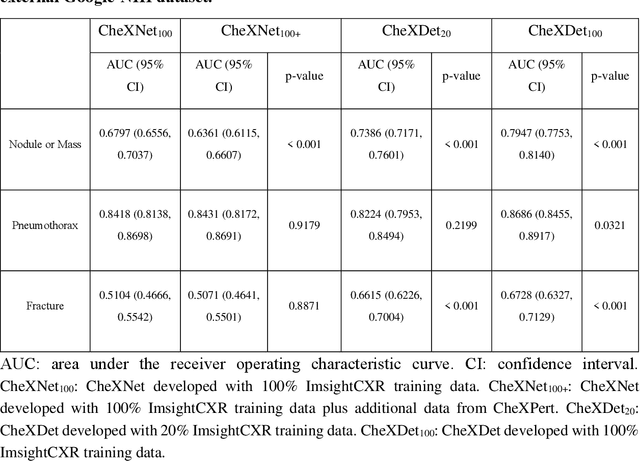
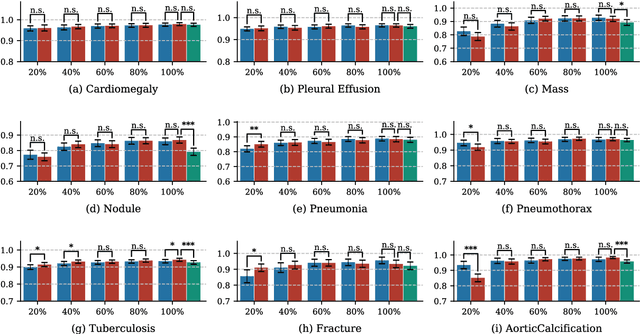
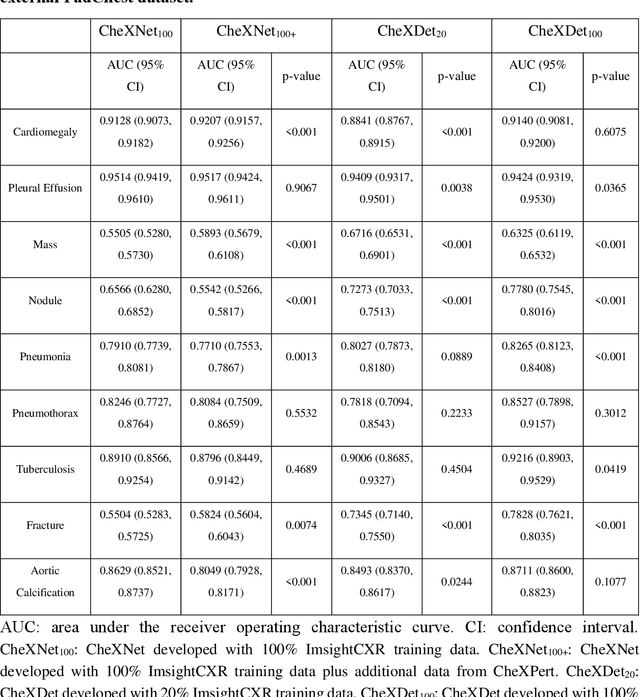
Abstract:Deep learning has demonstrated radiograph screening performances that are comparable or superior to radiologists. However, recent studies show that deep models for thoracic disease classification usually show degraded performance when applied to external data. Such phenomena can be categorized into shortcut learning, where the deep models learn unintended decision rules that can fit the identically distributed training and test set but fail to generalize to other distributions. A natural way to alleviate this defect is explicitly indicating the lesions and focusing the model on learning the intended features. In this paper, we conduct extensive retrospective experiments to compare a popular thoracic disease classification model, CheXNet, and a thoracic lesion detection model, CheXDet. We first showed that the two models achieved similar image-level classification performance on the internal test set with no significant differences under many scenarios. Meanwhile, we found incorporating external training data even led to performance degradation for CheXNet. Then, we compared the models' internal performance on the lesion localization task and showed that CheXDet achieved significantly better performance than CheXNet even when given 80% less training data. By further visualizing the models' decision-making regions, we revealed that CheXNet learned patterns other than the target lesions, demonstrating its shortcut learning defect. Moreover, CheXDet achieved significantly better external performance than CheXNet on both the image-level classification task and the lesion localization task. Our findings suggest improving annotation granularity for training deep learning systems as a promising way to elevate future deep learning-based diagnosis systems for clinical usage.
SINet: A Scale-insensitive Convolutional Neural Network for Fast Vehicle Detection
May 16, 2018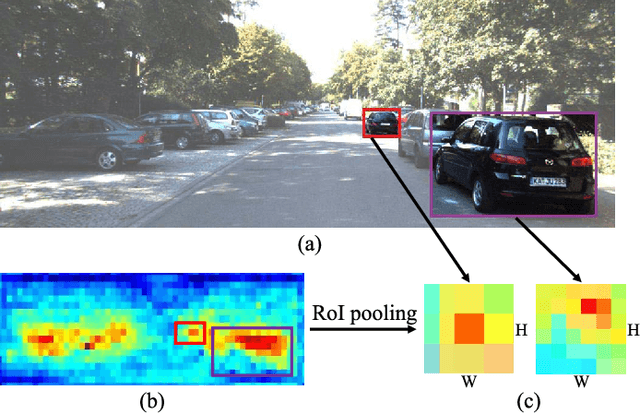
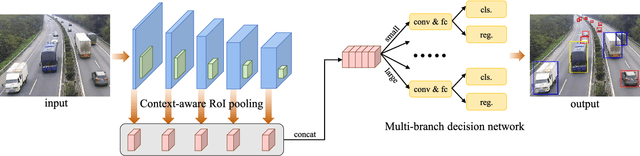
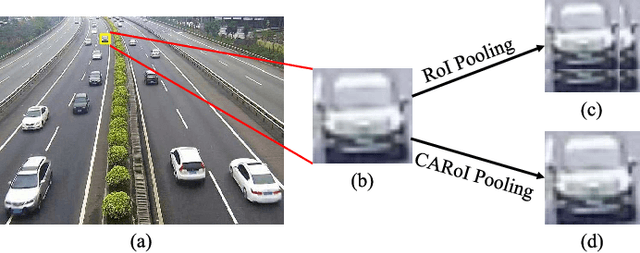
Abstract:Vision-based vehicle detection approaches achieve incredible success in recent years with the development of deep convolutional neural network (CNN). However, existing CNN based algorithms suffer from the problem that the convolutional features are scale-sensitive in object detection task but it is common that traffic images and videos contain vehicles with a large variance of scales. In this paper, we delve into the source of scale sensitivity, and reveal two key issues: 1) existing RoI pooling destroys the structure of small scale objects, 2) the large intra-class distance for a large variance of scales exceeds the representation capability of a single network. Based on these findings, we present a scale-insensitive convolutional neural network (SINet) for fast detecting vehicles with a large variance of scales. First, we present a context-aware RoI pooling to maintain the contextual information and original structure of small scale objects. Second, we present a multi-branch decision network to minimize the intra-class distance of features. These lightweight techniques bring zero extra time complexity but prominent detection accuracy improvement. The proposed techniques can be equipped with any deep network architectures and keep them trained end-to-end. Our SINet achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of accuracy and speed (up to 37 FPS) on the KITTI benchmark and a new highway dataset, which contains a large variance of scales and extremely small objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge