Minghang He
MOST: A Multi-Oriented Scene Text Detector with Localization Refinement
Apr 05, 2021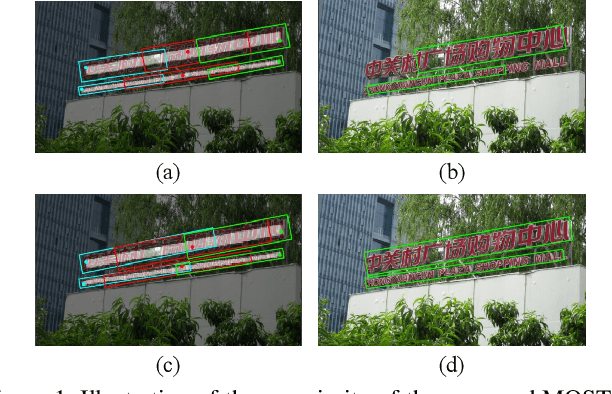
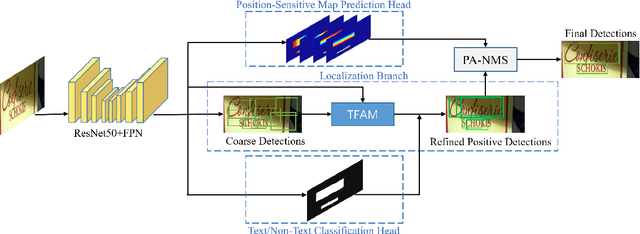
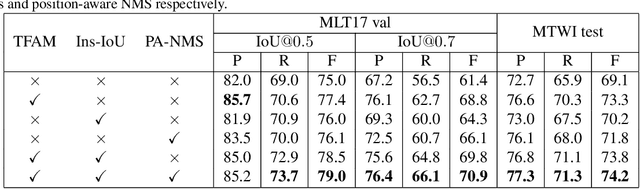
Abstract:Over the past few years, the field of scene text detection has progressed rapidly that modern text detectors are able to hunt text in various challenging scenarios. However, they might still fall short when handling text instances of extreme aspect ratios and varying scales. To tackle such difficulties, we propose in this paper a new algorithm for scene text detection, which puts forward a set of strategies to significantly improve the quality of text localization. Specifically, a Text Feature Alignment Module (TFAM) is proposed to dynamically adjust the receptive fields of features based on initial raw detections; a Position-Aware Non-Maximum Suppression (PA-NMS) module is devised to selectively concentrate on reliable raw detections and exclude unreliable ones; besides, we propose an Instance-wise IoU loss for balanced training to deal with text instances of different scales. An extensive ablation study demonstrates the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed strategies. The resulting text detection system, which integrates the proposed strategies with a leading scene text detector EAST, achieves state-of-the-art or competitive performance on various standard benchmarks for text detection while keeping a fast running speed.
TextScanner: Reading Characters in Order for Robust Scene Text Recognition
Jan 01, 2020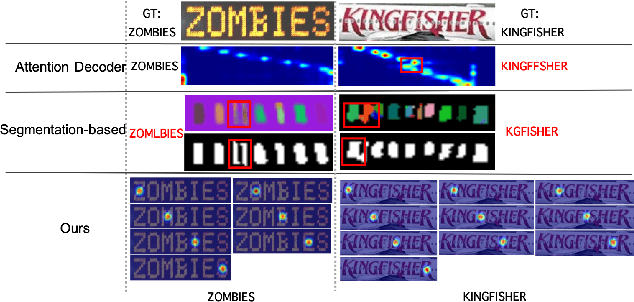
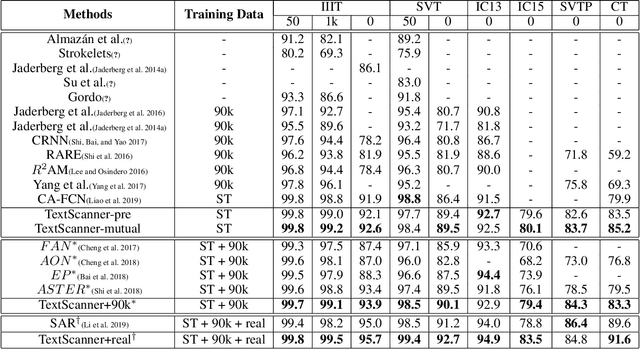
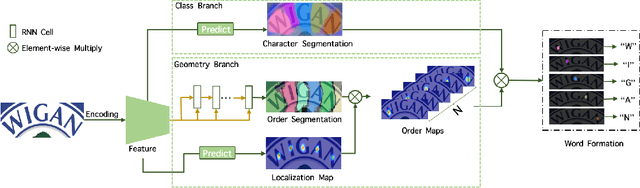
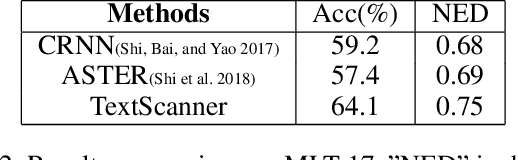
Abstract:Driven by deep learning and the large volume of data, scene text recognition has evolved rapidly in recent years. Formerly, RNN-attention based methods have dominated this field, but suffer from the problem of \textit{attention drift} in certain situations. Lately, semantic segmentation based algorithms have proven effective at recognizing text of different forms (horizontal, oriented and curved). However, these methods may produce spurious characters or miss genuine characters, as they rely heavily on a thresholding procedure operated on segmentation maps. To tackle these challenges, we propose in this paper an alternative approach, called TextScanner, for scene text recognition. TextScanner bears three characteristics: (1) Basically, it belongs to the semantic segmentation family, as it generates pixel-wise, multi-channel segmentation maps for character class, position and order; (2) Meanwhile, akin to RNN-attention based methods, it also adopts RNN for context modeling; (3) Moreover, it performs paralleled prediction for character position and class, and ensures that characters are transcripted in correct order. The experiments on standard benchmark datasets demonstrate that TextScanner outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, TextScanner shows its superiority in recognizing more difficult text such Chinese transcripts and aligning with target characters.
Mask TextSpotter: An End-to-End Trainable Neural Network for Spotting Text with Arbitrary Shapes
Aug 22, 2019



Abstract:Unifying text detection and text recognition in an end-to-end training fashion has become a new trend for reading text in the wild, as these two tasks are highly relevant and complementary. In this paper, we investigate the problem of scene text spotting, which aims at simultaneous text detection and recognition in natural images. An end-to-end trainable neural network named as Mask TextSpotter is presented. Different from the previous text spotters that follow the pipeline consisting of a proposal generation network and a sequence-to-sequence recognition network, Mask TextSpotter enjoys a simple and smooth end-to-end learning procedure, in which both detection and recognition can be achieved directly from two-dimensional space via semantic segmentation. Further, a spatial attention module is proposed to enhance the performance and universality. Benefiting from the proposed two-dimensional representation on both detection and recognition, it easily handles text instances of irregular shapes, for instance, curved text. We evaluate it on four English datasets and one multi-language dataset, achieving consistently superior performance over state-of-the-art methods in both detection and end-to-end text recognition tasks. Moreover, we further investigate the recognition module of our method separately, which significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both regular and irregular text datasets for scene text recognition.
SynthText3D: Synthesizing Scene Text Images from 3D Virtual Worlds
Jul 13, 2019
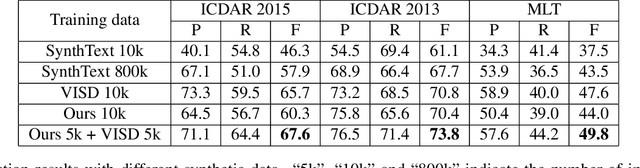
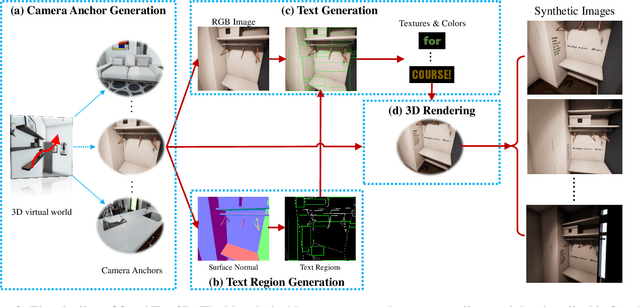
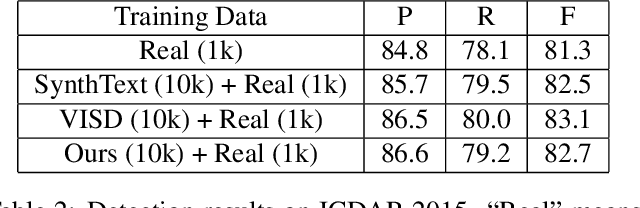
Abstract:With the development of deep neural networks, the demand for a significant amount of annotated training data becomes the performance bottlenecks in many fields of research and applications. Image synthesis can generate annotated images automatically and freely, which gains increasing attention recently. In this paper, we propose to synthesize scene text images from the 3D virtual worlds, where the precise descriptions of scenes, editable illumination/visibility, and realistic physics are provided. Different from the previous methods which paste the rendered text on static 2D images, our method can render the 3D virtual scene and text instances as an entirety. In this way, complex perspective transforms, various illuminations, and occlusions can be realized in our synthesized scene text images. Moreover, the same text instances with various viewpoints can be produced by randomly moving and rotating the virtual camera, which acts as human eyes. The experiments on the standard scene text detection benchmarks using the generated synthetic data demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method. The code and synthetic data will be made available at https://github.com/MhLiao/SynthText3D
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge