Junyi Zhang
VisGym: Diverse, Customizable, Scalable Environments for Multimodal Agents
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) remain poorly characterized in multi-step visual interactions, particularly in how they integrate perception, memory, and action over long horizons. We introduce VisGym, a gymnasium of 17 environments for evaluating and training VLMs. The suite spans symbolic puzzles, real-image understanding, navigation, and manipulation, and provides flexible controls over difficulty, input representation, planning horizon, and feedback. We also provide multi-step solvers that generate structured demonstrations, enabling supervised finetuning. Our evaluations show that all frontier models struggle in interactive settings, achieving low success rates in both the easy (46.6%) and hard (26.0%) configurations. Our experiments reveal notable limitations: models struggle to effectively leverage long context, performing worse with an unbounded history than with truncated windows. Furthermore, we find that several text-based symbolic tasks become substantially harder once rendered visually. However, explicit goal observations, textual feedback, and exploratory demonstrations in partially observable or unknown-dynamics settings for supervised finetuning yield consistent gains, highlighting concrete failure modes and pathways for improving multi-step visual decision-making. Code, data, and models can be found at: https://visgym.github.io/.
Spherical Geometry Diffusion: Generating High-quality 3D Face Geometry via Sphere-anchored Representations
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:A fundamental challenge in text-to-3D face generation is achieving high-quality geometry. The core difficulty lies in the arbitrary and intricate distribution of vertices in 3D space, making it challenging for existing models to establish clean connectivity and resulting in suboptimal geometry. To address this, our core insight is to simplify the underlying geometric structure by constraining the distribution onto a simple and regular manifold, a topological sphere. Building on this, we first propose the Spherical Geometry Representation, a novel face representation that anchors geometric signals to uniform spherical coordinates. This guarantees a regular point distribution, from which the mesh connectivity can be robustly reconstructed. Critically, this canonical sphere can be seamlessly unwrapped into a 2D map, creating a perfect synergy with powerful 2D generative models. We then introduce Spherical Geometry Diffusion, a conditional diffusion framework built upon this 2D map. It enables diverse and controllable generation by jointly modeling geometry and texture, where the geometry explicitly conditions the texture synthesis process. Our method's effectiveness is demonstrated through its success in a wide range of tasks: text-to-3D generation, face reconstruction, and text-based 3D editing. Extensive experiments show that our approach substantially outperforms existing methods in geometric quality, textual fidelity, and inference efficiency.
Selfi: Self Improving Reconstruction Engine via 3D Geometric Feature Alignment
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Novel View Synthesis (NVS) has traditionally relied on models with explicit 3D inductive biases combined with known camera parameters from Structure-from-Motion (SfM) beforehand. Recent vision foundation models like VGGT take an orthogonal approach -- 3D knowledge is gained implicitly through training data and loss objectives, enabling feed-forward prediction of both camera parameters and 3D representations directly from a set of uncalibrated images. While flexible, VGGT features lack explicit multi-view geometric consistency, and we find that improving such 3D feature consistency benefits both NVS and pose estimation tasks. We introduce Selfi, a self-improving 3D reconstruction pipeline via feature alignment, transforming a VGGT backbone into a high-fidelity 3D reconstruction engine by leveraging its own outputs as pseudo-ground-truth. Specifically, we train a lightweight feature adapter using a reprojection-based consistency loss, which distills VGGT outputs into a new geometrically-aligned feature space that captures spatial proximity in 3D. This enables state-of-the-art performance in both NVS and camera pose estimation, demonstrating that feature alignment is a highly beneficial step for downstream 3D reasoning.
Breaking Android with AI: A Deep Dive into LLM-Powered Exploitation
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:The rapid evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities in the area of cybersecurity, especially in the exploitation automation landscape and penetration testing. This study explores Android penetration testing automation using LLM-based tools, especially PentestGPT, to identify and execute rooting techniques. Through a comparison of the traditional manual rooting process and exploitation methods produced using AI, this study evaluates the efficacy, reliability, and scalability of automated penetration testing in achieving high-level privilege access on Android devices. With the use of an Android emulator (Genymotion) as the testbed, we fully execute both traditional and exploit-based rooting methods, automating the process using AI-generated scripts. Secondly, we create a web application by integrating OpenAI's API to facilitate automated script generation from LLM-processed responses. The research focuses on the effectiveness of AI-enabled exploitation by comparing automated and manual penetration testing protocols, by determining LLM weaknesses and strengths along the way. We also provide security suggestions of AI-enabled exploitation, including ethical factors and potential misuse. The findings exhibit that while LLMs can significantly streamline the workflow of exploitation, they need to be controlled by humans to ensure accuracy and ethical application. This study adds to the increasing body of literature on AI-powered cybersecurity and its effect on ethical hacking, security research, and mobile device security.
Visual Imitation Enables Contextual Humanoid Control
May 07, 2025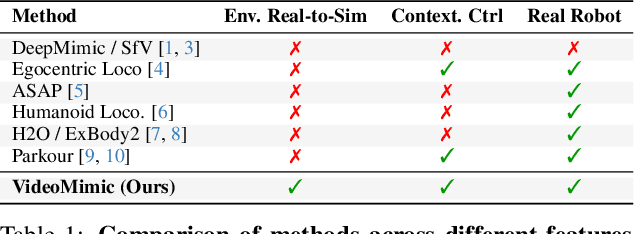
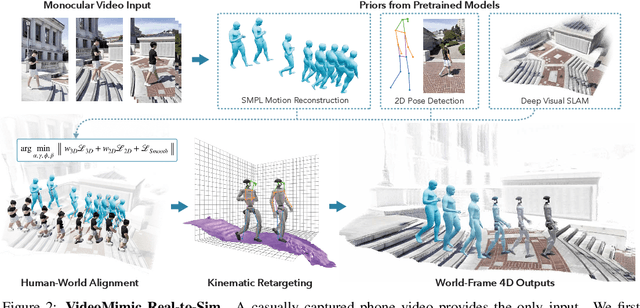

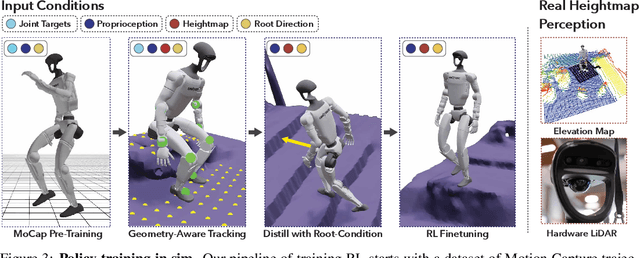
Abstract:How can we teach humanoids to climb staircases and sit on chairs using the surrounding environment context? Arguably, the simplest way is to just show them-casually capture a human motion video and feed it to humanoids. We introduce VIDEOMIMIC, a real-to-sim-to-real pipeline that mines everyday videos, jointly reconstructs the humans and the environment, and produces whole-body control policies for humanoid robots that perform the corresponding skills. We demonstrate the results of our pipeline on real humanoid robots, showing robust, repeatable contextual control such as staircase ascents and descents, sitting and standing from chairs and benches, as well as other dynamic whole-body skills-all from a single policy, conditioned on the environment and global root commands. VIDEOMIMIC offers a scalable path towards teaching humanoids to operate in diverse real-world environments.
St4RTrack: Simultaneous 4D Reconstruction and Tracking in the World
Apr 17, 2025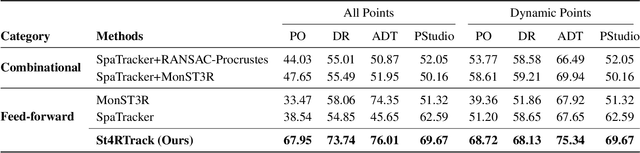
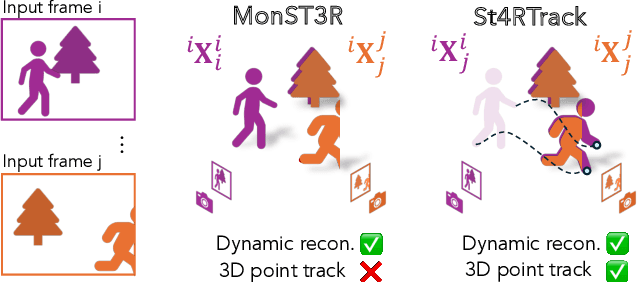
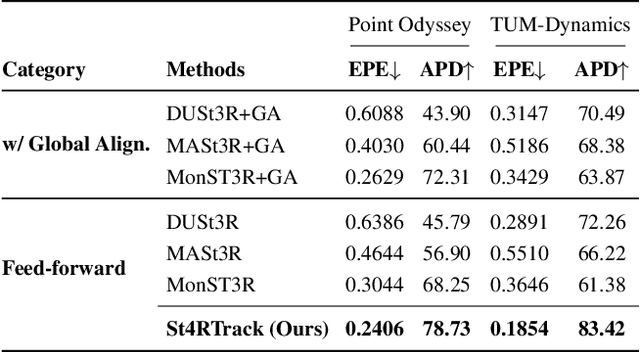
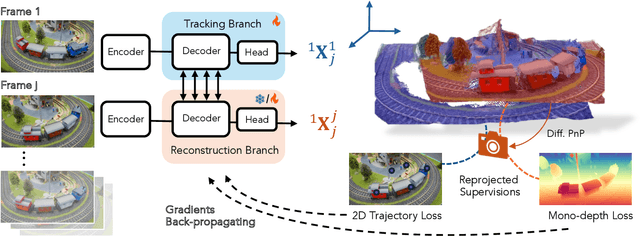
Abstract:Dynamic 3D reconstruction and point tracking in videos are typically treated as separate tasks, despite their deep connection. We propose St4RTrack, a feed-forward framework that simultaneously reconstructs and tracks dynamic video content in a world coordinate frame from RGB inputs. This is achieved by predicting two appropriately defined pointmaps for a pair of frames captured at different moments. Specifically, we predict both pointmaps at the same moment, in the same world, capturing both static and dynamic scene geometry while maintaining 3D correspondences. Chaining these predictions through the video sequence with respect to a reference frame naturally computes long-range correspondences, effectively combining 3D reconstruction with 3D tracking. Unlike prior methods that rely heavily on 4D ground truth supervision, we employ a novel adaptation scheme based on a reprojection loss. We establish a new extensive benchmark for world-frame reconstruction and tracking, demonstrating the effectiveness and efficiency of our unified, data-driven framework. Our code, model, and benchmark will be released.
Pre-training Auto-regressive Robotic Models with 4D Representations
Feb 18, 2025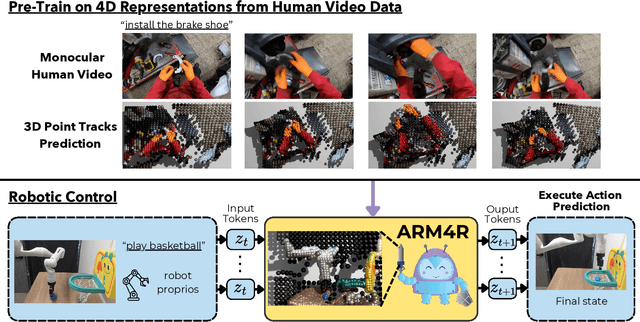
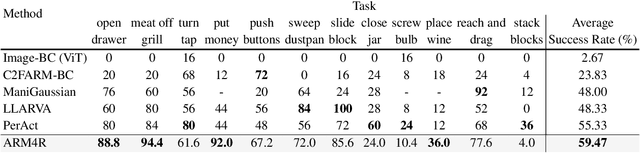
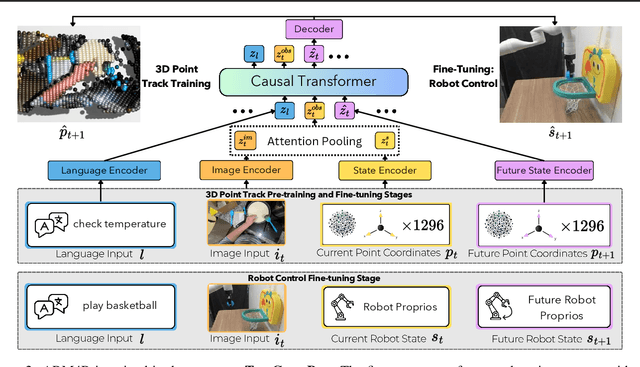
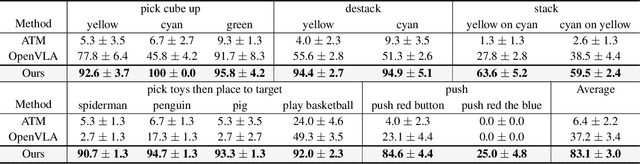
Abstract:Foundation models pre-trained on massive unlabeled datasets have revolutionized natural language and computer vision, exhibiting remarkable generalization capabilities, thus highlighting the importance of pre-training. Yet, efforts in robotics have struggled to achieve similar success, limited by either the need for costly robotic annotations or the lack of representations that effectively model the physical world. In this paper, we introduce ARM4R, an Auto-regressive Robotic Model that leverages low-level 4D Representations learned from human video data to yield a better pre-trained robotic model. Specifically, we focus on utilizing 3D point tracking representations from videos derived by lifting 2D representations into 3D space via monocular depth estimation across time. These 4D representations maintain a shared geometric structure between the points and robot state representations up to a linear transformation, enabling efficient transfer learning from human video data to low-level robotic control. Our experiments show that ARM4R can transfer efficiently from human video data to robotics and consistently improves performance on tasks across various robot environments and configurations.
How to Select Pre-Trained Code Models for Reuse? A Learning Perspective
Jan 07, 2025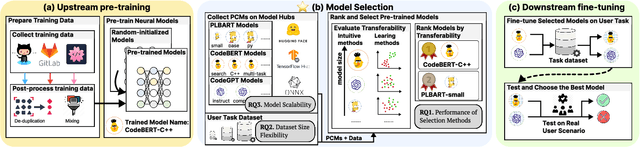
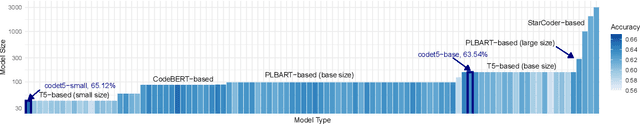
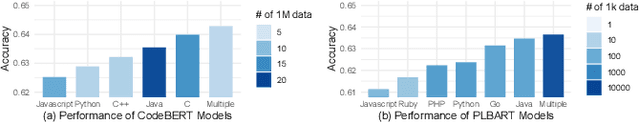
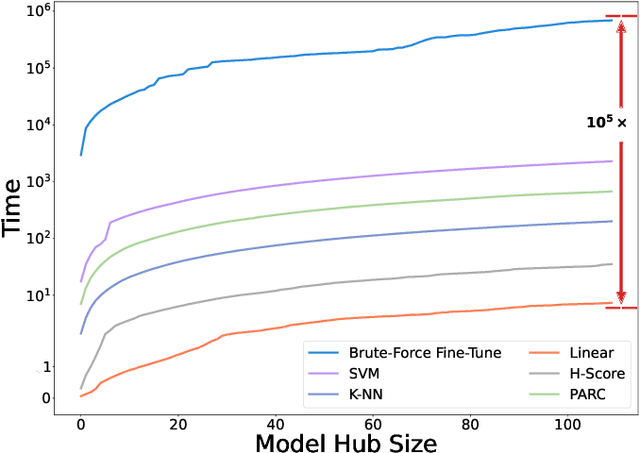
Abstract:Pre-training a language model and then fine-tuning it has shown to be an efficient and effective technique for a wide range of code intelligence tasks, such as code generation, code summarization, and vulnerability detection. However, pretraining language models on a large-scale code corpus is computationally expensive. Fortunately, many off-the-shelf Pre-trained Code Models (PCMs), such as CodeBERT, CodeT5, CodeGen, and Code Llama, have been released publicly. These models acquire general code understanding and generation capability during pretraining, which enhances their performance on downstream code intelligence tasks. With an increasing number of these public pre-trained models, selecting the most suitable one to reuse for a specific task is essential. In this paper, we systematically investigate the reusability of PCMs. We first explore three intuitive model selection methods that select by size, training data, or brute-force fine-tuning. Experimental results show that these straightforward techniques either perform poorly or suffer high costs. Motivated by these findings, we explore learning-based model selection strategies that utilize pre-trained models without altering their parameters. Specifically, we train proxy models to gauge the performance of pre-trained models, and measure the distribution deviation between a model's latent features and the task's labels, using their closeness as an indicator of model transferability. We conduct experiments on 100 widely-used opensource PCMs for code intelligence tasks, with sizes ranging from 42.5 million to 3 billion parameters. The results demonstrate that learning-based selection methods reduce selection time to 100 seconds, compared to 2,700 hours with brute-force fine-tuning, with less than 6% performance degradation across related tasks.
DenseMatcher: Learning 3D Semantic Correspondence for Category-Level Manipulation from a Single Demo
Dec 06, 2024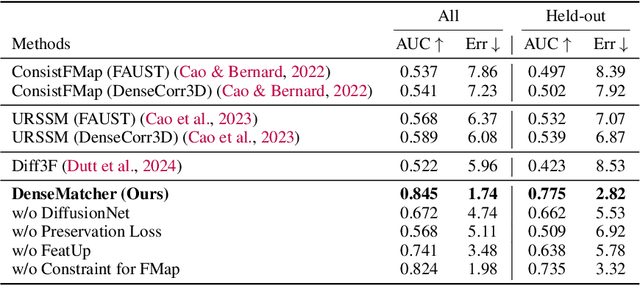

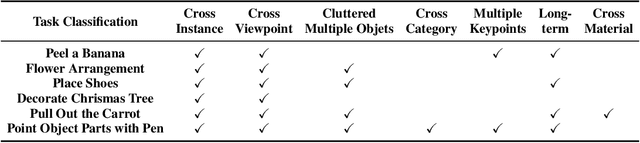

Abstract:Dense 3D correspondence can enhance robotic manipulation by enabling the generalization of spatial, functional, and dynamic information from one object to an unseen counterpart. Compared to shape correspondence, semantic correspondence is more effective in generalizing across different object categories. To this end, we present DenseMatcher, a method capable of computing 3D correspondences between in-the-wild objects that share similar structures. DenseMatcher first computes vertex features by projecting multiview 2D features onto meshes and refining them with a 3D network, and subsequently finds dense correspondences with the obtained features using functional map. In addition, we craft the first 3D matching dataset that contains colored object meshes across diverse categories. In our experiments, we show that DenseMatcher significantly outperforms prior 3D matching baselines by 43.5%. We demonstrate the downstream effectiveness of DenseMatcher in (i) robotic manipulation, where it achieves cross-instance and cross-category generalization on long-horizon complex manipulation tasks from observing only one demo; (ii) zero-shot color mapping between digital assets, where appearance can be transferred between different objects with relatable geometry.
SAN: Structure-Aware Network for Complex and Long-tailed Chinese Text Recognition
Nov 10, 2024Abstract:In text recognition, complex glyphs and tail classes have always been factors affecting model performance. Specifically for Chinese text recognition, the lack of shape-awareness can lead to confusion among close complex characters. Since such characters are often tail classes that appear less frequently in the training-set, making it harder for the model to capture its shape information. Hence in this work, we propose a structure-aware network utilizing the hierarchical composition information to improve the recognition performance of complex characters. Implementation-wise, we first propose an auxiliary radical branch and integrate it into the base recognition network as a regularization term, which distills hierarchical composition information into the feature extractor. A Tree-Similarity-based weighting mechanism is then proposed to further utilize the depth information in the hierarchical representation. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach can significantly improve the performances of complex characters and tail characters, yielding a better overall performance. Code is available at https://github.com/Levi-ZJY/SAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge