Haibo Liu
KeyframeFace: From Text to Expressive Facial Keyframes
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Generating dynamic 3D facial animation from natural language requires understanding both temporally structured semantics and fine-grained expression changes. Existing datasets and methods mainly focus on speech-driven animation or unstructured expression sequences and therefore lack the semantic grounding and temporal structures needed for expressive human performance generation. In this work, we introduce KeyframeFace, a large-scale multimodal dataset designed for text-to-animation research through keyframe-level supervision. KeyframeFace provides 2,100 expressive scripts paired with monocular videos, per-frame ARKit coefficients, contextual backgrounds, complex emotions, manually defined keyframes, and multi-perspective annotations based on ARKit coefficients and images via Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Beyond the dataset, we propose the first text-to-animation framework that explicitly leverages LLM priors for interpretable facial motion synthesis. This design aligns the semantic understanding capabilities of LLMs with the interpretable structure of ARKit's coefficients, enabling high-fidelity expressive animation. KeyframeFace and our LLM-based framework together establish a new foundation for interpretable, keyframe-guided, and context-aware text-to-animation. Code and data are available at https://github.com/wjc12345123/KeyframeFace.
Implicit Neural Shape Optimization for 3D High-Contrast Electrical Impedance Tomography
May 22, 2025



Abstract:We present a novel implicit neural shape optimization framework for 3D high-contrast Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT), addressing scenarios where conductivity exhibits sharp discontinuities across material interfaces. These high-contrast cases, prevalent in metallic implant monitoring and industrial defect detection, challenge traditional reconstruction methods due to severe ill-posedness. Our approach synergizes shape optimization with implicit neural representations, introducing key innovations including a shape derivative-based optimization scheme that explicitly incorporates high-contrast interface conditions and an efficient latent space representation that reduces variable dimensionality. Through rigorous theoretical analysis of algorithm convergence and extensive numerical experiments, we demonstrate substantial performance improvements, establishing our framework as promising for practical applications in medical imaging with metallic implants and industrial non-destructive testing.
PPLLaVA: Varied Video Sequence Understanding With Prompt Guidance
Nov 05, 2024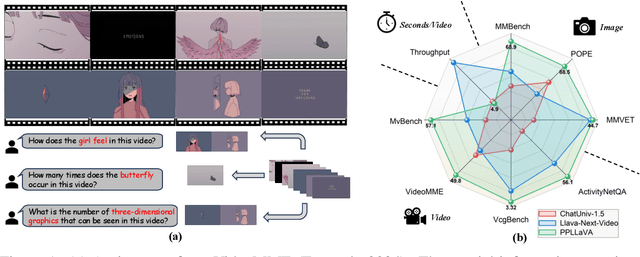
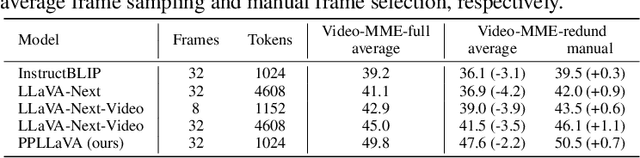
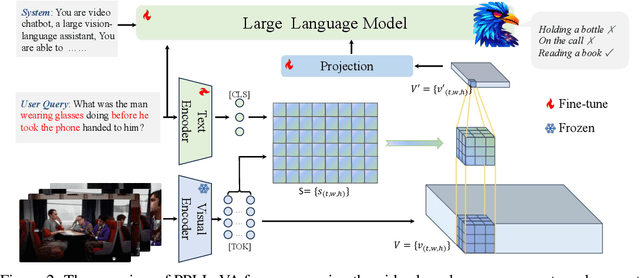
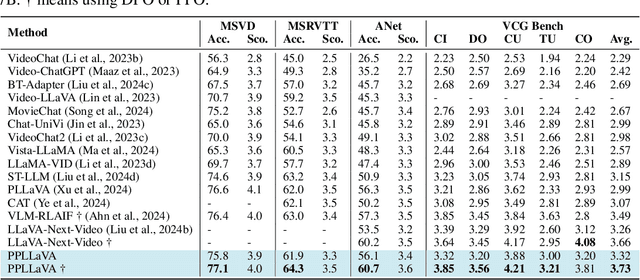
Abstract:The past year has witnessed the significant advancement of video-based large language models. However, the challenge of developing a unified model for both short and long video understanding remains unresolved. Most existing video LLMs cannot handle hour-long videos, while methods custom for long videos tend to be ineffective for shorter videos and images. In this paper, we identify the key issue as the redundant content in videos. To address this, we propose a novel pooling strategy that simultaneously achieves token compression and instruction-aware visual feature aggregation. Our model is termed Prompt-guided Pooling LLaVA, or PPLLaVA for short. Specifically, PPLLaVA consists of three core components: the CLIP-based visual-prompt alignment that extracts visual information relevant to the user's instructions, the prompt-guided pooling that compresses the visual sequence to arbitrary scales using convolution-style pooling, and the clip context extension designed for lengthy prompt common in visual dialogue. Moreover, our codebase also integrates the most advanced video Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and visual interleave training. Extensive experiments have validated the performance of our model. With superior throughput and only 1024 visual context, PPLLaVA achieves better results on image benchmarks as a video LLM, while achieving state-of-the-art performance across various video benchmarks, excelling in tasks ranging from caption generation to multiple-choice questions, and handling video lengths from seconds to hours. Codes have been available at https://github.com/farewellthree/PPLLaVA.
BER Analysis of SCMA-OFDM Systems in the Presence of Carrier Frequency Offset
Dec 02, 2023



Abstract:Sparse code multiple access (SCMA) building upon orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is a promising wireless technology for supporting massive connectivity in future machine-type communication networks. However, the sensitivity of OFDM to carrier frequency offset (CFO) poses a major challenge because it leads to orthogonality loss and incurs intercarrier interference (ICI). In this paper, we investigate the bit error rate (BER) performance of SCMA-OFDM systems in the presence of CFO over both Gaussian and multipath Rayleigh fading channels. We first model the ICI in SCMA-OFDM as Gaussian variables conditioned on a single channel realization for fading channels. The BER is then evaluated by averaging over all codeword pairs considering the fading statistics. Through simulations, we validate the accuracy of our BER analysis and reveal that there is a significant BER degradation for SCMA-OFDM systems when the normalized CFO exceeds 0.02.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge