Changwei Xu
Understanding Attention for Vision-and-Language Tasks
Aug 17, 2022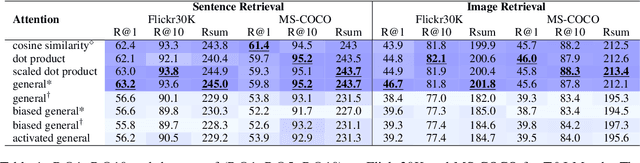
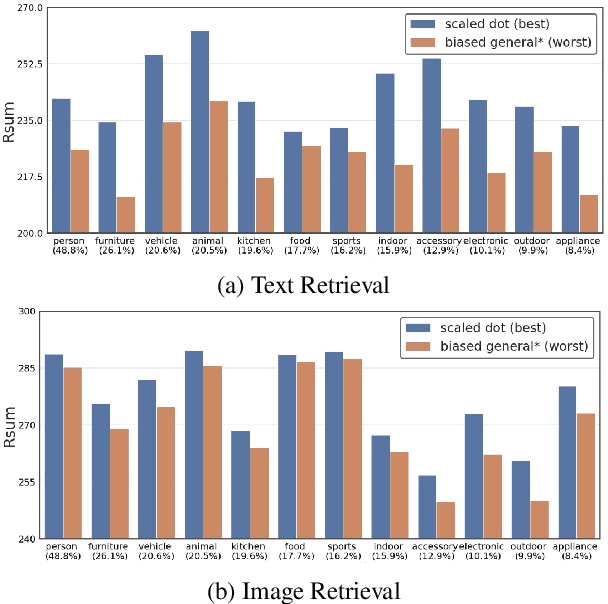
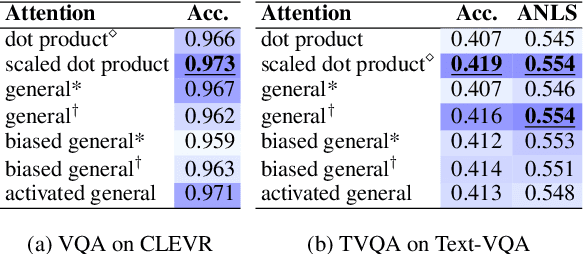
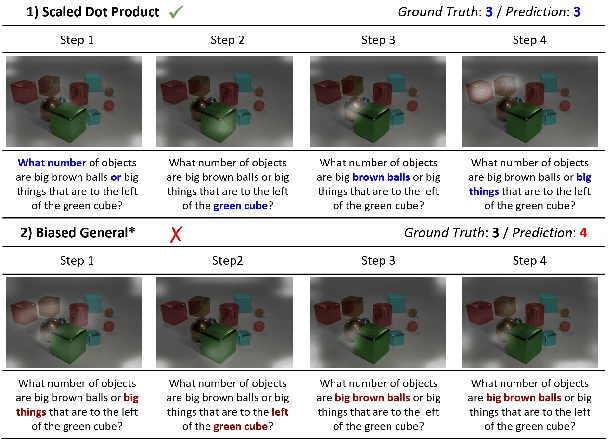
Abstract:Attention mechanism has been used as an important component across Vision-and-Language(VL) tasks in order to bridge the semantic gap between visual and textual features. While attention has been widely used in VL tasks, it has not been examined the capability of different attention alignment calculation in bridging the semantic gap between visual and textual clues. In this research, we conduct a comprehensive analysis on understanding the role of attention alignment by looking into the attention score calculation methods and check how it actually represents the visual region's and textual token's significance for the global assessment. We also analyse the conditions which attention score calculation mechanism would be more (or less) interpretable, and which may impact the model performance on three different VL tasks, including visual question answering, text-to-image generation, text-and-image matching (both sentence and image retrieval). Our analysis is the first of its kind and provides useful insights of the importance of each attention alignment score calculation when applied at the training phase of VL tasks, commonly ignored in attention-based cross modal models, and/or pretrained models.
Shuffle Augmentation of Features from Unlabeled Data for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Jan 28, 2022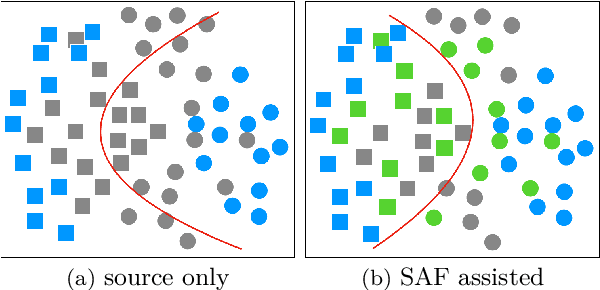



Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA), a branch of transfer learning where labels for target samples are unavailable, has been widely researched and developed in recent years with the help of adversarially trained models. Although existing UDA algorithms are able to guide neural networks to extract transferable and discriminative features, classifiers are merely trained under the supervision of labeled source data. Given the inevitable discrepancy between source and target domains, the classifiers can hardly be aware of the target classification boundaries. In this paper, Shuffle Augmentation of Features (SAF), a novel UDA framework, is proposed to address the problem by providing the classifier with supervisory signals from target feature representations. SAF learns from the target samples, adaptively distills class-aware target features, and implicitly guides the classifier to find comprehensive class borders. Demonstrated by extensive experiments, the SAF module can be integrated into any existing adversarial UDA models to achieve performance improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge