Siqu Long
Interpretable deep learning in single-cell omics
Jan 11, 2024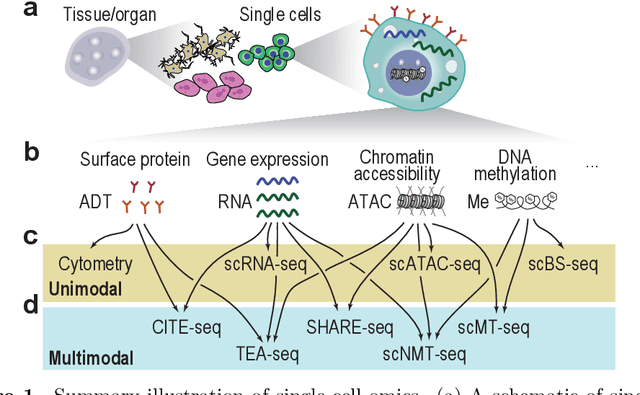
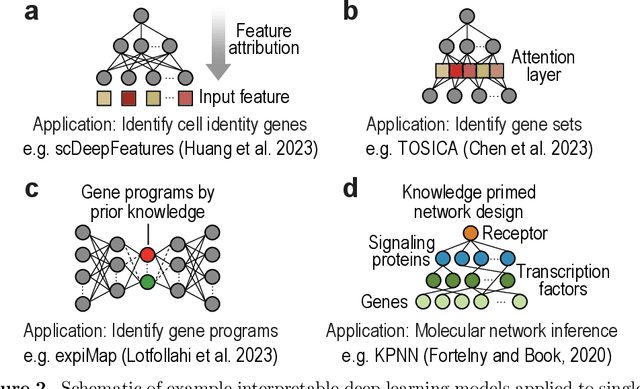
Abstract:Recent developments in single-cell omics technologies have enabled the quantification of molecular profiles in individual cells at an unparalleled resolution. Deep learning, a rapidly evolving sub-field of machine learning, has instilled a significant interest in single-cell omics research due to its remarkable success in analysing heterogeneous high-dimensional single-cell omics data. Nevertheless, the inherent multi-layer nonlinear architecture of deep learning models often makes them `black boxes' as the reasoning behind predictions is often unknown and not transparent to the user. This has stimulated an increasing body of research for addressing the lack of interpretability in deep learning models, especially in single-cell omics data analyses, where the identification and understanding of molecular regulators are crucial for interpreting model predictions and directing downstream experimental validations. In this work, we introduce the basics of single-cell omics technologies and the concept of interpretable deep learning. This is followed by a review of the recent interpretable deep learning models applied to various single-cell omics research. Lastly, we highlight the current limitations and discuss potential future directions. We anticipate this review to bring together the single-cell and machine learning research communities to foster future development and application of interpretable deep learning in single-cell omics research.
MC-DRE: Multi-Aspect Cross Integration for Drug Event/Entity Extraction
Aug 15, 2023Abstract:Extracting meaningful drug-related information chunks, such as adverse drug events (ADE), is crucial for preventing morbidity and saving many lives. Most ADEs are reported via an unstructured conversation with the medical context, so applying a general entity recognition approach is not sufficient enough. In this paper, we propose a new multi-aspect cross-integration framework for drug entity/event detection by capturing and aligning different context/language/knowledge properties from drug-related documents. We first construct multi-aspect encoders to describe semantic, syntactic, and medical document contextual information by conducting those slot tagging tasks, main drug entity/event detection, part-of-speech tagging, and general medical named entity recognition. Then, each encoder conducts cross-integration with other contextual information in three ways: the key-value cross, attention cross, and feedforward cross, so the multi-encoders are integrated in depth. Our model outperforms all SOTA on two widely used tasks, flat entity detection and discontinuous event extraction.
Tri-level Joint Natural Language Understanding for Multi-turn Conversational Datasets
May 28, 2023Abstract:Natural language understanding typically maps single utterances to a dual level semantic frame, sentence level intent and slot labels at the word level. The best performing models force explicit interaction between intent detection and slot filling. We present a novel tri-level joint natural language understanding approach, adding domain, and explicitly exchange semantic information between all levels. This approach enables the use of multi-turn datasets which are a more natural conversational environment than single utterance. We evaluate our model on two multi-turn datasets for which we are the first to conduct joint slot-filling and intent detection. Our model outperforms state-of-the-art joint models in slot filling and intent detection on multi-turn data sets. We provide an analysis of explicit interaction locations between the layers. We conclude that including domain information improves model performance.
Form-NLU: Dataset for the Form Language Understanding
Apr 05, 2023Abstract:Compared to general document analysis tasks, form document structure understanding and retrieval are challenging. Form documents are typically made by two types of authors; A form designer, who develops the form structure and keys, and a form user, who fills out form values based on the provided keys. Hence, the form values may not be aligned with the form designer's intention (structure and keys) if a form user gets confused. In this paper, we introduce Form-NLU, the first novel dataset for form structure understanding and its key and value information extraction, interpreting the form designer's intent and the alignment of user-written value on it. It consists of 857 form images, 6k form keys and values, and 4k table keys and values. Our dataset also includes three form types: digital, printed, and handwritten, which cover diverse form appearances and layouts. We propose a robust positional and logical relation-based form key-value information extraction framework. Using this dataset, Form-NLU, we first examine strong object detection models for the form layout understanding, then evaluate the key information extraction task on the dataset, providing fine-grained results for different types of forms and keys. Furthermore, we examine it with the off-the-shelf pdf layout extraction tool and prove its feasibility in real-world cases.
Spoken Language Understanding for Conversational AI: Recent Advances and Future Direction
Dec 21, 2022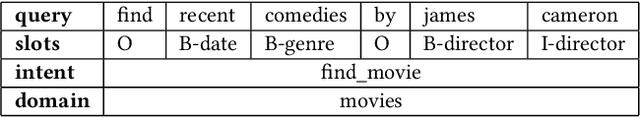
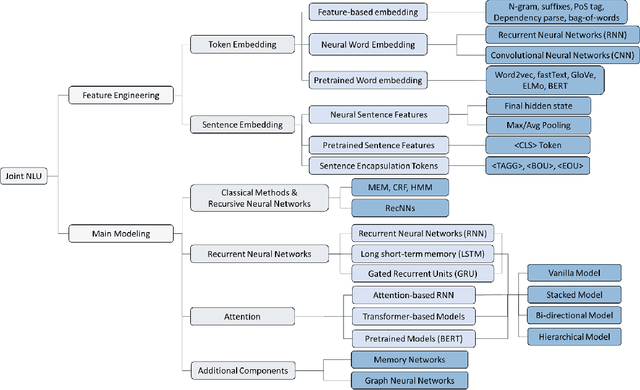
Abstract:When a human communicates with a machine using natural language on the web and online, how can it understand the human's intention and semantic context of their talk? This is an important AI task as it enables the machine to construct a sensible answer or perform a useful action for the human. Meaning is represented at the sentence level, identification of which is known as intent detection, and at the word level, a labelling task called slot filling. This dual-level joint task requires innovative thinking about natural language and deep learning network design, and as a result, many approaches and models have been proposed and applied. This tutorial will discuss how the joint task is set up and introduce Spoken Language Understanding/Natural Language Understanding (SLU/NLU) with Deep Learning techniques. We will cover the datasets, experiments and metrics used in the field. We will describe how the machine uses the latest NLP and Deep Learning techniques to address the joint task, including recurrent and attention-based Transformer networks and pre-trained models (e.g. BERT). We will then look in detail at a network that allows the two levels of the task, intent classification and slot filling, to interact to boost performance explicitly. We will do a code demonstration of a Python notebook for this model and attendees will have an opportunity to watch coding demo tasks on this joint NLU to further their understanding.
PiggyBack: Pretrained Visual Question Answering Environment for Backing up Non-deep Learning Professionals
Dec 01, 2022


Abstract:We propose a PiggyBack, a Visual Question Answering platform that allows users to apply the state-of-the-art visual-language pretrained models easily. The PiggyBack supports the full stack of visual question answering tasks, specifically data processing, model fine-tuning, and result visualisation. We integrate visual-language models, pretrained by HuggingFace, an open-source API platform of deep learning technologies; however, it cannot be runnable without programming skills or deep learning understanding. Hence, our PiggyBack supports an easy-to-use browser-based user interface with several deep learning visual language pretrained models for general users and domain experts. The PiggyBack includes the following benefits: Free availability under the MIT License, Portability due to web-based and thus runs on almost any platform, A comprehensive data creation and processing technique, and ease of use on deep learning-based visual language pretrained models. The demo video is available on YouTube and can be found at https://youtu.be/iz44RZ1lF4s.
SUPER-Rec: SUrrounding Position-Enhanced Representation for Recommendation
Sep 09, 2022



Abstract:Collaborative filtering problems are commonly solved based on matrix completion techniques which recover the missing values of user-item interaction matrices. In a matrix, the rating position specifically represents the user given and the item rated. Previous matrix completion techniques tend to neglect the position of each element (user, item and ratings) in the matrix but mainly focus on semantic similarity between users and items to predict the missing value in a matrix. This paper proposes a novel position-enhanced user/item representation training model for recommendation, SUPER-Rec. We first capture the rating position in the matrix using the relative positional rating encoding and store the position-enhanced rating information and its user-item relationship to the fixed dimension of embedding that is not affected by the matrix size. Then, we apply the trained position-enhanced user and item representations to the simplest traditional machine learning models to highlight the pure novelty of our representation learning model. We contribute the first formal introduction and quantitative analysis of position-enhanced item representation in the recommendation domain and produce a principled discussion about our SUPER-Rec to the outperformed performance of typical collaborative filtering recommendation tasks with both explicit and implicit feedback.
Doc-GCN: Heterogeneous Graph Convolutional Networks for Document Layout Analysis
Aug 22, 2022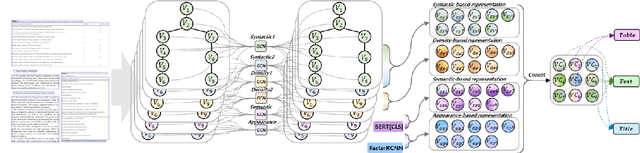
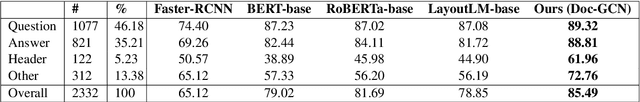
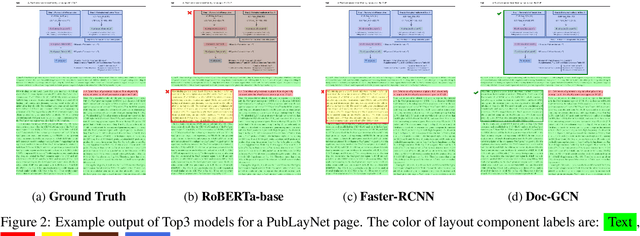
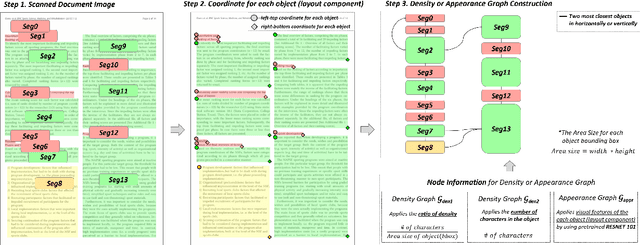
Abstract:Recognizing the layout of unstructured digital documents is crucial when parsing the documents into the structured, machine-readable format for downstream applications. Recent studies in Document Layout Analysis usually rely on computer vision models to understand documents while ignoring other information, such as context information or relation of document components, which are vital to capture. Our Doc-GCN presents an effective way to harmonize and integrate heterogeneous aspects for Document Layout Analysis. We first construct graphs to explicitly describe four main aspects, including syntactic, semantic, density, and appearance/visual information. Then, we apply graph convolutional networks for representing each aspect of information and use pooling to integrate them. Finally, we aggregate each aspect and feed them into 2-layer MLPs for document layout component classification. Our Doc-GCN achieves new state-of-the-art results in three widely used DLA datasets.
Understanding Attention for Vision-and-Language Tasks
Aug 17, 2022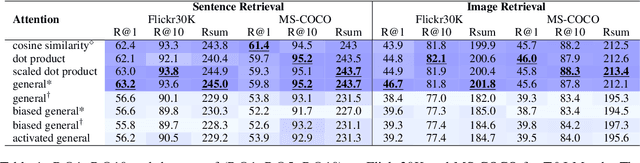
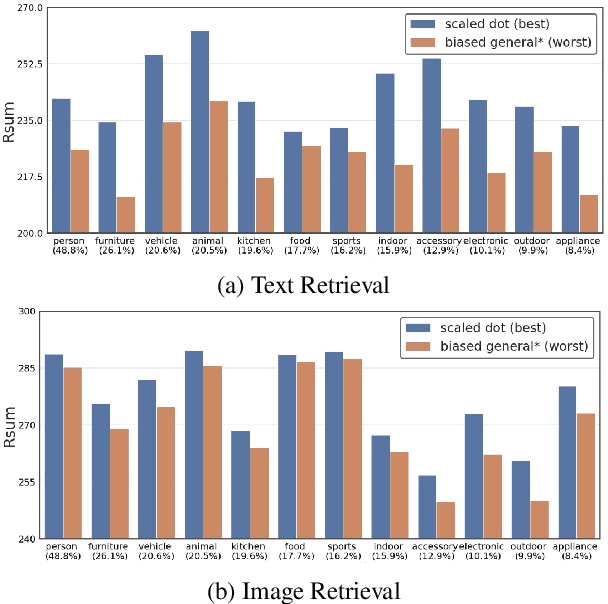
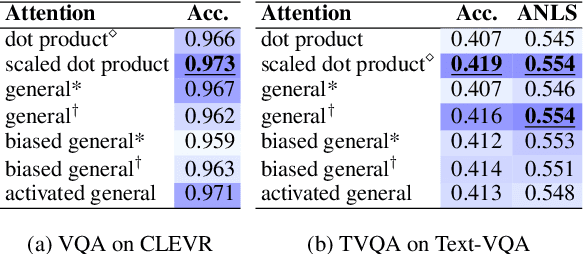
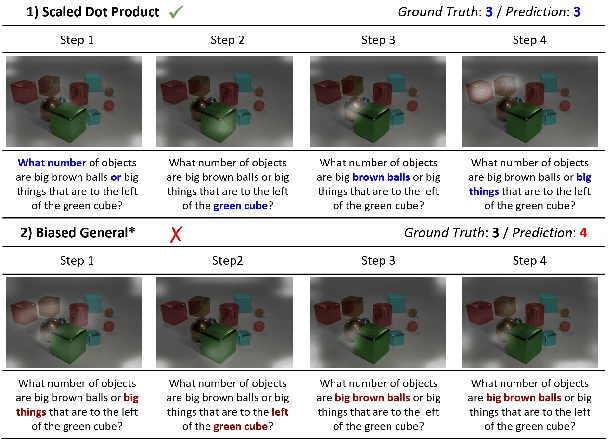
Abstract:Attention mechanism has been used as an important component across Vision-and-Language(VL) tasks in order to bridge the semantic gap between visual and textual features. While attention has been widely used in VL tasks, it has not been examined the capability of different attention alignment calculation in bridging the semantic gap between visual and textual clues. In this research, we conduct a comprehensive analysis on understanding the role of attention alignment by looking into the attention score calculation methods and check how it actually represents the visual region's and textual token's significance for the global assessment. We also analyse the conditions which attention score calculation mechanism would be more (or less) interpretable, and which may impact the model performance on three different VL tasks, including visual question answering, text-to-image generation, text-and-image matching (both sentence and image retrieval). Our analysis is the first of its kind and provides useful insights of the importance of each attention alignment score calculation when applied at the training phase of VL tasks, commonly ignored in attention-based cross modal models, and/or pretrained models.
A Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Suicide Ideation Detection using Deep Learning
Jun 17, 2022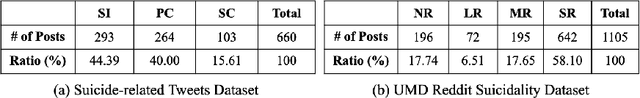
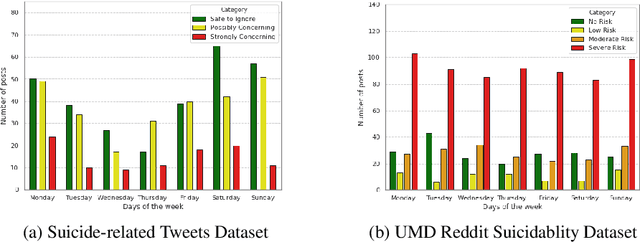
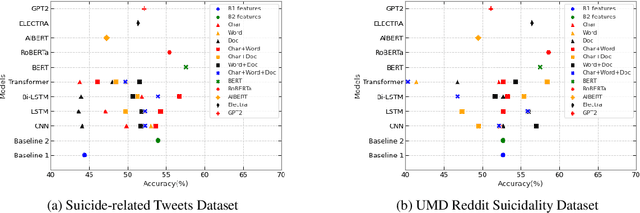
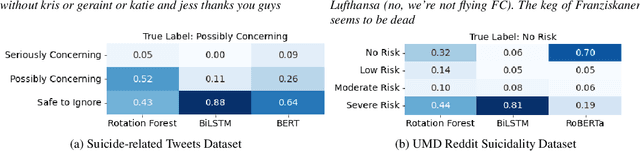
Abstract:For preventing youth suicide, social media platforms have received much attention from researchers. A few researches apply machine learning, or deep learning-based text classification approaches to classify social media posts containing suicidality risk. This paper replicated competitive social media-based suicidality detection/prediction models. We evaluated the feasibility of detecting suicidal ideation using multiple datasets and different state-of-the-art deep learning models, RNN-, CNN-, and Attention-based models. Using two suicidality evaluation datasets, we evaluated 28 combinations of 7 input embeddings with 4 commonly used deep learning models and 5 pretrained language models in quantitative and qualitative ways. Our replication study confirms that deep learning works well for social media-based suicidality detection in general, but it highly depends on the dataset's quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge