Taejun Lim
SUPER-Rec: SUrrounding Position-Enhanced Representation for Recommendation
Sep 09, 2022



Abstract:Collaborative filtering problems are commonly solved based on matrix completion techniques which recover the missing values of user-item interaction matrices. In a matrix, the rating position specifically represents the user given and the item rated. Previous matrix completion techniques tend to neglect the position of each element (user, item and ratings) in the matrix but mainly focus on semantic similarity between users and items to predict the missing value in a matrix. This paper proposes a novel position-enhanced user/item representation training model for recommendation, SUPER-Rec. We first capture the rating position in the matrix using the relative positional rating encoding and store the position-enhanced rating information and its user-item relationship to the fixed dimension of embedding that is not affected by the matrix size. Then, we apply the trained position-enhanced user and item representations to the simplest traditional machine learning models to highlight the pure novelty of our representation learning model. We contribute the first formal introduction and quantitative analysis of position-enhanced item representation in the recommendation domain and produce a principled discussion about our SUPER-Rec to the outperformed performance of typical collaborative filtering recommendation tasks with both explicit and implicit feedback.
K-MHaS: A Multi-label Hate Speech Detection Dataset in Korean Online News Comment
Aug 28, 2022

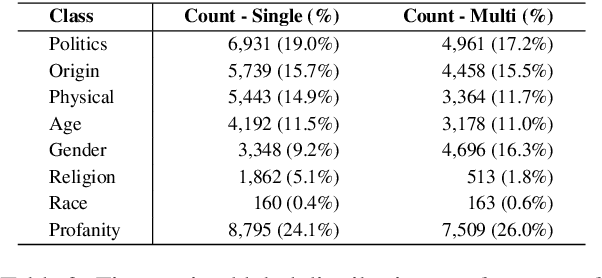

Abstract:Online Hate speech detection has become important with the growth of digital devices, but resources in languages other than English are extremely limited. We introduce K-MHaS, a new multi-label dataset for hate speech detection that effectively handles Korean language patterns. The dataset consists of 109k utterances from news comments and provides multi-label classification from 1 to 4 labels, and handling subjectivity and intersectionality. We evaluate strong baselines on K-MHaS. KR-BERT with sub-character tokenizer outperforms, recognising decomposed characters in each hate speech class.
GLocal-K: Global and Local Kernels for Recommender Systems
Aug 27, 2021



Abstract:Recommender systems typically operate on high-dimensional sparse user-item matrices. Matrix completion is a very challenging task to predict one's interest based on millions of other users having each seen a small subset of thousands of items. We propose a Global-Local Kernel-based matrix completion framework, named GLocal-K, that aims to generalise and represent a high-dimensional sparse user-item matrix entry into a low dimensional space with a small number of important features. Our GLocal-K can be divided into two major stages. First, we pre-train an auto encoder with the local kernelised weight matrix, which transforms the data from one space into the feature space by using a 2d-RBF kernel. Then, the pre-trained auto encoder is fine-tuned with the rating matrix, produced by a convolution-based global kernel, which captures the characteristics of each item. We apply our GLocal-K model under the extreme low-resource setting, which includes only a user-item rating matrix, with no side information. Our model outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines on three collaborative filtering benchmarks: ML-100K, ML-1M, and Douban.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge