Goran Nenadic
HealthcareNLP: where are we and what is next?
Dec 09, 2025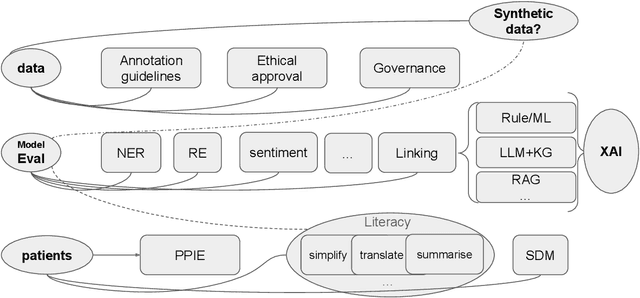
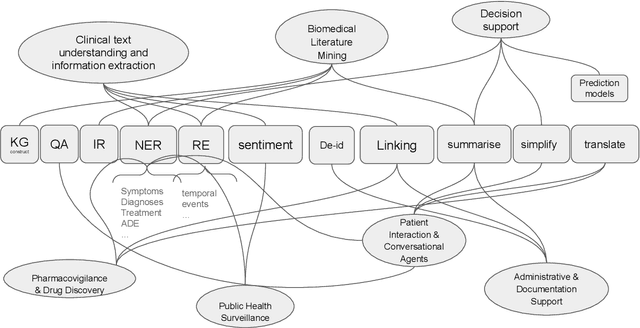
Abstract:This proposed tutorial focuses on Healthcare Domain Applications of NLP, what we have achieved around HealthcareNLP, and the challenges that lie ahead for the future. Existing reviews in this domain either overlook some important tasks, such as synthetic data generation for addressing privacy concerns, or explainable clinical NLP for improved integration and implementation, or fail to mention important methodologies, including retrieval augmented generation and the neural symbolic integration of LLMs and KGs. In light of this, the goal of this tutorial is to provide an introductory overview of the most important sub-areas of a patient- and resource-oriented HealthcareNLP, with three layers of hierarchy: data/resource layer: annotation guidelines, ethical approvals, governance, synthetic data; NLP-Eval layer: NLP tasks such as NER, RE, sentiment analysis, and linking/coding with categorised methods, leading to explainable HealthAI; patients layer: Patient Public Involvement and Engagement (PPIE), health literacy, translation, simplification, and summarisation (also NLP tasks), and shared decision-making support. A hands-on session will be included in the tutorial for the audience to use HealthcareNLP applications. The target audience includes NLP practitioners in the healthcare application domain, NLP researchers who are interested in domain applications, healthcare researchers, and students from NLP fields. The type of tutorial is "Introductory to CL/NLP topics (HealthcareNLP)" and the audience does not need prior knowledge to attend this. Tutorial materials: https://github.com/4dpicture/HealthNLP
SynBench: A Benchmark for Differentially Private Text Generation
Sep 18, 2025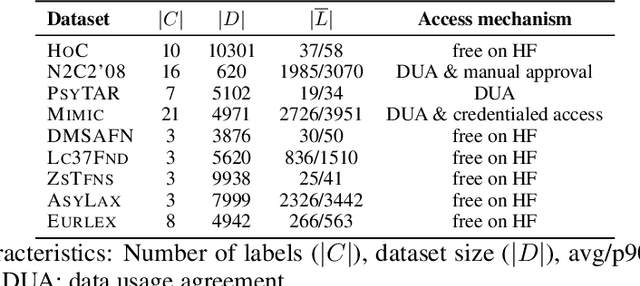
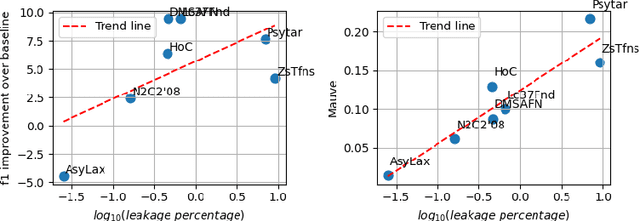
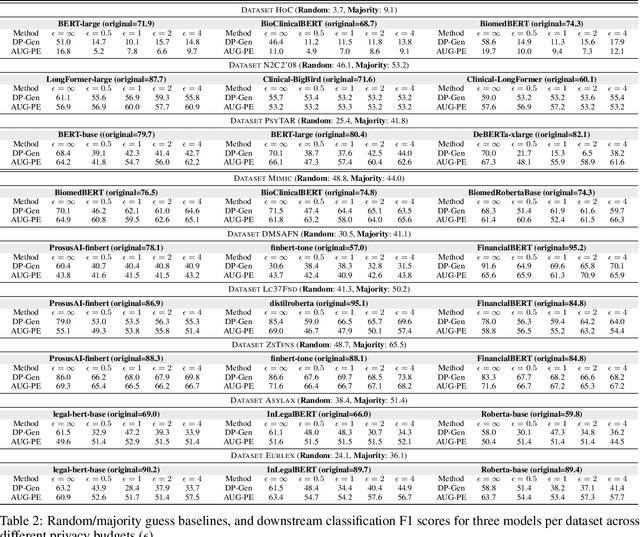
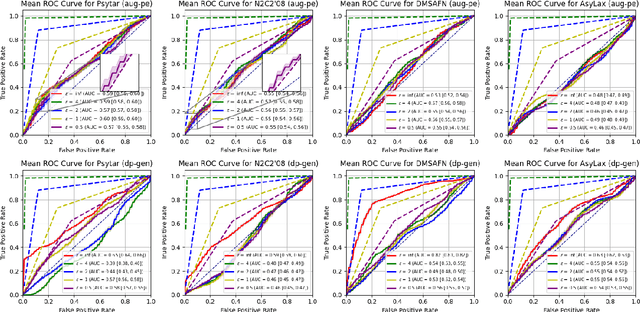
Abstract:Data-driven decision support in high-stakes domains like healthcare and finance faces significant barriers to data sharing due to regulatory, institutional, and privacy concerns. While recent generative AI models, such as large language models, have shown impressive performance in open-domain tasks, their adoption in sensitive environments remains limited by unpredictable behaviors and insufficient privacy-preserving datasets for benchmarking. Existing anonymization methods are often inadequate, especially for unstructured text, as redaction and masking can still allow re-identification. Differential Privacy (DP) offers a principled alternative, enabling the generation of synthetic data with formal privacy assurances. In this work, we address these challenges through three key contributions. First, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation framework with standardized utility and fidelity metrics, encompassing nine curated datasets that capture domain-specific complexities such as technical jargon, long-context dependencies, and specialized document structures. Second, we conduct a large-scale empirical study benchmarking state-of-the-art DP text generation methods and LLMs of varying sizes and different fine-tuning strategies, revealing that high-quality domain-specific synthetic data generation under DP constraints remains an unsolved challenge, with performance degrading as domain complexity increases. Third, we develop a membership inference attack (MIA) methodology tailored for synthetic text, providing first empirical evidence that the use of public datasets - potentially present in pre-training corpora - can invalidate claimed privacy guarantees. Our findings underscore the urgent need for rigorous privacy auditing and highlight persistent gaps between open-domain and specialist evaluations, informing responsible deployment of generative AI in privacy-sensitive, high-stakes settings.
Will Large Language Models Transform Clinical Prediction?
May 23, 2025Abstract:Background: Large language models (LLMs) are attracting increasing interest in healthcare. Their ability to summarise large datasets effectively, answer questions accurately, and generate synthesised text is widely recognised. These capabilities are already finding applications in healthcare. Body: This commentary discusses LLMs usage in the clinical prediction context and highlight potential benefits and existing challenges. In these early stages, the focus should be on extending the methodology, specifically on validation, fairness and bias evaluation, survival analysis and development of regulations. Conclusion: We conclude that further work and domain-specific considerations need to be made for full integration into the clinical prediction workflows.
BRIDGE: Bootstrapping Text to Control Time-Series Generation via Multi-Agent Iterative Optimization and Diffusion Modelling
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Time-series Generation (TSG) is a prominent research area with broad applications in simulations, data augmentation, and counterfactual analysis. While existing methods have shown promise in unconditional single-domain TSG, real-world applications demand for cross-domain approaches capable of controlled generation tailored to domain-specific constraints and instance-level requirements. In this paper, we argue that text can provide semantic insights, domain information and instance-specific temporal patterns, to guide and improve TSG. We introduce ``Text-Controlled TSG'', a task focused on generating realistic time series by incorporating textual descriptions. To address data scarcity in this setting, we propose a novel LLM-based Multi-Agent framework that synthesizes diverse, realistic text-to-TS datasets. Furthermore, we introduce BRIDGE, a hybrid text-controlled TSG framework that integrates semantic prototypes with text description for supporting domain-level guidance. This approach achieves state-of-the-art generation fidelity on 11 of 12 datasets, and improves controllability by 12.52% on MSE and 6.34% MAE compared to no text input generation, highlighting its potential for generating tailored time-series data.
BeeManc at the PLABA Track of TAC-2024: RoBERTa for task 1 and LLaMA3.1 and GPT-4o for task 2
Nov 11, 2024


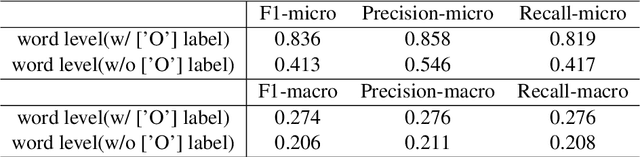
Abstract:This report is the system description of the BeeManc team for shared task Plain Language Adaptation of Biomedical Abstracts (PLABA) 2024. This report contains two sections corresponding to the two sub-tasks in PLABA 2024. In task one, we applied fine-tuned ReBERTa-Base models to identify and classify the difficult terms, jargon and acronyms in the biomedical abstracts and reported the F1 score. Due to time constraints, we didn't finish the replacement task. In task two, we leveraged Llamma3.1-70B-Instruct and GPT-4o with the one-shot prompts to complete the abstract adaptation and reported the scores in BLEU, SARI, BERTScore, LENS, and SALSA. From the official Evaluation from PLABA-2024 on Task 1A and 1B, our \textbf{much smaller fine-tuned RoBERTa-Base} model ranked 3rd and 2nd respectively on the two sub-task, and the \textbf{1st on averaged F1 scores across the two tasks} from 9 evaluated systems. Our share our fine-tuned models and related resources at \url{https://github.com/HECTA-UoM/PLABA2024}
TriG-NER: Triplet-Grid Framework for Discontinuous Named Entity Recognition
Nov 04, 2024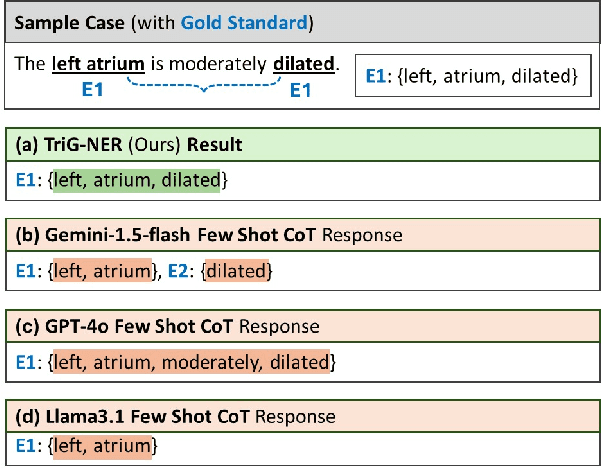
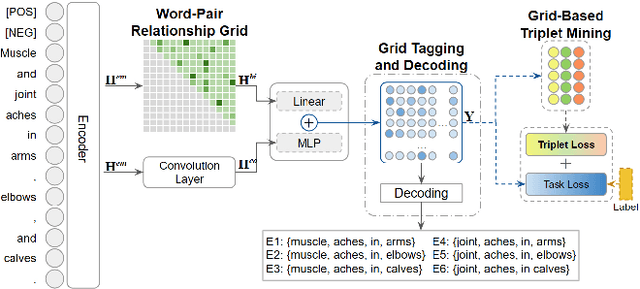
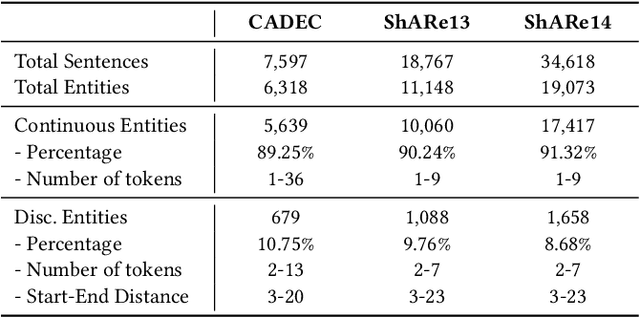
Abstract:Discontinuous Named Entity Recognition (DNER) presents a challenging problem where entities may be scattered across multiple non-adjacent tokens, making traditional sequence labelling approaches inadequate. Existing methods predominantly rely on custom tagging schemes to handle these discontinuous entities, resulting in models tightly coupled to specific tagging strategies and lacking generalisability across diverse datasets. To address these challenges, we propose TriG-NER, a novel Triplet-Grid Framework that introduces a generalisable approach to learning robust token-level representations for discontinuous entity extraction. Our framework applies triplet loss at the token level, where similarity is defined by word pairs existing within the same entity, effectively pulling together similar and pushing apart dissimilar ones. This approach enhances entity boundary detection and reduces the dependency on specific tagging schemes by focusing on word-pair relationships within a flexible grid structure. We evaluate TriG-NER on three benchmark DNER datasets and demonstrate significant improvements over existing grid-based architectures. These results underscore our framework's effectiveness in capturing complex entity structures and its adaptability to various tagging schemes, setting a new benchmark for discontinuous entity extraction.
CAST: Corpus-Aware Self-similarity Enhanced Topic modelling
Oct 19, 2024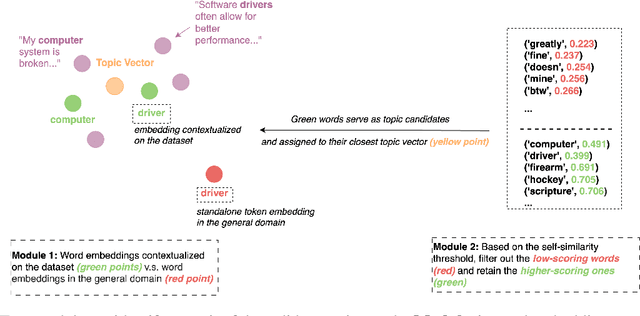
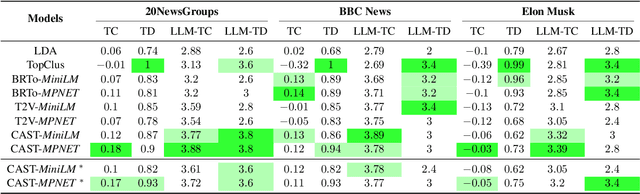
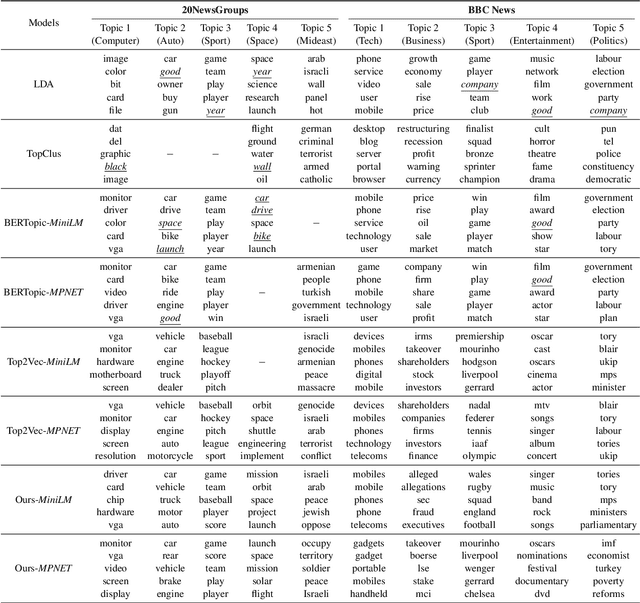
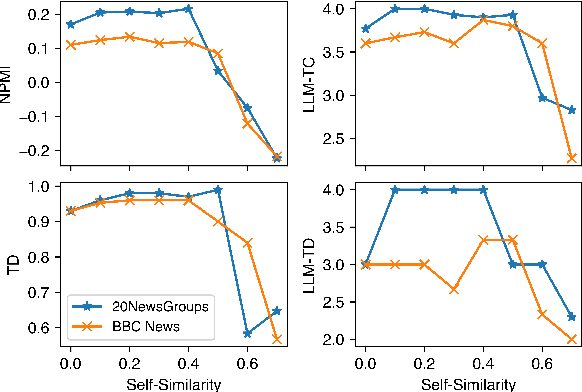
Abstract:Topic modelling is a pivotal unsupervised machine learning technique for extracting valuable insights from large document collections. Existing neural topic modelling methods often encode contextual information of documents, while ignoring contextual details of candidate centroid words, leading to the inaccurate selection of topic words due to the contextualization gap. In parallel, it is found that functional words are frequently selected over topical words. To address these limitations, we introduce CAST: Corpus-Aware Self-similarity Enhanced Topic modelling, a novel topic modelling method that builds upon candidate centroid word embeddings contextualized on the dataset, and a novel self-similarity-based method to filter out less meaningful tokens. Inspired by findings in contrastive learning that self-similarities of functional token embeddings in different contexts are much lower than topical tokens, we find self-similarity to be an effective metric to prevent functional words from acting as candidate topic words. Our approach significantly enhances the coherence and diversity of generated topics, as well as the topic model's ability to handle noisy data. Experiments on news benchmark datasets and one Twitter dataset demonstrate the method's superiority in generating coherent, diverse topics, and handling noisy data, outperforming strong baselines.
DeIDClinic: A Multi-Layered Framework for De-identification of Clinical Free-text Data
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:De-identification is important in protecting patients' privacy for healthcare text analytics. The MASK framework is one of the best on the de-identification shared task organised by n2c2/i2b2 challenges. This work enhances the MASK framework by integrating ClinicalBERT, a deep learning model specifically fine-tuned on clinical texts, alongside traditional de-identification methods like dictionary lookup and rule-based approaches. The system effectively identifies and either redacts or replaces sensitive identifiable entities within clinical documents, while also allowing users to customise the masked documents according to their specific needs. The integration of ClinicalBERT significantly improves the performance of entity recognition, achieving 0.9732 F1-score, especially for common entities such as names, dates, and locations. A risk assessment feature has also been developed, which analyses the uniqueness of context within documents to classify them into risk levels, guiding further de-identification efforts. While the system demonstrates strong overall performance, this work highlights areas for future improvement, including handling more complex entity occurrences and enhancing the system's adaptability to different clinical settings.
INSIGHTBUDDY-AI: Medication Extraction and Entity Linking using Large Language Models and Ensemble Learning
Sep 28, 2024



Abstract:Medication Extraction and Mining play an important role in healthcare NLP research due to its practical applications in hospital settings, such as their mapping into standard clinical knowledge bases (SNOMED-CT, BNF, etc.). In this work, we investigate state-of-the-art LLMs in text mining tasks on medications and their related attributes such as dosage, route, strength, and adverse effects. In addition, we explore different ensemble learning methods (\textsc{Stack-Ensemble} and \textsc{Voting-Ensemble}) to augment the model performances from individual LLMs. Our ensemble learning result demonstrated better performances than individually fine-tuned base models BERT, RoBERTa, RoBERTa-L, BioBERT, BioClinicalBERT, BioMedRoBERTa, ClinicalBERT, and PubMedBERT across general and specific domains. Finally, we build up an entity linking function to map extracted medical terminologies into the SNOMED-CT codes and the British National Formulary (BNF) codes, which are further mapped to the Dictionary of Medicines and Devices (dm+d), and ICD. Our model's toolkit and desktop applications are publicly available at \url{https://github.com/HECTA-UoM/ensemble-NER}.
LLM-CARD: Towards a Description and Landscape of Large Language Models
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:With the rapid growth of the Natural Language Processing (NLP) field, a vast variety of Large Language Models (LLMs) continue to emerge for diverse NLP tasks. As an increasing number of papers are presented, researchers and developers face the challenge of information overload. Thus, it is particularly important to develop a system that can automatically extract and organise key information about LLMs from academic papers (\textbf{LLM model card}). This work is to develop such a pioneer system by using Named Entity Recognition (\textbf{NER}) and Relation Extraction (\textbf{RE}) methods that automatically extract key information about large language models from the papers, helping researchers to efficiently access information about LLMs. These features include model \textit{licence}, model \textit{name}, and model \textit{application}. With these features, we can form a model card for each paper. \textbf{Data-contribution} wise, 106 academic papers were processed by defining three dictionaries - LLMs name, licence, and application. 11,051 sentences were extracted through dictionary lookup, and the dataset was constructed through manual review of the final selection of 129 sentences that have a link between the name and the licence, and 106 sentences that have a link between the model name and the application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge