Pablo Romero
INSIGHTBUDDY-AI: Medication Extraction and Entity Linking using Large Language Models and Ensemble Learning
Sep 28, 2024



Abstract:Medication Extraction and Mining play an important role in healthcare NLP research due to its practical applications in hospital settings, such as their mapping into standard clinical knowledge bases (SNOMED-CT, BNF, etc.). In this work, we investigate state-of-the-art LLMs in text mining tasks on medications and their related attributes such as dosage, route, strength, and adverse effects. In addition, we explore different ensemble learning methods (\textsc{Stack-Ensemble} and \textsc{Voting-Ensemble}) to augment the model performances from individual LLMs. Our ensemble learning result demonstrated better performances than individually fine-tuned base models BERT, RoBERTa, RoBERTa-L, BioBERT, BioClinicalBERT, BioMedRoBERTa, ClinicalBERT, and PubMedBERT across general and specific domains. Finally, we build up an entity linking function to map extracted medical terminologies into the SNOMED-CT codes and the British National Formulary (BNF) codes, which are further mapped to the Dictionary of Medicines and Devices (dm+d), and ICD. Our model's toolkit and desktop applications are publicly available at \url{https://github.com/HECTA-UoM/ensemble-NER}.
Accelerated Design and Deployment of Low-Carbon Concrete for Data Centers
Apr 11, 2022
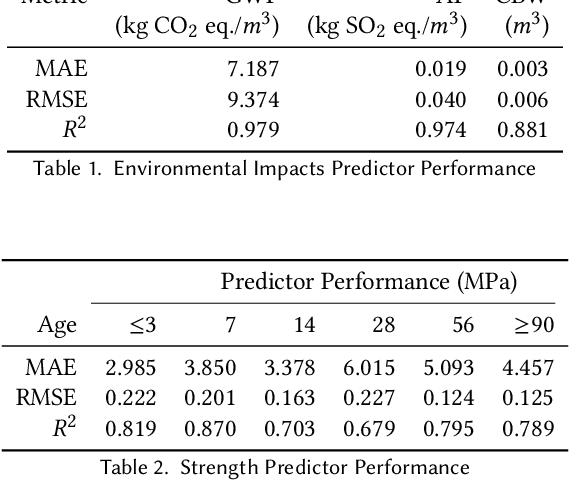
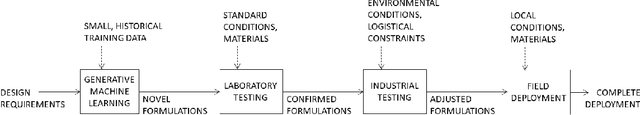
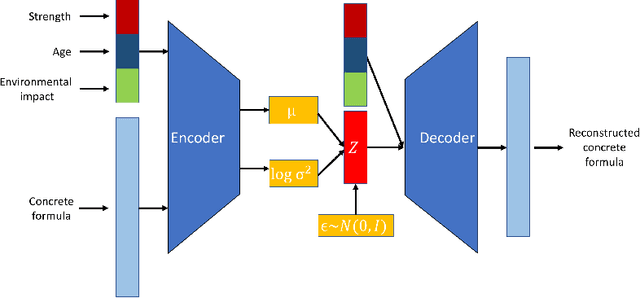
Abstract:Concrete is the most widely used engineered material in the world with more than 10 billion tons produced annually. Unfortunately, with that scale comes a significant burden in terms of energy, water, and release of greenhouse gases and other pollutants; indeed 8% of worldwide carbon emissions are attributed to the production of cement, a key ingredient in concrete. As such, there is interest in creating concrete formulas that minimize this environmental burden, while satisfying engineering performance requirements including compressive strength. Specifically for computing, concrete is a major ingredient in the construction of data centers. In this work, we use conditional variational autoencoders (CVAEs), a type of semi-supervised generative artificial intelligence (AI) model, to discover concrete formulas with desired properties. Our model is trained just using a small open dataset from the UCI Machine Learning Repository joined with environmental impact data from standard lifecycle analysis. Computational predictions demonstrate CVAEs can design concrete formulas with much lower carbon requirements than existing formulations while meeting design requirements. Next we report laboratory-based compressive strength experiments for five AI-generated formulations, which demonstrate that the formulations exceed design requirements. The resulting formulations were then used by Ozinga Ready Mix -- a concrete supplier -- to generate field-ready concrete formulations, based on local conditions and their expertise in concrete design. Finally, we report on how these formulations were used in the construction of buildings and structures in a Meta data center in DeKalb, IL, USA. Results from field experiments as part of this real-world deployment corroborate the efficacy of AI-generated low-carbon concrete mixes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge