Hongyan Liu
ActAvatar: Temporally-Aware Precise Action Control for Talking Avatars
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Despite significant advances in talking avatar generation, existing methods face critical challenges: insufficient text-following capability for diverse actions, lack of temporal alignment between actions and audio content, and dependency on additional control signals such as pose skeletons. We present ActAvatar, a framework that achieves phase-level precision in action control through textual guidance by capturing both action semantics and temporal context. Our approach introduces three core innovations: (1) Phase-Aware Cross-Attention (PACA), which decomposes prompts into a global base block and temporally-anchored phase blocks, enabling the model to concentrate on phase-relevant tokens for precise temporal-semantic alignment; (2) Progressive Audio-Visual Alignment, which aligns modality influence with the hierarchical feature learning process-early layers prioritize text for establishing action structure while deeper layers emphasize audio for refining lip movements, preventing modality interference; (3) A two-stage training strategy that first establishes robust audio-visual correspondence on diverse data, then injects action control through fine-tuning on structured annotations, maintaining both audio-visual alignment and the model's text-following capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ActAvatar significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both action control and visual quality.
MACE-Dance: Motion-Appearance Cascaded Experts for Music-Driven Dance Video Generation
Dec 20, 2025



Abstract:With the rise of online dance-video platforms and rapid advances in AI-generated content (AIGC), music-driven dance generation has emerged as a compelling research direction. Despite substantial progress in related domains such as music-driven 3D dance generation, pose-driven image animation, and audio-driven talking-head synthesis, existing methods cannot be directly adapted to this task. Moreover, the limited studies in this area still struggle to jointly achieve high-quality visual appearance and realistic human motion. Accordingly, we present MACE-Dance, a music-driven dance video generation framework with cascaded Mixture-of-Experts (MoE). The Motion Expert performs music-to-3D motion generation while enforcing kinematic plausibility and artistic expressiveness, whereas the Appearance Expert carries out motion- and reference-conditioned video synthesis, preserving visual identity with spatiotemporal coherence. Specifically, the Motion Expert adopts a diffusion model with a BiMamba-Transformer hybrid architecture and a Guidance-Free Training (GFT) strategy, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in 3D dance generation. The Appearance Expert employs a decoupled kinematic-aesthetic fine-tuning strategy, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in pose-driven image animation. To better benchmark this task, we curate a large-scale and diverse dataset and design a motion-appearance evaluation protocol. Based on this protocol, MACE-Dance also achieves state-of-the-art performance. Project page: https://macedance.github.io/
SyncTalk++: High-Fidelity and Efficient Synchronized Talking Heads Synthesis Using Gaussian Splatting
Jun 17, 2025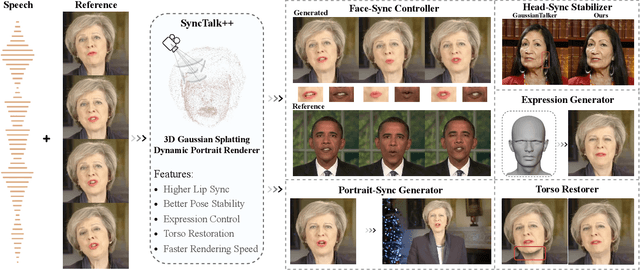
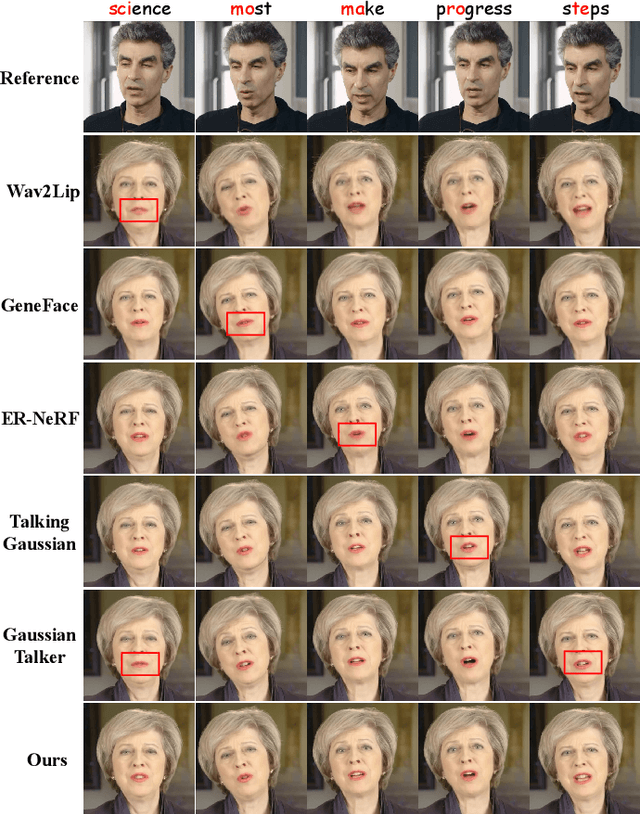


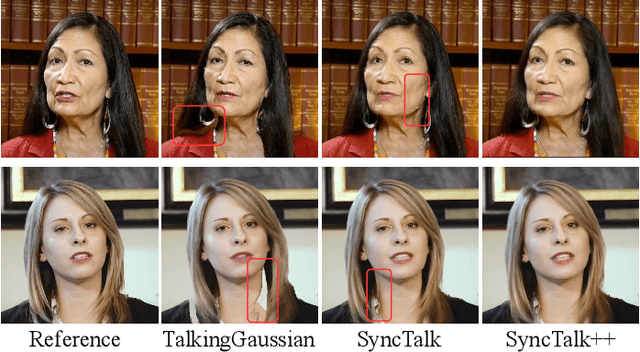
Abstract:Achieving high synchronization in the synthesis of realistic, speech-driven talking head videos presents a significant challenge. A lifelike talking head requires synchronized coordination of subject identity, lip movements, facial expressions, and head poses. The absence of these synchronizations is a fundamental flaw, leading to unrealistic results. To address the critical issue of synchronization, identified as the ''devil'' in creating realistic talking heads, we introduce SyncTalk++, which features a Dynamic Portrait Renderer with Gaussian Splatting to ensure consistent subject identity preservation and a Face-Sync Controller that aligns lip movements with speech while innovatively using a 3D facial blendshape model to reconstruct accurate facial expressions. To ensure natural head movements, we propose a Head-Sync Stabilizer, which optimizes head poses for greater stability. Additionally, SyncTalk++ enhances robustness to out-of-distribution (OOD) audio by incorporating an Expression Generator and a Torso Restorer, which generate speech-matched facial expressions and seamless torso regions. Our approach maintains consistency and continuity in visual details across frames and significantly improves rendering speed and quality, achieving up to 101 frames per second. Extensive experiments and user studies demonstrate that SyncTalk++ outperforms state-of-the-art methods in synchronization and realism. We recommend watching the supplementary video: https://ziqiaopeng.github.io/synctalk++.
OmniSync: Towards Universal Lip Synchronization via Diffusion Transformers
May 27, 2025Abstract:Lip synchronization is the task of aligning a speaker's lip movements in video with corresponding speech audio, and it is essential for creating realistic, expressive video content. However, existing methods often rely on reference frames and masked-frame inpainting, which limit their robustness to identity consistency, pose variations, facial occlusions, and stylized content. In addition, since audio signals provide weaker conditioning than visual cues, lip shape leakage from the original video will affect lip sync quality. In this paper, we present OmniSync, a universal lip synchronization framework for diverse visual scenarios. Our approach introduces a mask-free training paradigm using Diffusion Transformer models for direct frame editing without explicit masks, enabling unlimited-duration inference while maintaining natural facial dynamics and preserving character identity. During inference, we propose a flow-matching-based progressive noise initialization to ensure pose and identity consistency, while allowing precise mouth-region editing. To address the weak conditioning signal of audio, we develop a Dynamic Spatiotemporal Classifier-Free Guidance (DS-CFG) mechanism that adaptively adjusts guidance strength over time and space. We also establish the AIGC-LipSync Benchmark, the first evaluation suite for lip synchronization in diverse AI-generated videos. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OmniSync significantly outperforms prior methods in both visual quality and lip sync accuracy, achieving superior results in both real-world and AI-generated videos.
DualTalk: Dual-Speaker Interaction for 3D Talking Head Conversations
May 26, 2025Abstract:In face-to-face conversations, individuals need to switch between speaking and listening roles seamlessly. Existing 3D talking head generation models focus solely on speaking or listening, neglecting the natural dynamics of interactive conversation, which leads to unnatural interactions and awkward transitions. To address this issue, we propose a new task -- multi-round dual-speaker interaction for 3D talking head generation -- which requires models to handle and generate both speaking and listening behaviors in continuous conversation. To solve this task, we introduce DualTalk, a novel unified framework that integrates the dynamic behaviors of speakers and listeners to simulate realistic and coherent dialogue interactions. This framework not only synthesizes lifelike talking heads when speaking but also generates continuous and vivid non-verbal feedback when listening, effectively capturing the interplay between the roles. We also create a new dataset featuring 50 hours of multi-round conversations with over 1,000 characters, where participants continuously switch between speaking and listening roles. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly enhances the naturalness and expressiveness of 3D talking heads in dual-speaker conversations. We recommend watching the supplementary video: https://ziqiaopeng.github.io/dualtalk.
MEGADance: Mixture-of-Experts Architecture for Genre-Aware 3D Dance Generation
May 23, 2025



Abstract:Music-driven 3D dance generation has attracted increasing attention in recent years, with promising applications in choreography, virtual reality, and creative content creation. Previous research has generated promising realistic dance movement from audio signals. However, traditional methods underutilize genre conditioning, often treating it as auxiliary modifiers rather than core semantic drivers. This oversight compromises music-motion synchronization and disrupts dance genre continuity, particularly during complex rhythmic transitions, thereby leading to visually unsatisfactory effects. To address the challenge, we propose MEGADance, a novel architecture for music-driven 3D dance generation. By decoupling choreographic consistency into dance generality and genre specificity, MEGADance demonstrates significant dance quality and strong genre controllability. It consists of two stages: (1) High-Fidelity Dance Quantization Stage (HFDQ), which encodes dance motions into a latent representation by Finite Scalar Quantization (FSQ) and reconstructs them with kinematic-dynamic constraints, and (2) Genre-Aware Dance Generation Stage (GADG), which maps music into the latent representation by synergistic utilization of Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) mechanism with Mamba-Transformer hybrid backbone. Extensive experiments on the FineDance and AIST++ dataset demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of MEGADance both qualitatively and quantitatively. Code will be released upon acceptance.
MatchDance: Collaborative Mamba-Transformer Architecture Matching for High-Quality 3D Dance Synthesis
May 21, 2025Abstract:Music-to-dance generation represents a challenging yet pivotal task at the intersection of choreography, virtual reality, and creative content generation. Despite its significance, existing methods face substantial limitation in achieving choreographic consistency. To address the challenge, we propose MatchDance, a novel framework for music-to-dance generation that constructs a latent representation to enhance choreographic consistency. MatchDance employs a two-stage design: (1) a Kinematic-Dynamic-based Quantization Stage (KDQS), which encodes dance motions into a latent representation by Finite Scalar Quantization (FSQ) with kinematic-dynamic constraints and reconstructs them with high fidelity, and (2) a Hybrid Music-to-Dance Generation Stage(HMDGS), which uses a Mamba-Transformer hybrid architecture to map music into the latent representation, followed by the KDQS decoder to generate 3D dance motions. Additionally, a music-dance retrieval framework and comprehensive metrics are introduced for evaluation. Extensive experiments on the FineDance dataset demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Code will be released upon acceptance.
ExGes: Expressive Human Motion Retrieval and Modulation for Audio-Driven Gesture Synthesis
Mar 09, 2025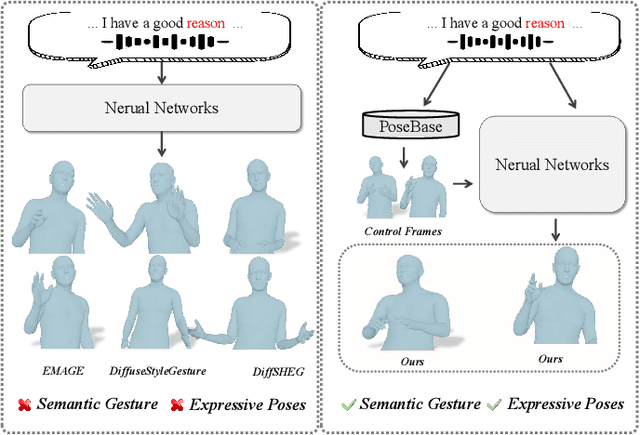
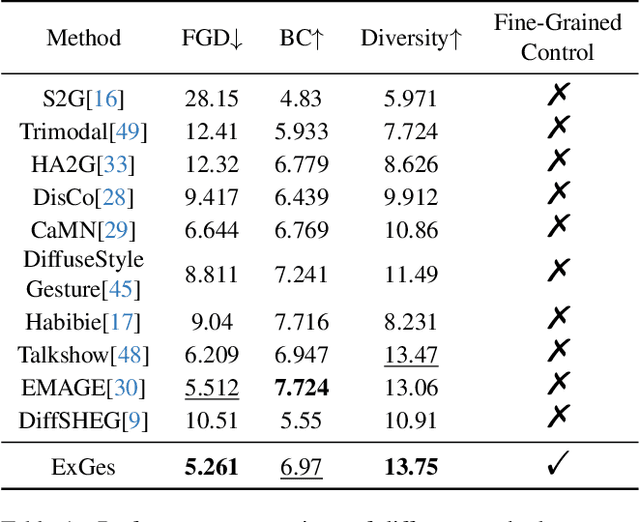
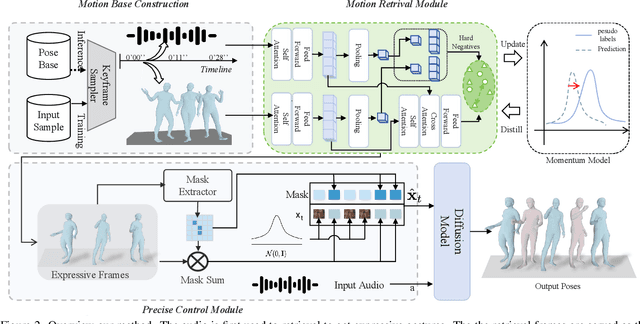
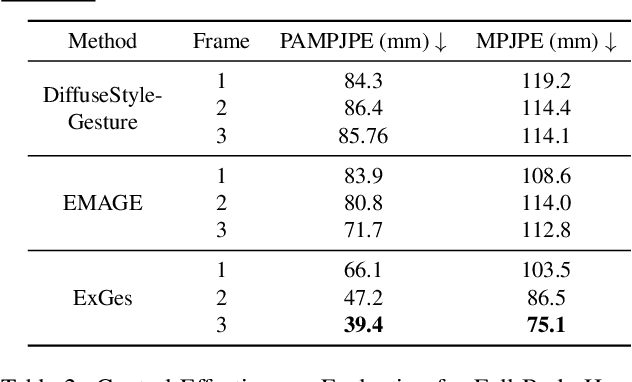
Abstract:Audio-driven human gesture synthesis is a crucial task with broad applications in virtual avatars, human-computer interaction, and creative content generation. Despite notable progress, existing methods often produce gestures that are coarse, lack expressiveness, and fail to fully align with audio semantics. To address these challenges, we propose ExGes, a novel retrieval-enhanced diffusion framework with three key designs: (1) a Motion Base Construction, which builds a gesture library using training dataset; (2) a Motion Retrieval Module, employing constrative learning and momentum distillation for fine-grained reference poses retreiving; and (3) a Precision Control Module, integrating partial masking and stochastic masking to enable flexible and fine-grained control. Experimental evaluations on BEAT2 demonstrate that ExGes reduces Fr\'echet Gesture Distance by 6.2\% and improves motion diversity by 5.3\% over EMAGE, with user studies revealing a 71.3\% preference for its naturalness and semantic relevance. Code will be released upon acceptance.
CoheDancers: Enhancing Interactive Group Dance Generation through Music-Driven Coherence Decomposition
Dec 26, 2024



Abstract:Dance generation is crucial and challenging, particularly in domains like dance performance and virtual gaming. In the current body of literature, most methodologies focus on Solo Music2Dance. While there are efforts directed towards Group Music2Dance, these often suffer from a lack of coherence, resulting in aesthetically poor dance performances. Thus, we introduce CoheDancers, a novel framework for Music-Driven Interactive Group Dance Generation. CoheDancers aims to enhance group dance generation coherence by decomposing it into three key aspects: synchronization, naturalness, and fluidity. Correspondingly, we develop a Cycle Consistency based Dance Synchronization strategy to foster music-dance correspondences, an Auto-Regressive-based Exposure Bias Correction strategy to enhance the fluidity of the generated dances, and an Adversarial Training Strategy to augment the naturalness of the group dance output. Collectively, these strategies enable CohdeDancers to produce highly coherent group dances with superior quality. Furthermore, to establish better benchmarks for Group Music2Dance, we construct the most diverse and comprehensive open-source dataset to date, I-Dancers, featuring rich dancer interactions, and create comprehensive evaluation metrics. Experimental evaluations on I-Dancers and other extant datasets substantiate that CoheDancers achieves unprecedented state-of-the-art performance. Code will be released.
LEADRE: Multi-Faceted Knowledge Enhanced LLM Empowered Display Advertisement Recommender System
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Display advertising provides significant value to advertisers, publishers, and users. Traditional display advertising systems utilize a multi-stage architecture consisting of retrieval, coarse ranking, and final ranking. However, conventional retrieval methods rely on ID-based learning to rank mechanisms and fail to adequately utilize the content information of ads, which hampers their ability to provide diverse recommendation lists. To address this limitation, we propose leveraging the extensive world knowledge of LLMs. However, three key challenges arise when attempting to maximize the effectiveness of LLMs: "How to capture user interests", "How to bridge the knowledge gap between LLMs and advertising system", and "How to efficiently deploy LLMs". To overcome these challenges, we introduce a novel LLM-based framework called LLM Empowered Display ADvertisement REcommender system (LEADRE). LEADRE consists of three core modules: (1) The Intent-Aware Prompt Engineering introduces multi-faceted knowledge and designs intent-aware <Prompt, Response> pairs that fine-tune LLMs to generate ads tailored to users' personal interests. (2) The Advertising-Specific Knowledge Alignment incorporates auxiliary fine-tuning tasks and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to align LLMs with ad semantic and business value. (3) The Efficient System Deployment deploys LEADRE in an online environment by integrating both latency-tolerant and latency-sensitive service. Extensive offline experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of LEADRE and validate the contributions of individual modules. Online A/B test shows that LEADRE leads to a 1.57% and 1.17% GMV lift for serviced users on WeChat Channels and Moments separately. LEADRE has been deployed on both platforms, serving tens of billions of requests each day.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge