Yunfei Cheng
VGG-Tex: A Vivid Geometry-Guided Facial Texture Estimation Model for High Fidelity Monocular 3D Face Reconstruction
Sep 17, 2024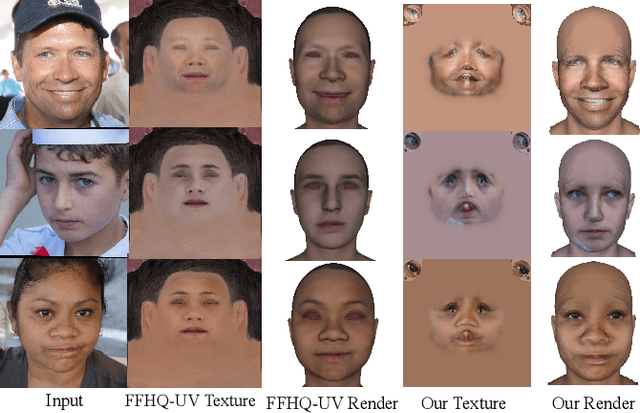
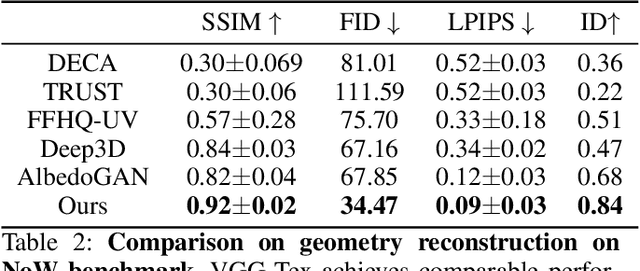
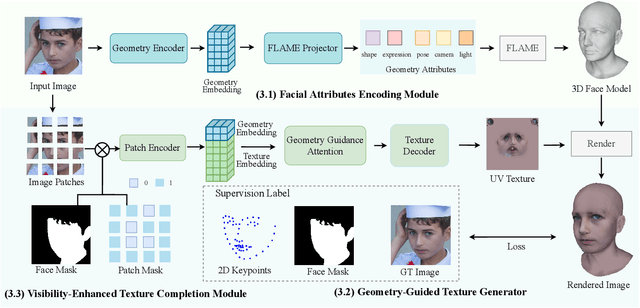
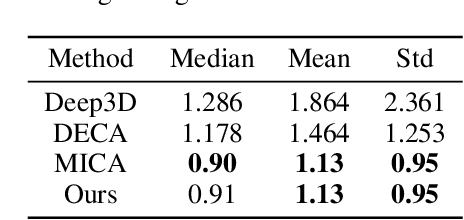
Abstract:3D face reconstruction from monocular images has promoted the development of various applications such as augmented reality. Though existing methods have made remarkable progress, most of them emphasize geometric reconstruction, while overlooking the importance of texture prediction. To address this issue, we propose VGG-Tex, a novel Vivid Geometry-Guided Facial Texture Estimation model designed for High Fidelity Monocular 3D Face Reconstruction. The core of this approach is leveraging 3D parametric priors to enhance the outcomes of 2D UV texture estimation. Specifically, VGG-Tex includes a Facial Attributes Encoding Module, a Geometry-Guided Texture Generator, and a Visibility-Enhanced Texture Completion Module. These components are responsible for extracting parametric priors, generating initial textures, and refining texture details, respectively. Based on the geometry-texture complementarity principle, VGG-Tex also introduces a Texture-guided Geometry Refinement Module to further balance the overall fidelity of the reconstructed 3D faces, along with corresponding losses. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly improves texture reconstruction performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
Recurrent Drafter for Fast Speculative Decoding in Large Language Models
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce an improved approach of speculative decoding aimed at enhancing the efficiency of serving large language models. Our method capitalizes on the strengths of two established techniques: the classic two-model speculative decoding approach, and the more recent single-model approach, Medusa. Drawing inspiration from Medusa, our approach adopts a single-model strategy for speculative decoding. However, our method distinguishes itself by employing a single, lightweight draft head with a recurrent dependency design, akin in essence to the small, draft model uses in classic speculative decoding, but without the complexities of the full transformer architecture. And because of the recurrent dependency, we can use beam search to swiftly filter out undesired candidates with the draft head. The outcome is a method that combines the simplicity of single-model design and avoids the need to create a data-dependent tree attention structure only for inference in Medusa. We empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method on several popular open source language models, along with a comprehensive analysis of the trade-offs involved in adopting this approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge