Deva Ramanan
CRISP: Contact-Guided Real2Sim from Monocular Video with Planar Scene Primitives
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:We introduce CRISP, a method that recovers simulatable human motion and scene geometry from monocular video. Prior work on joint human-scene reconstruction relies on data-driven priors and joint optimization with no physics in the loop, or recovers noisy geometry with artifacts that cause motion tracking policies with scene interactions to fail. In contrast, our key insight is to recover convex, clean, and simulation-ready geometry by fitting planar primitives to a point cloud reconstruction of the scene, via a simple clustering pipeline over depth, normals, and flow. To reconstruct scene geometry that might be occluded during interactions, we make use of human-scene contact modeling (e.g., we use human posture to reconstruct the occluded seat of a chair). Finally, we ensure that human and scene reconstructions are physically-plausible by using them to drive a humanoid controller via reinforcement learning. Our approach reduces motion tracking failure rates from 55.2\% to 6.9\% on human-centric video benchmarks (EMDB, PROX), while delivering a 43\% faster RL simulation throughput. We further validate it on in-the-wild videos including casually-captured videos, Internet videos, and even Sora-generated videos. This demonstrates CRISP's ability to generate physically-valid human motion and interaction environments at scale, greatly advancing real-to-sim applications for robotics and AR/VR.
Any4D: Unified Feed-Forward Metric 4D Reconstruction
Dec 11, 2025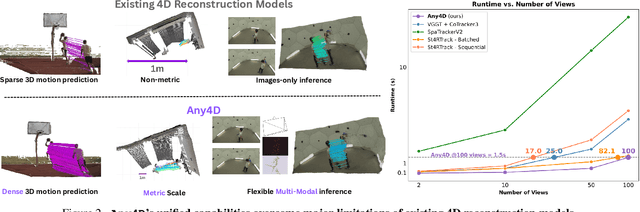
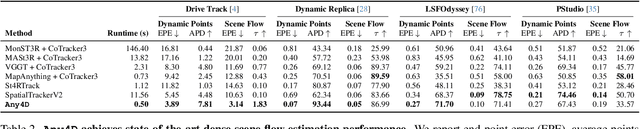
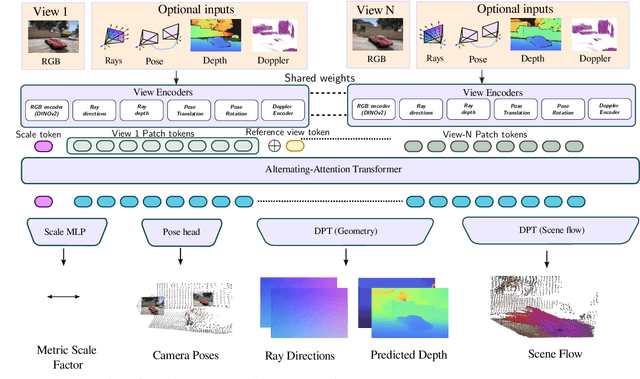
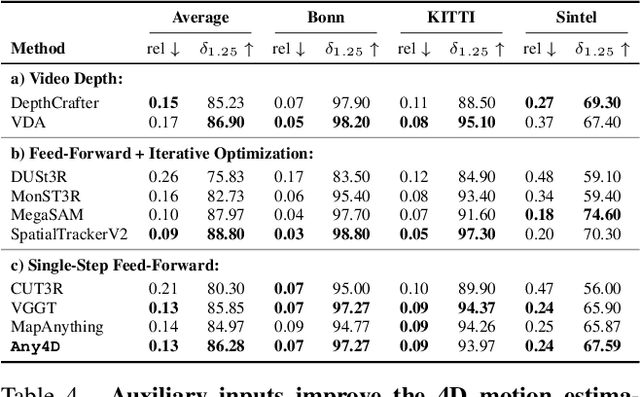
Abstract:We present Any4D, a scalable multi-view transformer for metric-scale, dense feed-forward 4D reconstruction. Any4D directly generates per-pixel motion and geometry predictions for N frames, in contrast to prior work that typically focuses on either 2-view dense scene flow or sparse 3D point tracking. Moreover, unlike other recent methods for 4D reconstruction from monocular RGB videos, Any4D can process additional modalities and sensors such as RGB-D frames, IMU-based egomotion, and Radar Doppler measurements, when available. One of the key innovations that allows for such a flexible framework is a modular representation of a 4D scene; specifically, per-view 4D predictions are encoded using a variety of egocentric factors (depthmaps and camera intrinsics) represented in local camera coordinates, and allocentric factors (camera extrinsics and scene flow) represented in global world coordinates. We achieve superior performance across diverse setups - both in terms of accuracy (2-3X lower error) and compute efficiency (15X faster), opening avenues for multiple downstream applications.
RF-DETR: Neural Architecture Search for Real-Time Detection Transformers
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary detectors achieve impressive performance on COCO, but often fail to generalize to real-world datasets with out-of-distribution classes not typically found in their pre-training. Rather than simply fine-tuning a heavy-weight vision-language model (VLM) for new domains, we introduce RF-DETR, a light-weight specialist detection transformer that discovers accuracy-latency Pareto curves for any target dataset with weight-sharing neural architecture search (NAS). Our approach fine-tunes a pre-trained base network on a target dataset and evaluates thousands of network configurations with different accuracy-latency tradeoffs without re-training. Further, we revisit the "tunable knobs" for NAS to improve the transferability of DETRs to diverse target domains. Notably, RF-DETR significantly improves on prior state-of-the-art real-time methods on COCO and Roboflow100-VL. RF-DETR (nano) achieves 48.0 AP on COCO, beating D-FINE (nano) by 5.3 AP at similar latency, and RF-DETR (2x-large) outperforms GroundingDINO (tiny) by 1.2 AP on Roboflow100-VL while running 20x as fast. To the best of our knowledge, RF-DETR (2x-large) is the first real-time detector to surpass 60 AP on COCO. Our code is at https://github.com/roboflow/rf-detr
Towards Foundational Models for Single-Chip Radar
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:mmWave radars are compact, inexpensive, and durable sensors that are robust to occlusions and work regardless of environmental conditions, such as weather and darkness. However, this comes at the cost of poor angular resolution, especially for inexpensive single-chip radars, which are typically used in automotive and indoor sensing applications. Although many have proposed learning-based methods to mitigate this weakness, no standardized foundational models or large datasets for the mmWave radar have emerged, and practitioners have largely trained task-specific models from scratch using relatively small datasets. In this paper, we collect (to our knowledge) the largest available raw radar dataset with 1M samples (29 hours) and train a foundational model for 4D single-chip radar, which can predict 3D occupancy and semantic segmentation with quality that is typically only possible with much higher resolution sensors. We demonstrate that our Generalizable Radar Transformer (GRT) generalizes across diverse settings, can be fine-tuned for different tasks, and shows logarithmic data scaling of 20\% per $10\times$ data. We also run extensive ablations on common design decisions, and find that using raw radar data significantly outperforms widely-used lossy representations, equivalent to a $10\times$ increase in training data. Finally, we roughly estimate that $\approx$100M samples (3000 hours) of data are required to fully exploit the potential of GRT.
Less is More Tokens: Efficient Math Reasoning via Difficulty-Aware Chain-of-Thought Distillation
Sep 05, 2025



Abstract:Chain-of-thought reasoning, while powerful, can produce unnecessarily verbose output for simpler problems. We present a framework for difficulty-aware reasoning that teaches models to dynamically adjust reasoning depth based on problem complexity. Remarkably, we show that models can be endowed with such dynamic inference pathways without any architectural modifications; we simply post-train on data that is carefully curated to include chain-of-thought traces that are proportional in length to problem difficulty. Our analysis reveals that post-training via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) primarily captures patterns like reasoning length and format, while direct preference optimization (DPO) preserves reasoning accuracy, with their combination reducing length and maintaining or improving performance. Both quantitative metrics and qualitative assessments confirm that models can learn to "think proportionally", reasoning minimally on simple problems while maintaining depth for complex ones.
Prompt-to-Product: Generative Assembly via Bimanual Manipulation
Aug 28, 2025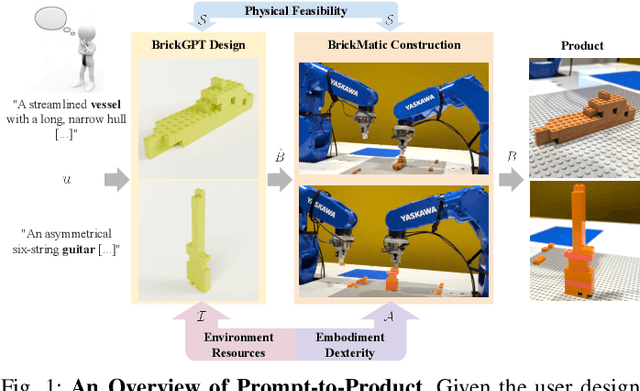
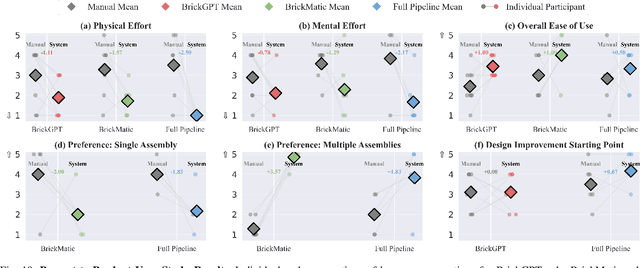
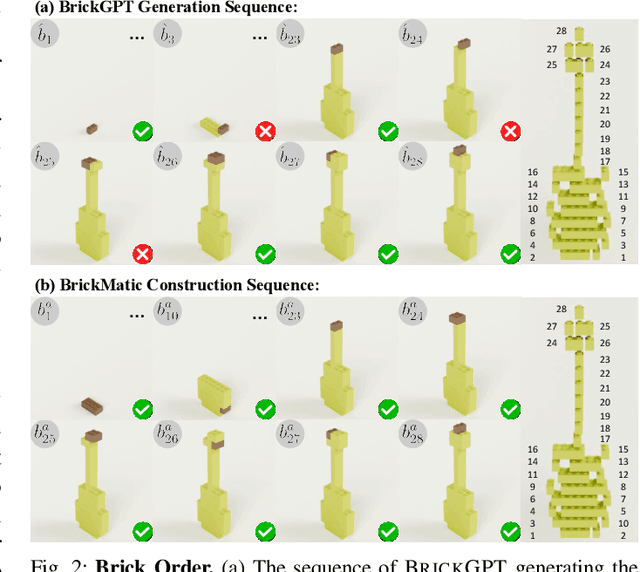
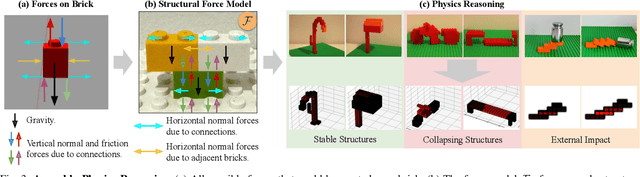
Abstract:Creating assembly products demands significant manual effort and expert knowledge in 1) designing the assembly and 2) constructing the product. This paper introduces Prompt-to-Product, an automated pipeline that generates real-world assembly products from natural language prompts. Specifically, we leverage LEGO bricks as the assembly platform and automate the process of creating brick assembly structures. Given the user design requirements, Prompt-to-Product generates physically buildable brick designs, and then leverages a bimanual robotic system to construct the real assembly products, bringing user imaginations into the real world. We conduct a comprehensive user study, and the results demonstrate that Prompt-to-Product significantly lowers the barrier and reduces manual effort in creating assembly products from imaginative ideas.
MonoFusion: Sparse-View 4D Reconstruction via Monocular Fusion
Jul 31, 2025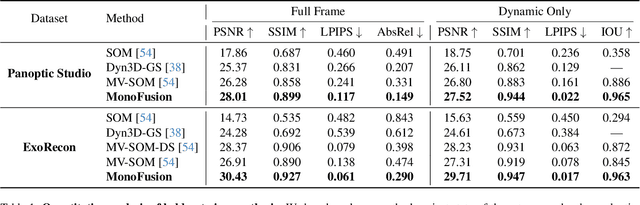
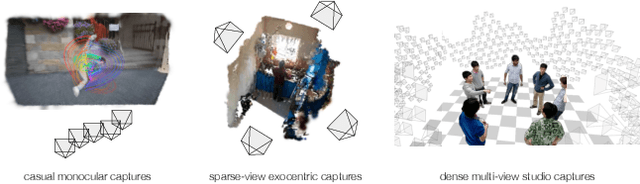
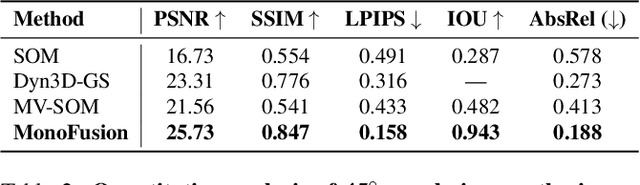
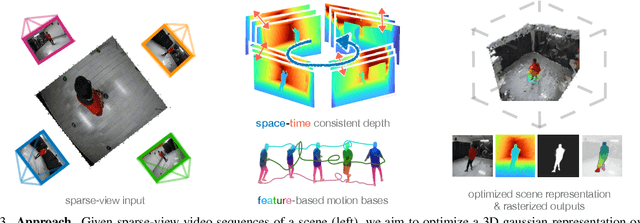
Abstract:We address the problem of dynamic scene reconstruction from sparse-view videos. Prior work often requires dense multi-view captures with hundreds of calibrated cameras (e.g. Panoptic Studio). Such multi-view setups are prohibitively expensive to build and cannot capture diverse scenes in-the-wild. In contrast, we aim to reconstruct dynamic human behaviors, such as repairing a bike or dancing, from a small set of sparse-view cameras with complete scene coverage (e.g. four equidistant inward-facing static cameras). We find that dense multi-view reconstruction methods struggle to adapt to this sparse-view setup due to limited overlap between viewpoints. To address these limitations, we carefully align independent monocular reconstructions of each camera to produce time- and view-consistent dynamic scene reconstructions. Extensive experiments on PanopticStudio and Ego-Exo4D demonstrate that our method achieves higher quality reconstructions than prior art, particularly when rendering novel views. Code, data, and data-processing scripts are available on https://github.com/ImNotPrepared/MonoFusion.
Activation Reward Models for Few-Shot Model Alignment
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) to human preferences is a central challenge in improving the quality of the models' generative outputs for real-world applications. A common approach is to use reward modeling to encode preferences, enabling alignment via post-training using reinforcement learning. However, traditional reward modeling is not easily adaptable to new preferences because it requires a separate reward model, commonly trained on large preference datasets. To address this, we introduce Activation Reward Models (Activation RMs) -- a novel few-shot reward modeling method that leverages activation steering to construct well-aligned reward signals using minimal supervision and no additional model finetuning. Activation RMs outperform existing few-shot reward modeling approaches such as LLM-as-a-judge with in-context learning, voting-based scoring, and token probability scoring on standard reward modeling benchmarks. Furthermore, we demonstrate the effectiveness of Activation RMs in mitigating reward hacking behaviors, highlighting their utility for safety-critical applications. Toward this end, we propose PreferenceHack, a novel few-shot setting benchmark, the first to test reward models on reward hacking in a paired preference format. Finally, we show that Activation RM achieves state-of-the-art performance on this benchmark, surpassing even GPT-4o.
ONLY: One-Layer Intervention Sufficiently Mitigates Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Recent Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have introduced a new paradigm for understanding and reasoning about image input through textual responses. Although they have achieved remarkable performance across a range of multi-modal tasks, they face the persistent challenge of hallucination, which introduces practical weaknesses and raises concerns about their reliable deployment in real-world applications. Existing work has explored contrastive decoding approaches to mitigate this issue, where the output of the original LVLM is compared and contrasted with that of a perturbed version. However, these methods require two or more queries that slow down LVLM response generation, making them less suitable for real-time applications. To overcome this limitation, we propose ONLY, a training-free decoding approach that requires only a single query and a one-layer intervention during decoding, enabling efficient real-time deployment. Specifically, we enhance textual outputs by selectively amplifying crucial textual information using a text-to-visual entropy ratio for each token. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed ONLY consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various benchmarks while requiring minimal implementation effort and computational cost. Code is available at https://github.com/zifuwan/ONLY.
UFM: A Simple Path towards Unified Dense Correspondence with Flow
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Dense image correspondence is central to many applications, such as visual odometry, 3D reconstruction, object association, and re-identification. Historically, dense correspondence has been tackled separately for wide-baseline scenarios and optical flow estimation, despite the common goal of matching content between two images. In this paper, we develop a Unified Flow & Matching model (UFM), which is trained on unified data for pixels that are co-visible in both source and target images. UFM uses a simple, generic transformer architecture that directly regresses the (u,v) flow. It is easier to train and more accurate for large flows compared to the typical coarse-to-fine cost volumes in prior work. UFM is 28% more accurate than state-of-the-art flow methods (Unimatch), while also having 62% less error and 6.7x faster than dense wide-baseline matchers (RoMa). UFM is the first to demonstrate that unified training can outperform specialized approaches across both domains. This result enables fast, general-purpose correspondence and opens new directions for multi-modal, long-range, and real-time correspondence tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge