Zifeng Cheng
Who Transfers Safety? Identifying and Targeting Cross-Lingual Shared Safety Neurons
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Multilingual safety remains significantly imbalanced, leaving non-high-resource (NHR) languages vulnerable compared to robust high-resource (HR) ones. Moreover, the neural mechanisms driving safety alignment remain unclear despite observed cross-lingual representation transfer. In this paper, we find that LLMs contain a set of cross-lingual shared safety neurons (SS-Neurons), a remarkably small yet critical neuronal subset that jointly regulates safety behavior across languages. We first identify monolingual safety neurons (MS-Neurons) and validate their causal role in safety refusal behavior through targeted activation and suppression. Our cross-lingual analyses then identify SS-Neurons as the subset of MS-Neurons shared between HR and NHR languages, serving as a bridge to transfer safety capabilities from HR to NHR domains. We observe that suppressing these neurons causes concurrent safety drops across NHR languages, whereas reinforcing them improves cross-lingual defensive consistency. Building on these insights, we propose a simple neuron-oriented training strategy that targets SS-Neurons based on language resource distribution and model architecture. Experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning this tiny neuronal subset outperforms state-of-the-art methods, significantly enhancing NHR safety while maintaining the model's general capabilities. The code and dataset will be available athttps://github.com/1518630367/SS-Neuron-Expansion.
TraceRouter: Robust Safety for Large Foundation Models via Path-Level Intervention
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Despite their capabilities, large foundation models (LFMs) remain susceptible to adversarial manipulation. Current defenses predominantly rely on the "locality hypothesis", suppressing isolated neurons or features. However, harmful semantics act as distributed, cross-layer circuits, rendering such localized interventions brittle and detrimental to utility. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{TraceRouter}, a path-level framework that traces and disconnects the causal propagation circuits of illicit semantics. TraceRouter operates in three stages: (1) it pinpoints a sensitive onset layer by analyzing attention divergence; (2) it leverages sparse autoencoders (SAEs) and differential activation analysis to disentangle and isolate malicious features; and (3) it maps these features to downstream causal pathways via feature influence scores (FIS) derived from zero-out interventions. By selectively suppressing these causal chains, TraceRouter physically severs the flow of harmful information while leaving orthogonal computation routes intact. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TraceRouter significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving a superior trade-off between adversarial robustness and general utility. Our code will be publicly released. WARNING: This paper contains unsafe model responses.
RegionMarker: A Region-Triggered Semantic Watermarking Framework for Embedding-as-a-Service Copyright Protection
Nov 17, 2025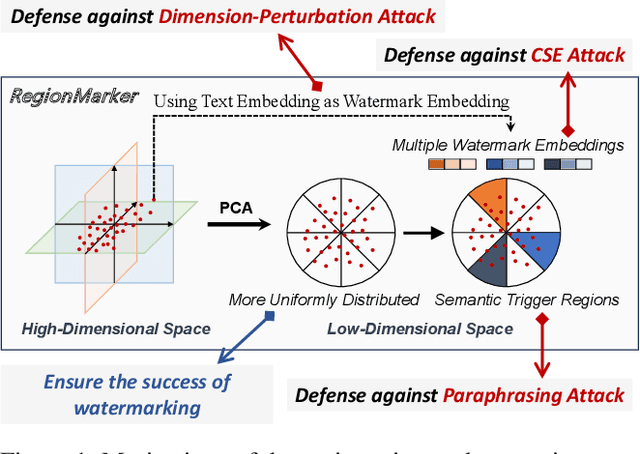
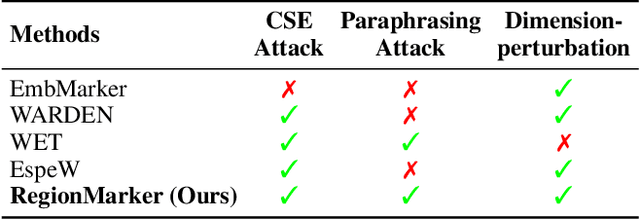
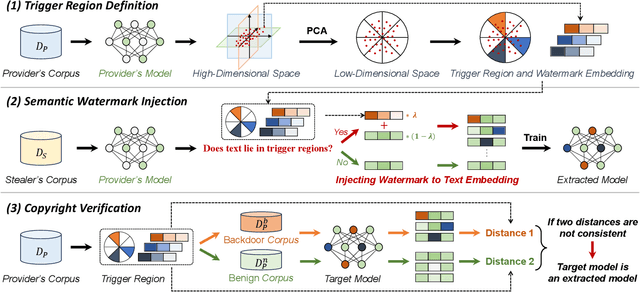
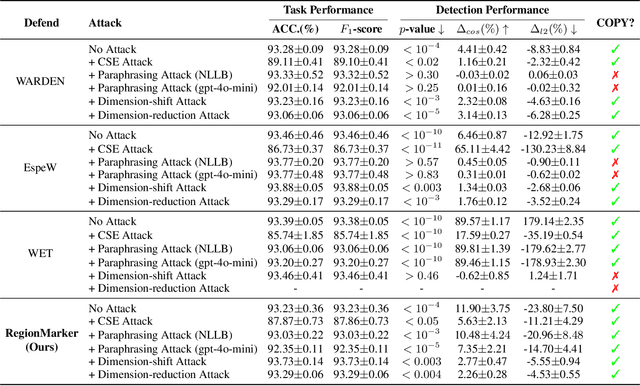
Abstract:Embedding-as-a-Service (EaaS) is an effective and convenient deployment solution for addressing various NLP tasks. Nevertheless, recent research has shown that EaaS is vulnerable to model extraction attacks, which could lead to significant economic losses for model providers. For copyright protection, existing methods inject watermark embeddings into text embeddings and use them to detect copyright infringement. However, current watermarking methods often resist only a subset of attacks and fail to provide \textit{comprehensive} protection. To this end, we present the region-triggered semantic watermarking framework called RegionMarker, which defines trigger regions within a low-dimensional space and injects watermarks into text embeddings associated with these regions. By utilizing a secret dimensionality reduction matrix to project onto this subspace and randomly selecting trigger regions, RegionMarker makes it difficult for watermark removal attacks to evade detection. Furthermore, by embedding watermarks across the entire trigger region and using the text embedding as the watermark, RegionMarker is resilient to both paraphrasing and dimension-perturbation attacks. Extensive experiments on various datasets show that RegionMarker is effective in resisting different attack methods, thereby protecting the copyright of EaaS.
Steering When Necessary: Flexible Steering Large Language Models with Backtracking
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance across many generation tasks. Nevertheless, effectively aligning them with desired behaviors remains a significant challenge. Activation steering is an effective and cost-efficient approach that directly modifies the activations of LLMs during the inference stage, aligning their responses with the desired behaviors and avoiding the high cost of fine-tuning. Existing methods typically indiscriminately intervene to all generations or rely solely on the question to determine intervention, which limits the accurate assessment of the intervention strength. To this end, we propose the Flexible Activation Steering with Backtracking (FASB) framework, which dynamically determines both the necessity and strength of intervention by tracking the internal states of the LLMs during generation, considering both the question and the generated content. Since intervening after detecting a deviation from the desired behavior is often too late, we further propose the backtracking mechanism to correct the deviated tokens and steer the LLMs toward the desired behavior. Extensive experiments on the TruthfulQA dataset and six multiple-choice datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms baselines. Our code will be released at https://github.com/gjw185/FASB.
Contrastive Prompting Enhances Sentence Embeddings in LLMs through Inference-Time Steering
May 19, 2025Abstract:Extracting sentence embeddings from large language models (LLMs) is a practical direction, as it requires neither additional data nor fine-tuning. Previous studies usually focus on prompt engineering to guide LLMs to encode the core semantic information of the sentence into the embedding of the last token. However, the last token in these methods still encodes an excess of non-essential information, such as stop words, limiting its encoding capacity. To this end, we propose a Contrastive Prompting (CP) method that introduces an extra auxiliary prompt to elicit better sentence embedding. By contrasting with the auxiliary prompt, CP can steer existing prompts to encode the core semantics of the sentence, rather than non-essential information. CP is a plug-and-play inference-time intervention method that can be combined with various prompt-based methods. Extensive experiments on Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) tasks and downstream classification tasks demonstrate that our method can improve the performance of existing prompt-based methods across different LLMs. Our code will be released at https://github.com/zifengcheng/CP.
Token Prepending: A Training-Free Approach for Eliciting Better Sentence Embeddings from LLMs
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Extracting sentence embeddings from large language models (LLMs) is a promising direction, as LLMs have demonstrated stronger semantic understanding capabilities. Previous studies typically focus on prompt engineering to elicit sentence embeddings from LLMs by prompting the model to encode sentence information into the embedding of the last token. However, LLMs are mostly decoder-only models with causal attention and the earlier tokens in the sentence cannot attend to the latter tokens, resulting in biased encoding of sentence information and cascading effects on the final decoded token. To this end, we propose a novel Token Prepending (TP) technique that prepends each layer's decoded sentence embedding to the beginning of the sentence in the next layer's input, allowing earlier tokens to attend to the complete sentence information under the causal attention mechanism. The proposed TP technique is a plug-and-play and training-free technique, which means it can be seamlessly integrated with various prompt-based sentence embedding methods and autoregressive LLMs. Extensive experiments on various Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) tasks and downstream classification tasks demonstrate that our proposed TP technique can significantly improve the performance of existing prompt-based sentence embedding methods across different LLMs, while incurring negligible additional inference cost.
A Debiased Nearest Neighbors Framework for Multi-Label Text Classification
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:Multi-Label Text Classification (MLTC) is a practical yet challenging task that involves assigning multiple non-exclusive labels to each document. Previous studies primarily focus on capturing label correlations to assist label prediction by introducing special labeling schemes, designing specific model structures, or adding auxiliary tasks. Recently, the $k$ Nearest Neighbor ($k$NN) framework has shown promise by retrieving labeled samples as references to mine label co-occurrence information in the embedding space. However, two critical biases, namely embedding alignment bias and confidence estimation bias, are often overlooked, adversely affecting prediction performance. In this paper, we introduce a DEbiased Nearest Neighbors (DENN) framework for MLTC, specifically designed to mitigate these biases. To address embedding alignment bias, we propose a debiased contrastive learning strategy, enhancing neighbor consistency on label co-occurrence. For confidence estimation bias, we present a debiased confidence estimation strategy, improving the adaptive combination of predictions from $k$NN and inductive binary classifications. Extensive experiments conducted on four public benchmark datasets (i.e., AAPD, RCV1-V2, Amazon-531, and EUR-LEX57K) showcase the effectiveness of our proposed method. Besides, our method does not introduce any extra parameters.
Multi-Prompting Decoder Helps Better Language Understanding
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:Recent Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) usually only provide users with the inference APIs, namely the emerging Model-as-a-Service (MaaS) setting. To adapt MaaS PLMs to downstream tasks without accessing their parameters and gradients, some existing methods focus on the output-side adaptation of PLMs, viewing the PLM as an encoder and then optimizing a task-specific decoder for decoding the output hidden states and class scores of the PLM. Despite the effectiveness of these methods, they only use a single prompt to query PLMs for decoding, leading to a heavy reliance on the quality of the adopted prompt. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective Multi-Prompting Decoder (MPD) framework for MaaS adaptation. The core idea is to query PLMs with multiple different prompts for each sample, thereby obtaining multiple output hidden states and class scores for subsequent decoding. Such multi-prompting decoding paradigm can simultaneously mitigate reliance on the quality of a single prompt, alleviate the issue of data scarcity under the few-shot setting, and provide richer knowledge extracted from PLMs. Specifically, we propose two decoding strategies: multi-prompting decoding with optimal transport for hidden states and calibrated decoding for class scores. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves new state-of-the-art results on multiple natural language understanding datasets under the few-shot setting.
Unifying Token and Span Level Supervisions for Few-Shot Sequence Labeling
Jul 20, 2023Abstract:Few-shot sequence labeling aims to identify novel classes based on only a few labeled samples. Existing methods solve the data scarcity problem mainly by designing token-level or span-level labeling models based on metric learning. However, these methods are only trained at a single granularity (i.e., either token level or span level) and have some weaknesses of the corresponding granularity. In this paper, we first unify token and span level supervisions and propose a Consistent Dual Adaptive Prototypical (CDAP) network for few-shot sequence labeling. CDAP contains the token-level and span-level networks, jointly trained at different granularities. To align the outputs of two networks, we further propose a consistent loss to enable them to learn from each other. During the inference phase, we propose a consistent greedy inference algorithm that first adjusts the predicted probability and then greedily selects non-overlapping spans with maximum probability. Extensive experiments show that our model achieves new state-of-the-art results on three benchmark datasets.
Controlling Class Layout for Deep Ordinal Classification via Constrained Proxies Learning
Mar 01, 2023



Abstract:For deep ordinal classification, learning a well-structured feature space specific to ordinal classification is helpful to properly capture the ordinal nature among classes. Intuitively, when Euclidean distance metric is used, an ideal ordinal layout in feature space would be that the sample clusters are arranged in class order along a straight line in space. However, enforcing samples to conform to a specific layout in the feature space is a challenging problem. To address this problem, in this paper, we propose a novel Constrained Proxies Learning (CPL) method, which can learn a proxy for each ordinal class and then adjusts the global layout of classes by constraining these proxies. Specifically, we propose two kinds of strategies: hard layout constraint and soft layout constraint. The hard layout constraint is realized by directly controlling the generation of proxies to force them to be placed in a strict linear layout or semicircular layout (i.e., two instantiations of strict ordinal layout). The soft layout constraint is realized by constraining that the proxy layout should always produce unimodal proxy-to-proxies similarity distribution for each proxy (i.e., to be a relaxed ordinal layout). Experiments show that the proposed CPL method outperforms previous deep ordinal classification methods under the same setting of feature extractor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge