Xiang Luo
LinkDoc Technology, Beijing, China
MalRAG: A Retrieval-Augmented LLM Framework for Open-set Malicious Traffic Identification
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Fine-grained identification of IDS-flagged suspicious traffic is crucial in cybersecurity. In practice, cyber threats evolve continuously, making the discovery of novel malicious traffic a critical necessity as well as the identification of known classes. Recent studies have advanced this goal with deep models, but they often rely on task-specific architectures that limit transferability and require per-dataset tuning. In this paper we introduce MalRAG, the first LLM driven retrieval-augmented framework for open-set malicious traffic identification. MalRAG freezes the LLM and operates via comprehensive traffic knowledge construction, adaptive retrieval, and prompt engineering. Concretely, we construct a multi-view traffic database by mining prior malicious traffic from content, structural, and temporal perspectives. Furthermore, we introduce a Coverage-Enhanced Retrieval Algorithm that queries across these views to assemble the most probable candidates, thereby improving the inclusion of correct evidence. We then employ Traffic-Aware Adaptive Pruning to select a variable subset of these candidates based on traffic-aware similarity scores, suppressing incorrect matches and yielding reliable retrieved evidence. Moreover, we develop a suite of guidance prompts where task instruction, evidence referencing, and decision guidance are integrated with the retrieved evidence to improve LLM performance. Across diverse real-world datasets and settings, MalRAG delivers state-of-the-art results in both fine-grained identification of known classes and novel malicious traffic discovery. Ablation and deep-dive analyses further show that MalRAG effective leverages LLM capabilities yet achieves open-set malicious traffic identification without relying on a specific LLM.
Steering When Necessary: Flexible Steering Large Language Models with Backtracking
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance across many generation tasks. Nevertheless, effectively aligning them with desired behaviors remains a significant challenge. Activation steering is an effective and cost-efficient approach that directly modifies the activations of LLMs during the inference stage, aligning their responses with the desired behaviors and avoiding the high cost of fine-tuning. Existing methods typically indiscriminately intervene to all generations or rely solely on the question to determine intervention, which limits the accurate assessment of the intervention strength. To this end, we propose the Flexible Activation Steering with Backtracking (FASB) framework, which dynamically determines both the necessity and strength of intervention by tracking the internal states of the LLMs during generation, considering both the question and the generated content. Since intervening after detecting a deviation from the desired behavior is often too late, we further propose the backtracking mechanism to correct the deviated tokens and steer the LLMs toward the desired behavior. Extensive experiments on the TruthfulQA dataset and six multiple-choice datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms baselines. Our code will be released at https://github.com/gjw185/FASB.
Zero-Shot Cross-Domain Dialogue State Tracking via Dual Low-Rank Adaptation
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot dialogue state tracking (DST) seeks to enable dialogue systems to transition to unfamiliar domains without manual annotation or extensive retraining. Prior research has approached this objective by embedding prompts into language models (LMs). Common methodologies include integrating prompts at the input layer or introducing learnable variables at each transformer layer. Nonetheless, each strategy exhibits inherent limitations. Prompts integrated at the input layer risk underutilization, with their impact potentially diminishing across successive transformer layers. Conversely, the addition of learnable variables to each layer can complicate the training process and increase inference latency. To tackle the issues mentioned above, this paper proposes Dual Low-Rank Adaptation (DualLoRA), a plug-and-play architecture designed for zero-shot DST. DualLoRA incorporates two distinct Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) components, targeting both dialogue context processing and prompt optimization, to ensure the comprehensive influence of prompts throughout the transformer model layers. This is achieved without incurring additional inference latency, showcasing an efficient integration into existing architectures. Through rigorous evaluation on the MultiWOZ and SGD datasets, DualLoRA demonstrates notable improvements across multiple domains, outperforming traditional baseline methods in zero-shot settings. Our code is accessible at: \url{https://github.com/suntea233/DualLoRA}.
DuetSim: Building User Simulator with Dual Large Language Models for Task-Oriented Dialogues
May 16, 2024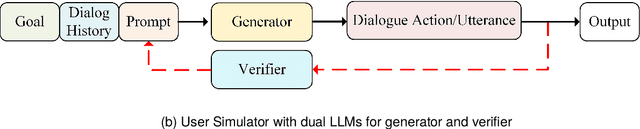
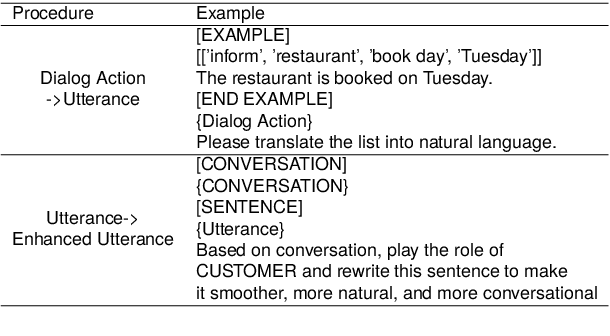
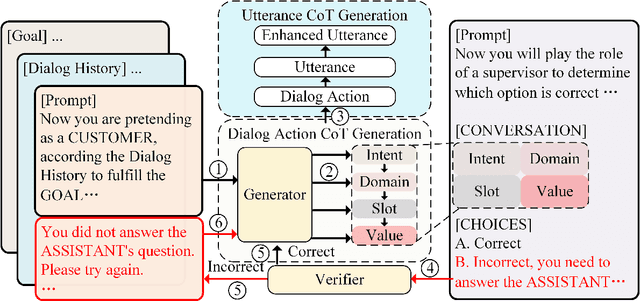
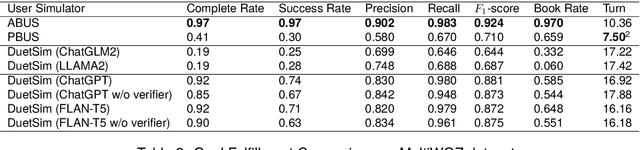
Abstract:User Simulators play a pivotal role in training and evaluating task-oriented dialogue systems. Traditional user simulators typically rely on human-engineered agendas, resulting in generated responses that often lack diversity and spontaneity. Although large language models (LLMs) exhibit a remarkable capacity for generating coherent and contextually appropriate utterances, they may fall short when tasked with generating responses that effectively guide users towards their goals, particularly in dialogues with intricate constraints and requirements. This paper introduces DuetSim, a novel framework designed to address the intricate demands of task-oriented dialogues by leveraging LLMs. DuetSim stands apart from conventional approaches by employing two LLMs in tandem: one dedicated to response generation and the other focused on verification. This dual LLM approach empowers DuetSim to produce responses that not only exhibit diversity but also demonstrate accuracy and are preferred by human users. We validate the efficacy of our method through extensive experiments conducted on the MultiWOZ dataset, highlighting improvements in response quality and correctness, largely attributed to the incorporation of the second LLM. Our code is accessible at: https://github.com/suntea233/DuetSim.
Key-frame Guided Network for Thyroid Nodule Recognition using Ultrasound Videos
Jun 30, 2022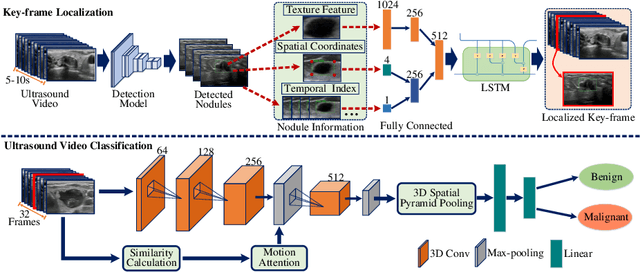
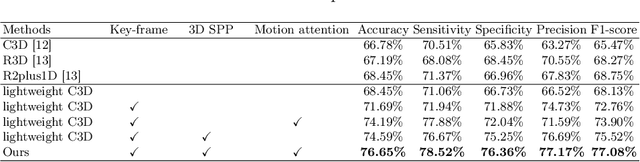
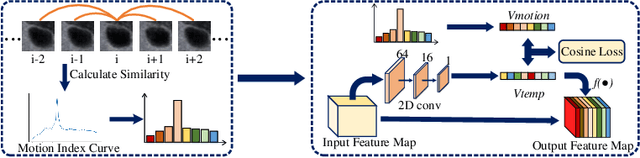
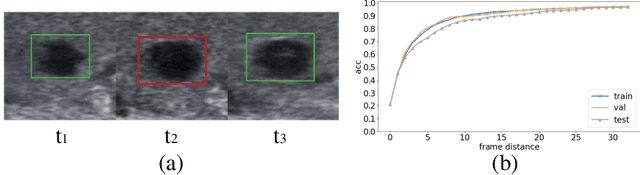
Abstract:Ultrasound examination is widely used in the clinical diagnosis of thyroid nodules (benign/malignant). However, the accuracy relies heavily on radiologist experience. Although deep learning techniques have been investigated for thyroid nodules recognition. Current solutions are mainly based on static ultrasound images, with limited temporal information used and inconsistent with clinical diagnosis. This paper proposes a novel method for the automated recognition of thyroid nodules through an exhaustive exploration of ultrasound videos and key-frames. We first propose a detection-localization framework to automatically identify the clinical key-frame with a typical nodule in each ultrasound video. Based on the localized key-frame, we develop a key-frame guided video classification model for thyroid nodule recognition. Besides, we introduce a motion attention module to help the network focus on significant frames in an ultrasound video, which is consistent with clinical diagnosis. The proposed thyroid nodule recognition framework is validated on clinically collected ultrasound videos, demonstrating superior performance compared with other state-of-the-art methods.
2nd Place Solution to Instance Segmentation of IJCAI 3D AI Challenge 2020
Oct 21, 2020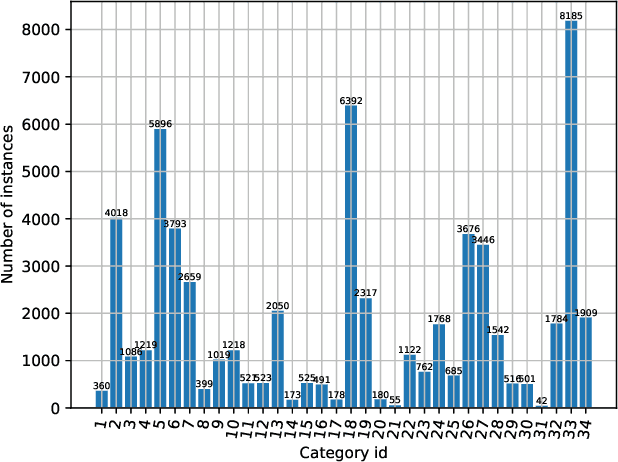
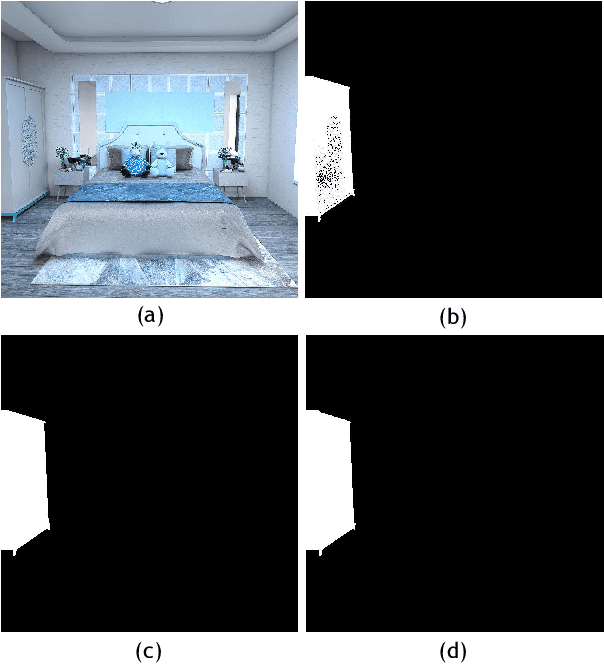
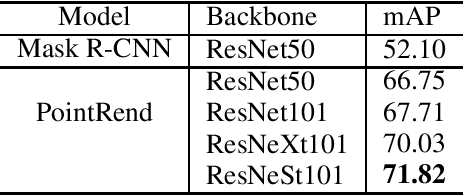

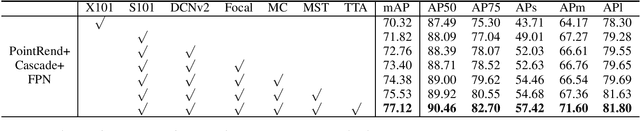
Abstract:Compared with MS-COCO, the dataset for the competition has a larger proportion of large objects which area is greater than 96x96 pixels. As getting fine boundaries is vitally important for large object segmentation, Mask R-CNN with PointRend is selected as the base segmentation framework to output high-quality object boundaries. Besides, a better engine that integrates ResNeSt, FPN and DCNv2, and a range of effective tricks that including multi-scale training and test time augmentation are applied to improve segmentation performance. Our best performance is an ensemble of four models (three PointRend-based models and SOLOv2), which won the 2nd place in IJCAI-PRICAI 3D AI Challenge 2020: Instance Segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge