Zhiwen Tang
SYMPHONY: Synergistic Multi-agent Planning with Heterogeneous Language Model Assembly
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements have increasingly focused on leveraging large language models (LLMs) to construct autonomous agents for complex problem-solving tasks. However, existing approaches predominantly employ a single-agent framework to generate search branches and estimate rewards during Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) planning. This single-agent paradigm inherently limits exploration capabilities, often resulting in insufficient diversity among generated branches and suboptimal planning performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose Synergistic Multi-agent Planning with Heterogeneous langauge model assembly (SYMPHONY), a novel multi-agent planning framework that integrates a pool of heterogeneous language model-based agents. By leveraging diverse reasoning patterns across agents, SYMPHONY enhances rollout diversity and facilitates more effective exploration. Empirical results across multiple benchmark tasks show that SYMPHONY achieves strong performance even when instantiated with open-source LLMs deployable on consumer-grade hardware. When enhanced with cloud-based LLMs accessible via API, SYMPHONY demonstrates further improvements, outperforming existing state-of-the-art baselines and underscoring the effectiveness of heterogeneous multi-agent coordination in planning tasks.
Task-Aware LLM Council with Adaptive Decision Pathways for Decision Support
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown strong capabilities across diverse decision-making tasks. However, existing approaches often overlook the specialization differences among available models, treating all LLMs as uniformly applicable regardless of task characteristics. This limits their ability to adapt to varying reasoning demands and task complexities. In this work, we propose Task-Aware LLM Council (TALC), a task-adaptive decision framework that integrates a council of LLMs with Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to enable dynamic expert selection and efficient multi-step planning. Each LLM is equipped with a structured success memory profile derived from prior task trajectories, enabling semantic matching between current reasoning context and past successes. At each decision point, TALC routes control to the most contextually appropriate model and estimates node value using a dual-signal mechanism that fuses model-based evaluations with historical utility scores. These signals are adaptively weighted based on intra-node variance and used to guide MCTS selection, allowing the system to balance exploration depth with planning confidence. Experiments on WebShop, HumanEval, and the Game of 24 demonstrate that TALC achieves superior task success rates and improved search efficiency compared to strong baselines, validating the benefits of specialization-aware routing and adaptive planning.
Zero-Shot Cross-Domain Dialogue State Tracking via Dual Low-Rank Adaptation
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot dialogue state tracking (DST) seeks to enable dialogue systems to transition to unfamiliar domains without manual annotation or extensive retraining. Prior research has approached this objective by embedding prompts into language models (LMs). Common methodologies include integrating prompts at the input layer or introducing learnable variables at each transformer layer. Nonetheless, each strategy exhibits inherent limitations. Prompts integrated at the input layer risk underutilization, with their impact potentially diminishing across successive transformer layers. Conversely, the addition of learnable variables to each layer can complicate the training process and increase inference latency. To tackle the issues mentioned above, this paper proposes Dual Low-Rank Adaptation (DualLoRA), a plug-and-play architecture designed for zero-shot DST. DualLoRA incorporates two distinct Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) components, targeting both dialogue context processing and prompt optimization, to ensure the comprehensive influence of prompts throughout the transformer model layers. This is achieved without incurring additional inference latency, showcasing an efficient integration into existing architectures. Through rigorous evaluation on the MultiWOZ and SGD datasets, DualLoRA demonstrates notable improvements across multiple domains, outperforming traditional baseline methods in zero-shot settings. Our code is accessible at: \url{https://github.com/suntea233/DualLoRA}.
DuetSim: Building User Simulator with Dual Large Language Models for Task-Oriented Dialogues
May 16, 2024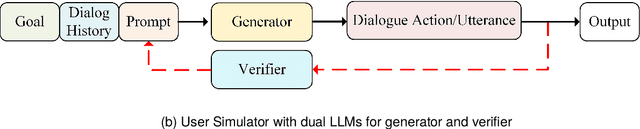
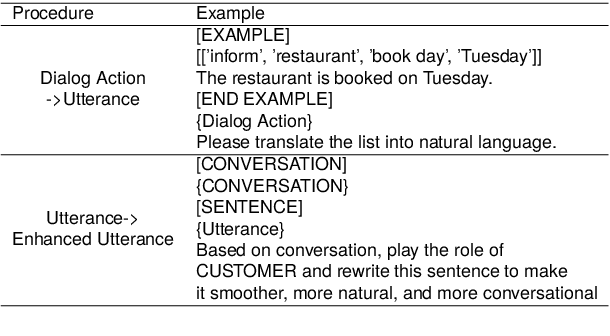
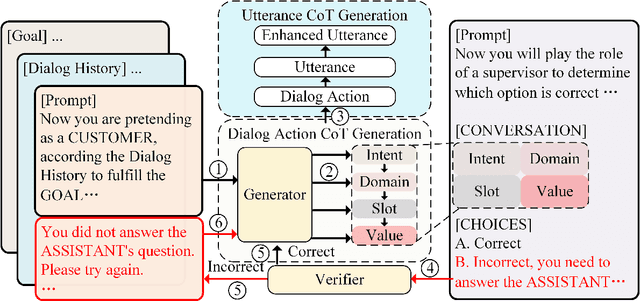
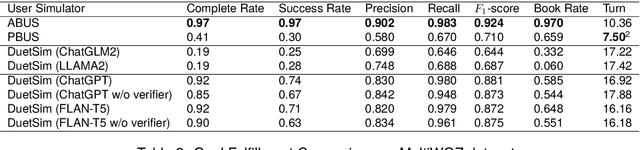
Abstract:User Simulators play a pivotal role in training and evaluating task-oriented dialogue systems. Traditional user simulators typically rely on human-engineered agendas, resulting in generated responses that often lack diversity and spontaneity. Although large language models (LLMs) exhibit a remarkable capacity for generating coherent and contextually appropriate utterances, they may fall short when tasked with generating responses that effectively guide users towards their goals, particularly in dialogues with intricate constraints and requirements. This paper introduces DuetSim, a novel framework designed to address the intricate demands of task-oriented dialogues by leveraging LLMs. DuetSim stands apart from conventional approaches by employing two LLMs in tandem: one dedicated to response generation and the other focused on verification. This dual LLM approach empowers DuetSim to produce responses that not only exhibit diversity but also demonstrate accuracy and are preferred by human users. We validate the efficacy of our method through extensive experiments conducted on the MultiWOZ dataset, highlighting improvements in response quality and correctness, largely attributed to the incorporation of the second LLM. Our code is accessible at: https://github.com/suntea233/DuetSim.
High-Quality Diversification for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Jun 09, 2021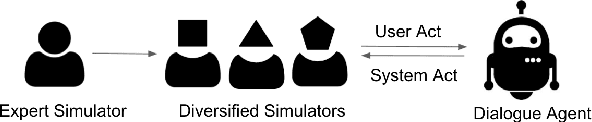
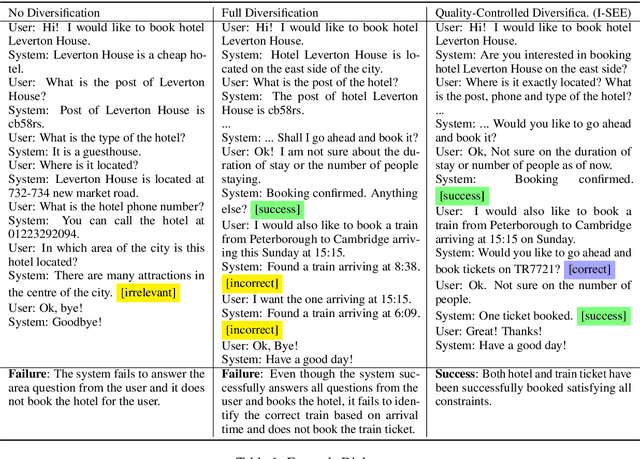
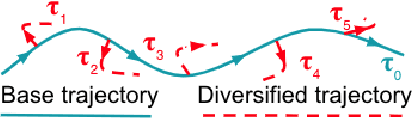
Abstract:Many task-oriented dialogue systems use deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to learn policies that respond to the user appropriately and complete the tasks successfully. Training DRL agents with diverse dialogue trajectories prepare them well for rare user requests and unseen situations. One effective diversification method is to let the agent interact with a diverse set of learned user models. However, trajectories created by these artificial user models may contain generation errors, which can quickly propagate into the agent's policy. It is thus important to control the quality of the diversification and resist the noise. In this paper, we propose a novel dialogue diversification method for task-oriented dialogue systems trained in simulators. Our method, Intermittent Short Extension Ensemble (I-SEE), constrains the intensity to interact with an ensemble of diverse user models and effectively controls the quality of the diversification. Evaluations on the Multiwoz dataset show that I-SEE successfully boosts the performance of several state-of-the-art DRL dialogue agents.
Balancing Reinforcement Learning Training Experiences in Interactive Information Retrieval
Jun 05, 2020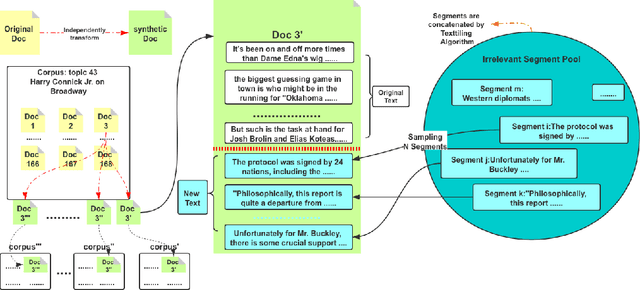
Abstract:Interactive Information Retrieval (IIR) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) share many commonalities, including an agent who learns while interacts, a long-term and complex goal, and an algorithm that explores and adapts. To successfully apply RL methods to IIR, one challenge is to obtain sufficient relevance labels to train the RL agents, which are infamously known as sample inefficient. However, in a text corpus annotated for a given query, it is not the relevant documents but the irrelevant documents that predominate. This would cause very unbalanced training experiences for the agent and prevent it from learning any policy that is effective. Our paper addresses this issue by using domain randomization to synthesize more relevant documents for the training. Our experimental results on the Text REtrieval Conference (TREC) Dynamic Domain (DD) 2017 Track show that the proposed method is able to boost an RL agent's learning effectiveness by 22\% in dealing with unseen situations.
Corpus-Level End-to-End Exploration for Interactive Systems
Nov 23, 2019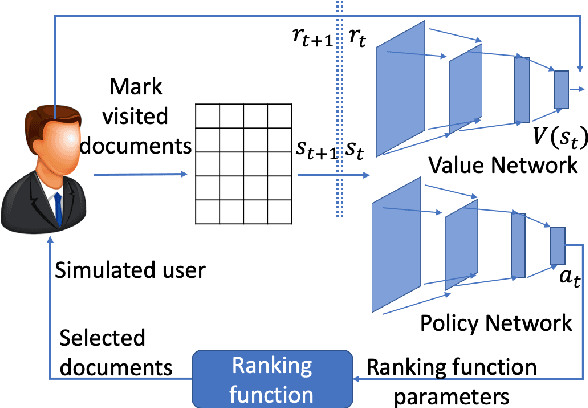


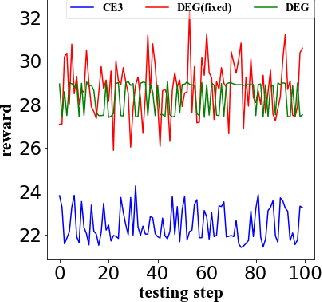
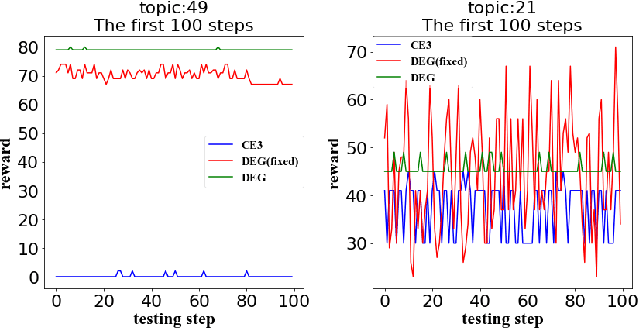
Abstract:A core interest in building Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents is to let them interact with and assist humans. One example is Dynamic Search (DS), which models the process that a human works with a search engine agent to accomplish a complex and goal-oriented task. Early DS agents using Reinforcement Learning (RL) have only achieved limited success for (1) their lack of direct control over which documents to return and (2) the difficulty to recover from wrong search trajectories. In this paper, we present a novel corpus-level end-to-end exploration (CE3) method to address these issues. In our method, an entire text corpus is compressed into a global low-dimensional representation, which enables the agent to gain access to the full state and action spaces, including the under-explored areas. We also propose a new form of retrieval function, whose linear approximation allows end-to-end manipulation of documents. Experiments on the Text REtrieval Conference (TREC) Dynamic Domain (DD) Track show that CE3 outperforms the state-of-the-art DS systems.
Dynamic Search -- Optimizing the Game of Information Seeking
Sep 26, 2019



Abstract:This article presents the emerging topic of dynamic search (DS). To position dynamic search in a larger research landscape, the article discusses in detail its relationship to related research topics and disciplines. The article reviews approaches to modeling dynamics during information seeking, with an emphasis on Reinforcement Learning (RL)-enabled methods. Details are given for how different approaches are used to model interactions among the human user, the search system, and the environment. The paper ends with a review of evaluations of dynamic search systems.
DeepTileBars: Visualizing Term Distribution for Neural Information Retrieval
Nov 01, 2018



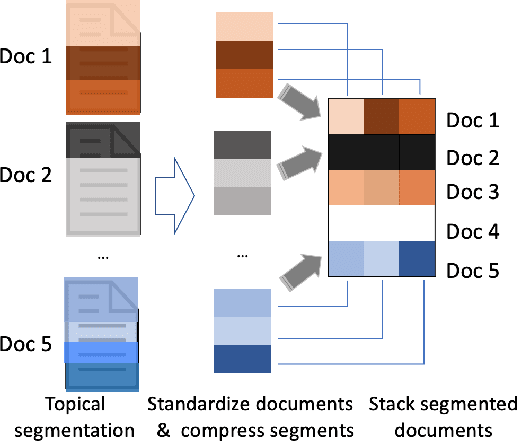
Abstract:Most neural Information Retrieval (Neu-IR) models derive query-to-document ranking scores based on term-level matching. Inspired by TileBars, a classic term distribution visualization method, in this paper, we propose a novel Neu-IR model that models query-to-document matching at the subtopic and higher levels. Our system first splits the documents into topical segments, "visualizes" the matching between the query and the segments, and then feeds the interaction matrix into a Neu-IR model, DeepTileBars, to obtain the final ranking score. DeepTileBars models the relevance signals happening at different granularities in a document's topic hierarchy. It thus better captures the discourse structure of the document and the matching patterns. Although its design and implementation are light-weight, DeepTileBars outperforms other state-of-the-art Neu-IR models on benchmark datasets including the Text REtrieval Conference (TREC) 2010-2012 Web Tracks and LETOR 4.0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge