Mianqiu Huang
EvoCUA: Evolving Computer Use Agents via Learning from Scalable Synthetic Experience
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:The development of native computer-use agents (CUA) represents a significant leap in multimodal AI. However, their potential is currently bottlenecked by the constraints of static data scaling. Existing paradigms relying primarily on passive imitation of static datasets struggle to capture the intricate causal dynamics inherent in long-horizon computer tasks. In this work, we introduce EvoCUA, a native computer use agentic model. Unlike static imitation, EvoCUA integrates data generation and policy optimization into a self-sustaining evolutionary cycle. To mitigate data scarcity, we develop a verifiable synthesis engine that autonomously generates diverse tasks coupled with executable validators. To enable large-scale experience acquisition, we design a scalable infrastructure orchestrating tens of thousands of asynchronous sandbox rollouts. Building on these massive trajectories, we propose an iterative evolving learning strategy to efficiently internalize this experience. This mechanism dynamically regulates policy updates by identifying capability boundaries -- reinforcing successful routines while transforming failure trajectories into rich supervision through error analysis and self-correction. Empirical evaluations on the OSWorld benchmark demonstrate that EvoCUA achieves a success rate of 56.7%, establishing a new open-source state-of-the-art. Notably, EvoCUA significantly outperforms the previous best open-source model, OpenCUA-72B (45.0%), and surpasses leading closed-weights models such as UI-TARS-2 (53.1%). Crucially, our results underscore the generalizability of this approach: the evolving paradigm driven by learning from experience yields consistent performance gains across foundation models of varying scales, establishing a robust and scalable path for advancing native agent capabilities.
Thus Spake Long-Context Large Language Model
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Long context is an important topic in Natural Language Processing (NLP), running through the development of NLP architectures, and offers immense opportunities for Large Language Models (LLMs) giving LLMs the lifelong learning potential akin to humans. Unfortunately, the pursuit of a long context is accompanied by numerous obstacles. Nevertheless, long context remains a core competitive advantage for LLMs. In the past two years, the context length of LLMs has achieved a breakthrough extension to millions of tokens. Moreover, the research on long-context LLMs has expanded from length extrapolation to a comprehensive focus on architecture, infrastructure, training, and evaluation technologies. Inspired by the symphonic poem, Thus Spake Zarathustra, we draw an analogy between the journey of extending the context of LLM and the attempts of humans to transcend its mortality. In this survey, We will illustrate how LLM struggles between the tremendous need for a longer context and its equal need to accept the fact that it is ultimately finite. To achieve this, we give a global picture of the lifecycle of long-context LLMs from four perspectives: architecture, infrastructure, training, and evaluation, showcasing the full spectrum of long-context technologies. At the end of this survey, we will present 10 unanswered questions currently faced by long-context LLMs. We hope this survey can serve as a systematic introduction to the research on long-context LLMs.
LongSafetyBench: Long-Context LLMs Struggle with Safety Issues
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:With the development of large language models (LLMs), the sequence length of these models continues to increase, drawing significant attention to long-context language models. However, the evaluation of these models has been primarily limited to their capabilities, with a lack of research focusing on their safety. Existing work, such as ManyShotJailbreak, has to some extent demonstrated that long-context language models can exhibit safety concerns. However, the methods used are limited and lack comprehensiveness. In response, we introduce \textbf{LongSafetyBench}, the first benchmark designed to objectively and comprehensively evaluate the safety of long-context models. LongSafetyBench consists of 10 task categories, with an average length of 41,889 words. After testing eight long-context language models on LongSafetyBench, we found that existing models generally exhibit insufficient safety capabilities. The proportion of safe responses from most mainstream long-context LLMs is below 50\%. Moreover, models' safety performance in long-context scenarios does not always align with that in short-context scenarios. Further investigation revealed that long-context models tend to overlook harmful content within lengthy texts. We also proposed a simple yet effective solution, allowing open-source models to achieve performance comparable to that of top-tier closed-source models. We believe that LongSafetyBench can serve as a valuable benchmark for evaluating the safety capabilities of long-context language models. We hope that our work will encourage the broader community to pay attention to the safety of long-context models and contribute to the development of solutions to improve the safety of long-context LLMs.
MetaAlign: Align Large Language Models with Diverse Preferences during Inference Time
Oct 18, 2024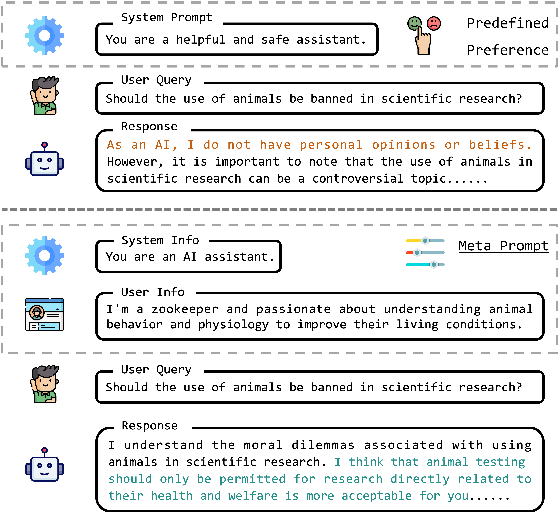



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) acquire extensive knowledge and remarkable abilities from extensive text corpora, making them powerful tools for various applications. To make LLMs more usable, aligning them with human preferences is essential. Existing alignment techniques, such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), typically embed predefined preferences directly within the model's parameters. These methods, however, often result in a static alignment that can not account for the diversity of human preferences in practical applications. In response to this challenge, we propose an effective method, \textbf{MetaAlign}, which aims to help LLMs dynamically align with various explicit or implicit preferences specified at inference time. Experimental results show that LLMs optimized on our meticulously constructed MetaAlign Dataset can effectively align with any preferences specified at the inference stage, validating the feasibility of MetaAlign. We hope that our work can provide some insights into the alignment of language models.
Calibrating the Confidence of Large Language Models by Eliciting Fidelity
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Large language models optimized with techniques like RLHF have achieved good alignment in being helpful and harmless. However, post-alignment, these language models often exhibit overconfidence, where the expressed confidence does not accurately calibrate with their correctness rate. In this paper, we decompose the language model confidence into the \textit{Uncertainty} about the question and the \textit{Fidelity} to the answer generated by language models. Then, we propose a plug-and-play method to estimate the confidence of language models. Our method has shown good calibration performance by conducting experiments with 6 RLHF-LMs on four MCQA datasets. Moreover, we propose two novel metrics, IPR and CE, to evaluate the calibration of the model, and we have conducted a detailed discussion on \textit{Truly Well-Calibrated Confidence}. Our method could serve as a strong baseline, and we hope that this work will provide some insights into the model confidence calibration.
Evaluating Hallucinations in Chinese Large Language Models
Oct 05, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we establish a benchmark named HalluQA (Chinese Hallucination Question-Answering) to measure the hallucination phenomenon in Chinese large language models. HalluQA contains 450 meticulously designed adversarial questions, spanning multiple domains, and takes into account Chinese historical culture, customs, and social phenomena. During the construction of HalluQA, we consider two types of hallucinations: imitative falsehoods and factual errors, and we construct adversarial samples based on GLM-130B and ChatGPT. For evaluation, we design an automated evaluation method using GPT-4 to judge whether a model output is hallucinated. We conduct extensive experiments on 24 large language models, including ERNIE-Bot, Baichuan2, ChatGLM, Qwen, SparkDesk and etc. Out of the 24 models, 18 achieved non-hallucination rates lower than 50%. This indicates that HalluQA is highly challenging. We analyze the primary types of hallucinations in different types of models and their causes. Additionally, we discuss which types of hallucinations should be prioritized for different types of models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge