Shuyue Hu
Organizing, Orchestrating, and Benchmarking Agent Skills at Ecosystem Scale
Mar 02, 2026Abstract:The rapid proliferation of Claude agent skills has raised the central question of how to effectively leverage, manage, and scale the agent skill ecosystem. In this paper, we propose AgentSkillOS, the first principled framework for skill selection, orchestration, and ecosystem-level management. AgentSkillOS comprises two stages: (i) Manage Skills, which organizes skills into a capability tree via node-level recursive categorization for efficient discovery; and (ii) Solve Tasks, which retrieves, orchestrates, and executes multiple skills through DAG-based pipelines. To evaluate the agent's ability to invoke skills, we construct a benchmark of 30 artifact-rich tasks across five categories: data computation, document creation, motion video, visual design, and web interaction. We assess the quality of task outputs using LLM-based pairwise evaluation, and the results are aggregated via a Bradley-Terry model to produce unified quality scores. Experiments across three skill ecosystem scales (200 to 200K skills) show that tree-based retrieval effectively approximates oracle skill selection, and that DAG-based orchestration substantially outperforms native flat invocation even when given the identical skill set. Our findings confirm that structured composition is the key to unlocking skill potential. Our GitHub repository is available at:https://github.com/ynulihao/AgentSkillOS.
InternAgent-1.5: A Unified Agentic Framework for Long-Horizon Autonomous Scientific Discovery
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:We introduce InternAgent-1.5, a unified system designed for end-to-end scientific discovery across computational and empirical domains. The system is built on a structured architecture composed of three coordinated subsystems for generation, verification, and evolution. These subsystems are supported by foundational capabilities for deep research, solution optimization, and long horizon memory. The architecture allows InternAgent-1.5 to operate continuously across extended discovery cycles while maintaining coherent and improving behavior. It also enables the system to coordinate computational modeling and laboratory experimentation within a single unified system. We evaluate InternAgent-1.5 on scientific reasoning benchmarks such as GAIA, HLE, GPQA, and FrontierScience, and the system achieves leading performance that demonstrates strong foundational capabilities. Beyond these benchmarks, we further assess two categories of discovery tasks. In algorithm discovery tasks, InternAgent-1.5 autonomously designs competitive methods for core machine learning problems. In empirical discovery tasks, it executes complete computational or wet lab experiments and produces scientific findings in earth, life, biological, and physical domains. Overall, these results show that InternAgent-1.5 provides a general and scalable framework for autonomous scientific discovery.
MARTI-MARS$^2$: Scaling Multi-Agent Self-Search via Reinforcement Learning for Code Generation
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:While the complex reasoning capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) has attracted significant attention, single-agent systems often encounter inherent performance ceilings in complex tasks such as code generation. Multi-agent collaboration offers a promising avenue to transcend these boundaries. However, existing frameworks typically rely on prompt-based test-time interactions or multi-role configurations trained with homogeneous parameters, limiting error correction capabilities and strategic diversity. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Agent Reinforced Training and Inference Framework with Self-Search Scaling (MARTI-MARS2), which integrates policy learning with multi-agent tree search by formulating the multi-agent collaborative exploration process as a dynamic and learnable environment. By allowing agents to iteratively explore and refine within the environment, the framework facilitates evolution from parameter-sharing homogeneous multi-role training to heterogeneous multi-agent training, breaking through single-agent capability limits. We also introduce an efficient inference strategy MARTI-MARS2-T+ to fully exploit the scaling potential of multi-agent collaboration at test time. We conduct extensive experiments across varied model scales (8B, 14B, and 32B) on challenging code generation benchmarks. Utilizing two collaborating 32B models, MARTI-MARS2 achieves 77.7%, outperforming strong baselines like GPT-5.1. Furthermore, MARTI-MARS2 reveals a novel scaling law: shifting from single-agent to homogeneous multi-role and ultimately to heterogeneous multi-agent paradigms progressively yields higher RL performance ceilings, robust TTS capabilities, and greater policy diversity, suggesting that policy diversity is critical for scaling intelligence via multi-agent reinforcement learning.
LLMRouterBench: A Massive Benchmark and Unified Framework for LLM Routing
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) routing assigns each query to the most suitable model from an ensemble. We introduce LLMRouterBench, a large-scale benchmark and unified framework for LLM routing. It comprises over 400K instances from 21 datasets and 33 models. Moreover, it provides comprehensive metrics for both performance-oriented routing and performance-cost trade-off routing, and integrates 10 representative routing baselines. Using LLMRouterBench, we systematically re-evaluate the field. While confirming strong model complementarity-the central premise of LLM routing-we find that many routing methods exhibit similar performance under unified evaluation, and several recent approaches, including commercial routers, fail to reliably outperform a simple baseline. Meanwhile, a substantial gap remains to the Oracle, driven primarily by persistent model-recall failures. We further show that backbone embedding models have limited impact, that larger ensembles exhibit diminishing returns compared to careful model curation, and that the benchmark also enables latency-aware analysis. All code and data are available at https://github.com/ynulihao/LLMRouterBench.
Beyond Gemini-3-Pro: Revisiting LLM Routing and Aggregation at Scale
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have rapidly advanced, with Gemini-3-Pro setting a new performance milestone. In this work, we explore collective intelligence as an alternative to monolithic scaling, and demonstrate that open-source LLMs' collaboration can surpass Gemini-3-Pro. We first revisit LLM routing and aggregation at scale and identify three key bottlenecks: (1) current train-free routers are limited by a query-based paradigm focusing solely on textual similarity; (2) recent aggregation methods remain largely static, failing to select appropriate aggregators for different tasks;(3) the complementarity of routing and aggregation remains underutilized. To address these problems, we introduce JiSi, a novel framework designed to release the full potential of LLMs' collaboration through three innovations: (1) Query-Response Mixed Routing capturing both semantic information and problem difficulty; (2) Support-Set-based Aggregator Selection jointly evaluating the aggregation and domain capacity of aggregators; (3) Adaptive Routing-Aggregation Switch dynamically leveraging the advantages of routing and aggregation. Comprehensive experiments on nine benchmarks demonstrate that JiSi can surpass Gemini-3-Pro with only 47% costs by orchestrating ten open-source LLMs, while outperforming mainstream baselines. It suggests that collective intelligence represents a novel path towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
Single-Agent Scaling Fails Multi-Agent Intelligence: Towards Foundation Models with Native Multi-Agent Intelligence
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) are increasingly assuming the role of the ''brain'' of AI agents. While recent efforts have begun to equip FMs with native single-agent abilities -- such as GUI interaction or integrated tool use -- we argue that the next frontier is endowing FMs with native multi-agent intelligence. We identify four core capabilities of FMs in multi-agent contexts: understanding, planning, efficient communication, and adaptation. Contrary to assumptions about the spontaneous emergence of such abilities, we provide extensive empirical evidence, across 41 large language models and 7 challenging benchmarks, showing that scaling single-agent performance alone does not automatically yield robust multi-agent intelligence. To address this gap, we outline key research directions -- spanning dataset construction, evaluation, training paradigms, and safety considerations -- for building FMs with native multi-agent intelligence.
Learning Compact Representations of LLM Abilities via Item Response Theory
Oct 01, 2025



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed a surge in the number of large language models (LLMs), yet efficiently managing and utilizing these vast resources remains a significant challenge. In this work, we explore how to learn compact representations of LLM abilities that can facilitate downstream tasks, such as model routing and performance prediction on new benchmarks. We frame this problem as estimating the probability that a given model will correctly answer a specific query. Inspired by the item response theory (IRT) in psychometrics, we model this probability as a function of three key factors: (i) the model's multi-skill ability vector, (2) the query's discrimination vector that separates models of differing skills, and (3) the query's difficulty scalar. To learn these parameters jointly, we introduce a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) network that couples model- and query-level embeddings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach leads to state-of-the-art performance in both model routing and benchmark accuracy prediction. Moreover, analysis validates that the learned parameters encode meaningful, interpretable information about model capabilities and query characteristics.
PerPilot: Personalizing VLM-based Mobile Agents via Memory and Exploration
Aug 25, 2025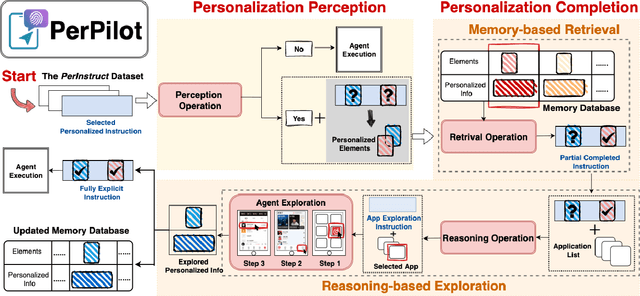
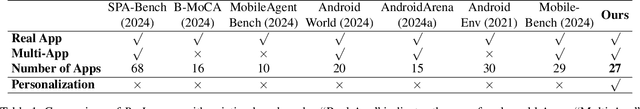
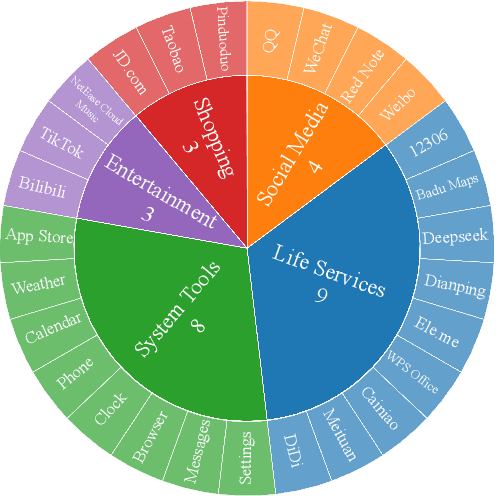
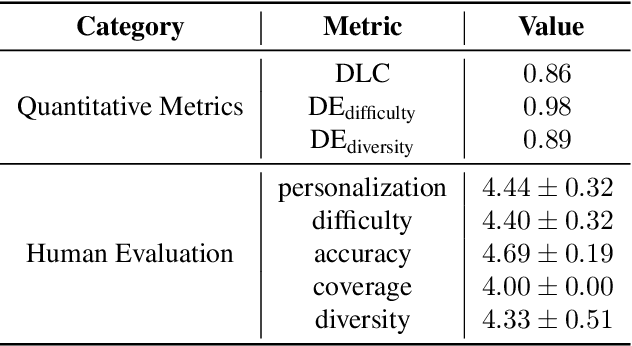
Abstract:Vision language model (VLM)-based mobile agents show great potential for assisting users in performing instruction-driven tasks. However, these agents typically struggle with personalized instructions -- those containing ambiguous, user-specific context -- a challenge that has been largely overlooked in previous research. In this paper, we define personalized instructions and introduce PerInstruct, a novel human-annotated dataset covering diverse personalized instructions across various mobile scenarios. Furthermore, given the limited personalization capabilities of existing mobile agents, we propose PerPilot, a plug-and-play framework powered by large language models (LLMs) that enables mobile agents to autonomously perceive, understand, and execute personalized user instructions. PerPilot identifies personalized elements and autonomously completes instructions via two complementary approaches: memory-based retrieval and reasoning-based exploration. Experimental results demonstrate that PerPilot effectively handles personalized tasks with minimal user intervention and progressively improves its performance with continued use, underscoring the importance of personalization-aware reasoning for next-generation mobile agents. The dataset and code are available at: https://github.com/xinwang-nwpu/PerPilot
Beyond GPT-5: Making LLMs Cheaper and Better via Performance-Efficiency Optimized Routing
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:Balancing performance and efficiency is a central challenge in large language model (LLM) advancement. GPT-5 addresses this with test-time routing, dynamically assigning queries to either an efficient or a high-capacity model during inference. In this work, we present Avengers-Pro, a test-time routing framework that ensembles LLMs of varying capacities and efficiencies, providing a unified solution for all performance-efficiency tradeoffs. The Avengers-Pro embeds and clusters incoming queries, then routes each to the most suitable model based on a performance-efficiency score. Across 6 challenging benchmarks and 8 leading models -- including GPT-5-medium, Gemini-2.5-pro, and Claude-opus-4.1 -- Avengers-Pro achieves state-of-the-art results: by varying a performance-efficiency trade-off parameter, it can surpass the strongest single model (GPT-5-medium) by +7% in average accuracy. Moreover, it can match the average accuracy of the strongest single model at 27% lower cost, and reach ~90% of that performance at 63% lower cost. Last but not least, it achieves a Pareto frontier, consistently yielding the highest accuracy for any given cost, and the lowest cost for any given accuracy, among all single models. Code is available at https://github.com/ZhangYiqun018/AvengersPro.
Regret Minimization in Population Network Games: Vanishing Heterogeneity and Convergence to Equilibria
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Understanding and predicting the behavior of large-scale multi-agents in games remains a fundamental challenge in multi-agent systems. This paper examines the role of heterogeneity in equilibrium formation by analyzing how smooth regret-matching drives a large number of heterogeneous agents with diverse initial policies toward unified behavior. By modeling the system state as a probability distribution of regrets and analyzing its evolution through the continuity equation, we uncover a key phenomenon in diverse multi-agent settings: the variance of the regret distribution diminishes over time, leading to the disappearance of heterogeneity and the emergence of consensus among agents. This universal result enables us to prove convergence to quantal response equilibria in both competitive and cooperative multi-agent settings. Our work advances the theoretical understanding of multi-agent learning and offers a novel perspective on equilibrium selection in diverse game-theoretic scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge