Shuxin Li
Tree-Based Stochastic Optimization for Solving Large-Scale Urban Network Security Games
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Urban Network Security Games (UNSGs), which model the strategic allocation of limited security resources on city road networks, are critical for urban safety. However, finding a Nash Equilibrium (NE) in large-scale UNSGs is challenging due to their massive and combinatorial action spaces. One common approach to addressing these games is the Policy-Space Response Oracle (PSRO) framework, which requires computing best responses (BR) at each iteration. However, precisely computing exact BRs is impractical in large-scale games, and employing reinforcement learning to approximate BRs inevitably introduces errors, which limits the overall effectiveness of the PSRO methods. Recent advancements in leveraging non-convex stochastic optimization to approximate an NE offer a promising alternative to the burdensome BR computation. However, utilizing existing stochastic optimization techniques with an unbiased loss function for UNSGs remains challenging because the action spaces are too vast to be effectively represented by neural networks. To address these issues, we introduce Tree-based Stochastic Optimization (TSO), a framework that bridges the gap between the stochastic optimization paradigm for NE-finding and the demands of UNSGs. Specifically, we employ the tree-based action representation that maps the whole action space onto a tree structure, addressing the challenge faced by neural networks in representing actions when the action space cannot be enumerated. We then incorporate this representation into the loss function and theoretically demonstrate its equivalence to the unbiased loss function. To further enhance the quality of the converged solution, we introduce a sample-and-prune mechanism that reduces the risk of being trapped in suboptimal local optima. Extensive experimental results indicate the superiority of TSO over other baseline algorithms in addressing the UNSGs.
VLM-3D:End-to-End Vision-Language Models for Open-World 3D Perception
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Open-set perception in complex traffic environments poses a critical challenge for autonomous driving systems, particularly in identifying previously unseen object categories, which is vital for ensuring safety. Visual Language Models (VLMs), with their rich world knowledge and strong semantic reasoning capabilities, offer new possibilities for addressing this task. However, existing approaches typically leverage VLMs to extract visual features and couple them with traditional object detectors, resulting in multi-stage error propagation that hinders perception accuracy. To overcome this limitation, we propose VLM-3D, the first end-to-end framework that enables VLMs to perform 3D geometric perception in autonomous driving scenarios. VLM-3D incorporates Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to efficiently adapt VLMs to driving tasks with minimal computational overhead, and introduces a joint semantic-geometric loss design: token-level semantic loss is applied during early training to ensure stable convergence, while 3D IoU loss is introduced in later stages to refine the accuracy of 3D bounding box predictions. Evaluations on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that the proposed joint semantic-geometric loss in VLM-3D leads to a 12.8% improvement in perception accuracy, fully validating the effectiveness and advancement of our method.
Nondeterministic Polynomial-time Problem Challenge: An Ever-Scaling Reasoning Benchmark for LLMs
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Reasoning is the fundamental capability of large language models (LLMs). Due to the rapid progress of LLMs, there are two main issues of current benchmarks: i) these benchmarks can be crushed in a short time (less than 1 year), and ii) these benchmarks may be easily hacked. To handle these issues, we propose the ever-scalingness for building the benchmarks which are uncrushable, unhackable, auto-verifiable and general. This paper presents Nondeterministic Polynomial-time Problem Challenge (NPPC), an ever-scaling reasoning benchmark for LLMs. Specifically, the NPPC has three main modules: i) npgym, which provides a unified interface of 25 well-known NP-complete problems and can generate any number of instances with any levels of complexities, ii) npsolver: which provides a unified interface to evaluate the problem instances with both online and offline models via APIs and local deployments, respectively, and iii) npeval: which provides the comprehensive and ready-to-use tools to analyze the performances of LLMs over different problems, the number of tokens, the aha moments, the reasoning errors and the solution errors. Extensive experiments over widely-used LLMs demonstrate: i) NPPC can successfully decrease the performances of advanced LLMs' performances to below 10%, demonstrating that NPPC is uncrushable, ii) DeepSeek-R1, Claude-3.7-Sonnet, and o1/o3-mini are the most powerful LLMs, where DeepSeek-R1 outperforms Claude-3.7-Sonnet and o1/o3-mini in most NP-complete problems considered, and iii) the numbers of tokens, aha moments in the advanced LLMs, e.g., Claude-3.7-Sonnet and DeepSeek-R1, are observed first to increase and then decrease when the problem instances become more and more difficult. We believe that NPPC is the first ever-scaling reasoning benchmark, serving as the uncrushable and unhackable testbed for LLMs toward artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Solving Urban Network Security Games: Learning Platform, Benchmark, and Challenge for AI Research
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:After the great achievement of solving two-player zero-sum games, more and more AI researchers focus on solving multiplayer games. To facilitate the development of designing efficient learning algorithms for solving multiplayer games, we propose a multiplayer game platform for solving Urban Network Security Games (\textbf{UNSG}) that model real-world scenarios. That is, preventing criminal activity is a highly significant responsibility assigned to police officers in cities, and police officers have to allocate their limited security resources to interdict the escaping criminal when a crime takes place in a city. This interaction between multiple police officers and the escaping criminal can be modeled as a UNSG. The variants of UNSGs can model different real-world settings, e.g., whether real-time information is available or not, and whether police officers can communicate or not. The main challenges of solving this game include the large size of the game and the co-existence of cooperation and competition. While previous efforts have been made to tackle UNSGs, they have been hampered by performance and scalability issues. Therefore, we propose an open-source UNSG platform (\textbf{GraphChase}) for designing efficient learning algorithms for solving UNSGs. Specifically, GraphChase offers a unified and flexible game environment for modeling various variants of UNSGs, supporting the development, testing, and benchmarking of algorithms. We believe that GraphChase not only facilitates the development of efficient algorithms for solving real-world problems but also paves the way for significant advancements in algorithmic development for solving general multiplayer games.
A Survey for Large Language Models in Biomedicine
Aug 29, 2024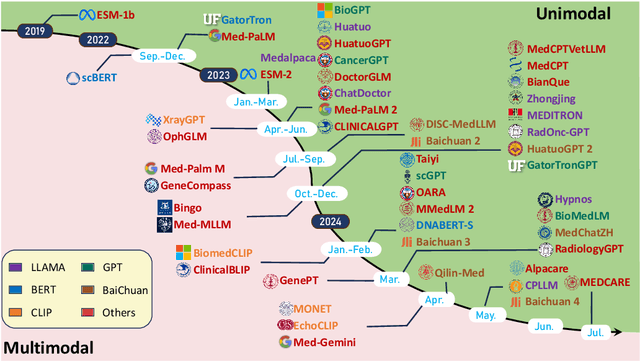
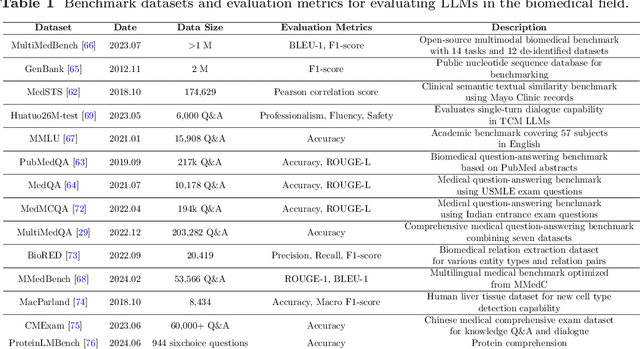
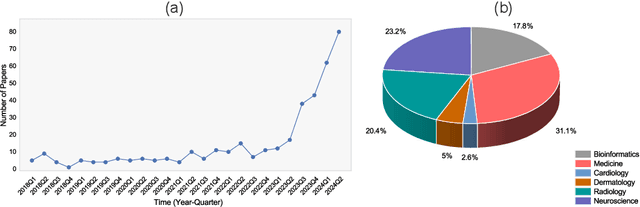
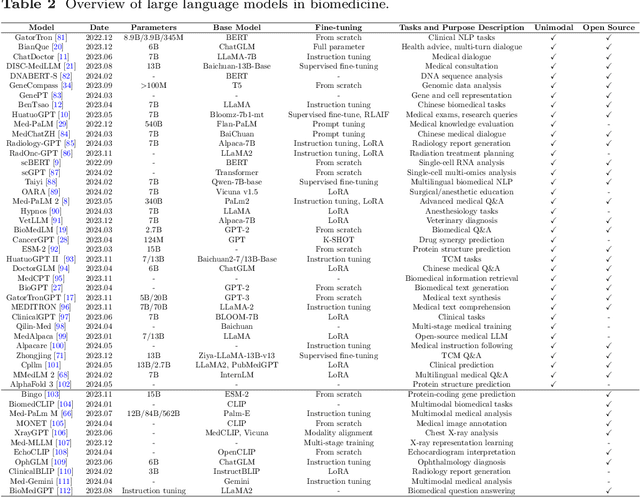
Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in large language models (LLMs) offer unprecedented natural language understanding and generation capabilities. However, existing surveys on LLMs in biomedicine often focus on specific applications or model architectures, lacking a comprehensive analysis that integrates the latest advancements across various biomedical domains. This review, based on an analysis of 484 publications sourced from databases including PubMed, Web of Science, and arXiv, provides an in-depth examination of the current landscape, applications, challenges, and prospects of LLMs in biomedicine, distinguishing itself by focusing on the practical implications of these models in real-world biomedical contexts. Firstly, we explore the capabilities of LLMs in zero-shot learning across a broad spectrum of biomedical tasks, including diagnostic assistance, drug discovery, and personalized medicine, among others, with insights drawn from 137 key studies. Then, we discuss adaptation strategies of LLMs, including fine-tuning methods for both uni-modal and multi-modal LLMs to enhance their performance in specialized biomedical contexts where zero-shot fails to achieve, such as medical question answering and efficient processing of biomedical literature. Finally, we discuss the challenges that LLMs face in the biomedicine domain including data privacy concerns, limited model interpretability, issues with dataset quality, and ethics due to the sensitive nature of biomedical data, the need for highly reliable model outputs, and the ethical implications of deploying AI in healthcare. To address these challenges, we also identify future research directions of LLM in biomedicine including federated learning methods to preserve data privacy and integrating explainable AI methodologies to enhance the transparency of LLMs.
In-Context Exploiter for Extensive-Form Games
Aug 10, 2024



Abstract:Nash equilibrium (NE) is a widely adopted solution concept in game theory due to its stability property. However, we observe that the NE strategy might not always yield the best results, especially against opponents who do not adhere to NE strategies. Based on this observation, we pose a new game-solving question: Can we learn a model that can exploit any, even NE, opponent to maximize their own utility? In this work, we make the first attempt to investigate this problem through in-context learning. Specifically, we introduce a novel method, In-Context Exploiter (ICE), to train a single model that can act as any player in the game and adaptively exploit opponents entirely by in-context learning. Our ICE algorithm involves generating diverse opponent strategies, collecting interactive history training data by a reinforcement learning algorithm, and training a transformer-based agent within a well-designed curriculum learning framework. Finally, comprehensive experimental results validate the effectiveness of our ICE algorithm, showcasing its in-context learning ability to exploit any unknown opponent, thereby positively answering our initial game-solving question.
Configurable Mirror Descent: Towards a Unification of Decision Making
May 20, 2024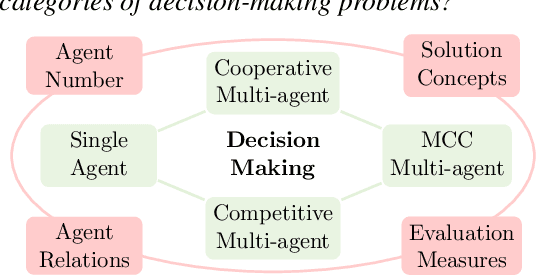



Abstract:Decision-making problems, categorized as single-agent, e.g., Atari, cooperative multi-agent, e.g., Hanabi, competitive multi-agent, e.g., Hold'em poker, and mixed cooperative and competitive, e.g., football, are ubiquitous in the real world. Various methods are proposed to address the specific decision-making problems. Despite the successes in specific categories, these methods typically evolve independently and cannot generalize to other categories. Therefore, a fundamental question for decision-making is: \emph{Can we develop \textbf{a single algorithm} to tackle \textbf{ALL} categories of decision-making problems?} There are several main challenges to address this question: i) different decision-making categories involve different numbers of agents and different relationships between agents, ii) different categories have different solution concepts and evaluation measures, and iii) there lacks a comprehensive benchmark covering all the categories. This work presents a preliminary attempt to address the question with three main contributions. i) We propose the generalized mirror descent (GMD), a generalization of MD variants, which considers multiple historical policies and works with a broader class of Bregman divergences. ii) We propose the configurable mirror descent (CMD) where a meta-controller is introduced to dynamically adjust the hyper-parameters in GMD conditional on the evaluation measures. iii) We construct the \textsc{GameBench} with 15 academic-friendly games across different decision-making categories. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CMD achieves empirically competitive or better outcomes compared to baselines while providing the capability of exploring diverse dimensions of decision making.
Grasper: A Generalist Pursuer for Pursuit-Evasion Problems
Apr 19, 2024
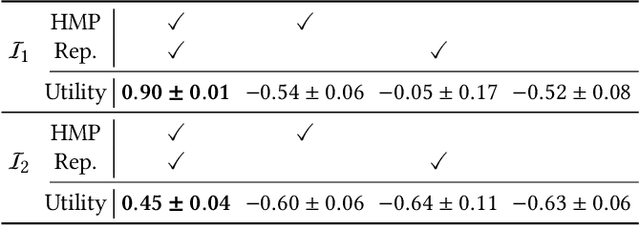

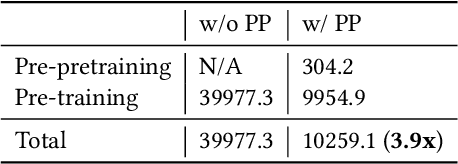
Abstract:Pursuit-evasion games (PEGs) model interactions between a team of pursuers and an evader in graph-based environments such as urban street networks. Recent advancements have demonstrated the effectiveness of the pre-training and fine-tuning paradigm in PSRO to improve scalability in solving large-scale PEGs. However, these methods primarily focus on specific PEGs with fixed initial conditions that may vary substantially in real-world scenarios, which significantly hinders the applicability of the traditional methods. To address this issue, we introduce Grasper, a GeneRAlist purSuer for Pursuit-Evasion pRoblems, capable of efficiently generating pursuer policies tailored to specific PEGs. Our contributions are threefold: First, we present a novel architecture that offers high-quality solutions for diverse PEGs, comprising critical components such as (i) a graph neural network (GNN) to encode PEGs into hidden vectors, and (ii) a hypernetwork to generate pursuer policies based on these hidden vectors. As a second contribution, we develop an efficient three-stage training method involving (i) a pre-pretraining stage for learning robust PEG representations through self-supervised graph learning techniques like GraphMAE, (ii) a pre-training stage utilizing heuristic-guided multi-task pre-training (HMP) where heuristic-derived reference policies (e.g., through Dijkstra's algorithm) regularize pursuer policies, and (iii) a fine-tuning stage that employs PSRO to generate pursuer policies on designated PEGs. Finally, we perform extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world maps, showcasing Grasper's significant superiority over baselines in terms of solution quality and generalizability. We demonstrate that Grasper provides a versatile approach for solving pursuit-evasion problems across a broad range of scenarios, enabling practical deployment in real-world situations.
Self-adaptive PSRO: Towards an Automatic Population-based Game Solver
Apr 17, 2024Abstract:Policy-Space Response Oracles (PSRO) as a general algorithmic framework has achieved state-of-the-art performance in learning equilibrium policies of two-player zero-sum games. However, the hand-crafted hyperparameter value selection in most of the existing works requires extensive domain knowledge, forming the main barrier to applying PSRO to different games. In this work, we make the first attempt to investigate the possibility of self-adaptively determining the optimal hyperparameter values in the PSRO framework. Our contributions are three-fold: (1) Using several hyperparameters, we propose a parametric PSRO that unifies the gradient descent ascent (GDA) and different PSRO variants. (2) We propose the self-adaptive PSRO (SPSRO) by casting the hyperparameter value selection of the parametric PSRO as a hyperparameter optimization (HPO) problem where our objective is to learn an HPO policy that can self-adaptively determine the optimal hyperparameter values during the running of the parametric PSRO. (3) To overcome the poor performance of online HPO methods, we propose a novel offline HPO approach to optimize the HPO policy based on the Transformer architecture. Experiments on various two-player zero-sum games demonstrate the superiority of SPSRO over different baselines.
Population-size-Aware Policy Optimization for Mean-Field Games
Feb 07, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we attempt to bridge the two fields of finite-agent and infinite-agent games, by studying how the optimal policies of agents evolve with the number of agents (population size) in mean-field games, an agent-centric perspective in contrast to the existing works focusing typically on the convergence of the empirical distribution of the population. To this end, the premise is to obtain the optimal policies of a set of finite-agent games with different population sizes. However, either deriving the closed-form solution for each game is theoretically intractable, training a distinct policy for each game is computationally intensive, or directly applying the policy trained in a game to other games is sub-optimal. We address these challenges through the Population-size-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO). Our contributions are three-fold. First, to efficiently generate efficient policies for games with different population sizes, we propose PAPO, which unifies two natural options (augmentation and hypernetwork) and achieves significantly better performance. PAPO consists of three components: i) the population-size encoding which transforms the original value of population size to an equivalent encoding to avoid training collapse, ii) a hypernetwork to generate a distinct policy for each game conditioned on the population size, and iii) the population size as an additional input to the generated policy. Next, we construct a multi-task-based training procedure to efficiently train the neural networks of PAPO by sampling data from multiple games with different population sizes. Finally, extensive experiments on multiple environments show the significant superiority of PAPO over baselines, and the analysis of the evolution of the generated policies further deepens our understanding of the two fields of finite-agent and infinite-agent games.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge