Zhiyao Cui
PerPilot: Personalizing VLM-based Mobile Agents via Memory and Exploration
Aug 25, 2025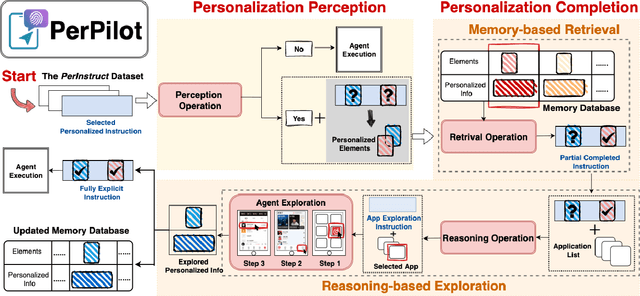
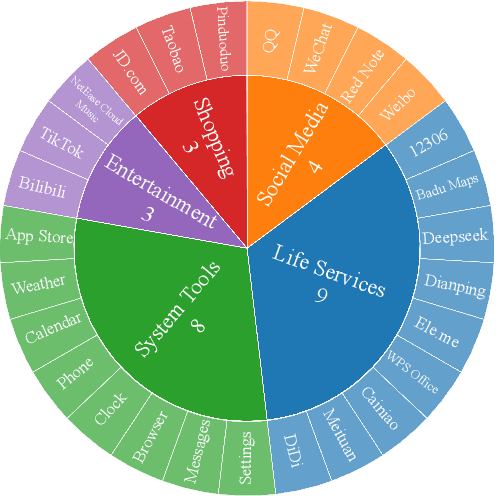
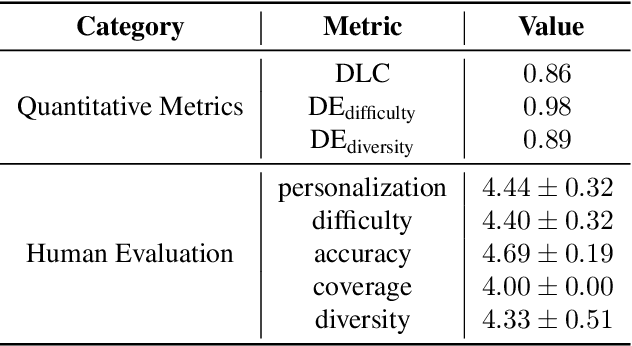
Abstract:Vision language model (VLM)-based mobile agents show great potential for assisting users in performing instruction-driven tasks. However, these agents typically struggle with personalized instructions -- those containing ambiguous, user-specific context -- a challenge that has been largely overlooked in previous research. In this paper, we define personalized instructions and introduce PerInstruct, a novel human-annotated dataset covering diverse personalized instructions across various mobile scenarios. Furthermore, given the limited personalization capabilities of existing mobile agents, we propose PerPilot, a plug-and-play framework powered by large language models (LLMs) that enables mobile agents to autonomously perceive, understand, and execute personalized user instructions. PerPilot identifies personalized elements and autonomously completes instructions via two complementary approaches: memory-based retrieval and reasoning-based exploration. Experimental results demonstrate that PerPilot effectively handles personalized tasks with minimal user intervention and progressively improves its performance with continued use, underscoring the importance of personalization-aware reasoning for next-generation mobile agents. The dataset and code are available at: https://github.com/xinwang-nwpu/PerPilot
If Multi-Agent Debate is the Answer, What is the Question?
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent debate (MAD) has emerged as a promising approach to enhance the factual accuracy and reasoning quality of large language models (LLMs) by engaging multiple agents in iterative discussions during inference. Despite its potential, we argue that current MAD research suffers from critical shortcomings in evaluation practices, including limited dataset overlap and inconsistent baselines, raising significant concerns about generalizability. Correspondingly, this paper presents a systematic evaluation of five representative MAD methods across nine benchmarks using four foundational models. Surprisingly, our findings reveal that MAD methods fail to reliably outperform simple single-agent baselines such as Chain-of-Thought and Self-Consistency, even when consuming additional inference-time computation. From our analysis, we found that model heterogeneity can significantly improve MAD frameworks. We propose Heter-MAD enabling a single LLM agent to access the output from heterogeneous foundation models, which boosts the performance of current MAD frameworks. Finally, we outline potential directions for advancing MAD, aiming to spark a broader conversation and inspire future work in this area.
Emergence of Social Norms in Large Language Model-based Agent Societies
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:The emergence of social norms has attracted much interest in a wide array of disciplines, ranging from social science and cognitive science to artificial intelligence. In this paper, we propose the first generative agent architecture that empowers the emergence of social norms within a population of large language model-based agents. Our architecture, named CRSEC, consists of four modules: Creation & Representation, Spreading, Evaluation, and Compliance. Our architecture addresses several important aspects of the emergent processes all in one: (i) where social norms come from, (ii) how they are formally represented, (iii) how they spread through agents' communications and observations, (iv) how they are examined with a sanity check and synthesized in the long term, and (v) how they are incorporated into agents' planning and actions. Our experiments deployed in the Smallville sandbox game environment demonstrate the capability of our architecture to establish social norms and reduce social conflicts within large language model-based multi-agent systems. The positive outcomes of our human evaluation, conducted with 30 evaluators, further affirm the effectiveness of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge