Yunxiang Li
TreePS-RAG: Tree-based Process Supervision for Reinforcement Learning in Agentic RAG
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Agentic retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) formulates question answering as a multi-step interaction between reasoning and information retrieval, and has recently been advanced by reinforcement learning (RL) with outcome-based supervision. While effective, relying solely on sparse final rewards limits step-wise credit assignment and provides weak guidance for intermediate reasoning and actions. Recent efforts explore process-level supervision, but typically depend on offline constructed training data, which risks distribution shift, or require costly intermediate annotations. We present TreePS-RAG, an online, tree-based RL framework for agentic RAG that enables step-wise credit assignment while retaining standard outcome-only rewards. Our key insight is to model agentic RAG reasoning as a rollout tree, where each reasoning step naturally maps to a node. This tree structure allows step utility to be estimated via Monte Carlo estimation over its descendant outcomes, yielding fine-grained process advantages without requiring intermediate labels. To make this paradigm practical, we introduce an efficient online tree construction strategy that preserves exploration diversity under a constrained computational budget. With a rollout cost comparable to strong baselines like Search-R1, experiments on seven multi-hop and general QA benchmarks across multiple model scales show that TreePS-RAG consistently and significantly outperforms both outcome-supervised and leading process-supervised RL methods.
Scale-aware Adaptive Supervised Network with Limited Medical Annotations
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Medical image segmentation faces critical challenges in semi-supervised learning scenarios due to severe annotation scarcity requiring expert radiological knowledge, significant inter-annotator variability across different viewpoints and expertise levels, and inadequate multi-scale feature integration for precise boundary delineation in complex anatomical structures. Existing semi-supervised methods demonstrate substantial performance degradation compared to fully supervised approaches, particularly in small target segmentation and boundary refinement tasks. To address these fundamental challenges, we propose SASNet (Scale-aware Adaptive Supervised Network), a dual-branch architecture that leverages both low-level and high-level feature representations through novel scale-aware adaptive reweight mechanisms. Our approach introduces three key methodological innovations, including the Scale-aware Adaptive Reweight strategy that dynamically weights pixel-wise predictions using temporal confidence accumulation, the View Variance Enhancement mechanism employing 3D Fourier domain transformations to simulate annotation variability, and segmentation-regression consistency learning through signed distance map algorithms for enhanced boundary precision. These innovations collectively address the core limitations of existing semi-supervised approaches by integrating spatial, temporal, and geometric consistency principles within a unified optimization framework. Comprehensive evaluation across LA, Pancreas-CT, and BraTS datasets demonstrates that SASNet achieves superior performance with limited labeled data, surpassing state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods while approaching fully supervised performance levels. The source code for SASNet is available at https://github.com/HUANGLIZI/SASNet.
Multi-directional Safe Rectangle Corridor-Based MPC for Nonholonomic Robots Navigation in Cluttered Environment
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) have become indispensable in industrial applications due to their operational flexibility and efficiency. Navigation serves as a crucial technical foundation for accomplishing complex tasks. However, navigating AMRs in dense, cluttered, and semi-structured environments remains challenging, primarily due to nonholonomic vehicle dynamics, interactions with mixed static/dynamic obstacles, and the non-convex constrained nature of such operational spaces. To solve these problems, this paper proposes an Improved Sequential Model Predictive Control (ISMPC) navigation framework that systematically reformulates navigation tasks as sequential switched optimal control problems. The framework addresses the aforementioned challenges through two key innovations: 1) Implementation of a Multi-Directional Safety Rectangular Corridor (MDSRC) algorithm, which encodes the free space through rectangular convex regions to avoid collision with static obstacles, eliminating redundant computational burdens and accelerating solver convergence; 2) A sequential MPC navigation framework that integrates corridor constraints with barrier function constraints is proposed to achieve static and dynamic obstacle avoidance. The ISMPC navigation framework enables direct velocity generation for AMRs, simplifying traditional navigation algorithm architectures. Comparative experiments demonstrate the framework's superiority in free-space utilization ( an increase of 41.05$\%$ in the average corridor area) while maintaining real-time computational performance (average corridors generation latency of 3 ms).
RAG-Zeval: Towards Robust and Interpretable Evaluation on RAG Responses through End-to-End Rule-Guided Reasoning
May 28, 2025



Abstract:Robust evaluation is critical for deploying trustworthy retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems. However, current LLM-based evaluation frameworks predominantly rely on directly prompting resource-intensive models with complex multi-stage prompts, underutilizing models' reasoning capabilities and introducing significant computational cost. In this paper, we present RAG-Zeval (RAG-Zero Evaluator), a novel end-to-end framework that formulates faithfulness and correctness evaluation as a rule-guided reasoning task. Our approach trains evaluators with reinforcement learning, facilitating compact models to generate comprehensive and sound assessments with detailed explanation in one-pass. We introduce a ranking-based outcome reward mechanism, using preference judgments rather than absolute scores, to address the challenge of obtaining precise pointwise reward signals. To this end, we synthesize the ranking references by generating quality-controlled responses with zero human annotation. Experiments demonstrate RAG-Zeval's superior performance, achieving the strongest correlation with human judgments and outperforming baselines that rely on LLMs with 10-100 times more parameters. Our approach also exhibits superior interpretability in response evaluation.
STPNet: Scale-aware Text Prompt Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Accurate segmentation of lesions plays a critical role in medical image analysis and diagnosis. Traditional segmentation approaches that rely solely on visual features often struggle with the inherent uncertainty in lesion distribution and size. To address these issues, we propose STPNet, a Scale-aware Text Prompt Network that leverages vision-language modeling to enhance medical image segmentation. Our approach utilizes multi-scale textual descriptions to guide lesion localization and employs retrieval-segmentation joint learning to bridge the semantic gap between visual and linguistic modalities. Crucially, STPNet retrieves relevant textual information from a specialized medical text repository during training, eliminating the need for text input during inference while retaining the benefits of cross-modal learning. We evaluate STPNet on three datasets: COVID-Xray, COVID-CT, and Kvasir-SEG. Experimental results show that our vision-language approach outperforms state-of-the-art segmentation methods, demonstrating the effectiveness of incorporating textual semantic knowledge into medical image analysis. The code has been made publicly on https://github.com/HUANGLIZI/STPNet.
ReMA: Learning to Meta-think for LLMs with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Recent research on Reasoning of Large Language Models (LLMs) has sought to further enhance their performance by integrating meta-thinking -- enabling models to monitor, evaluate, and control their reasoning processes for more adaptive and effective problem-solving. However, current single-agent work lacks a specialized design for acquiring meta-thinking, resulting in low efficacy. To address this challenge, we introduce Reinforced Meta-thinking Agents (ReMA), a novel framework that leverages Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) to elicit meta-thinking behaviors, encouraging LLMs to think about thinking. ReMA decouples the reasoning process into two hierarchical agents: a high-level meta-thinking agent responsible for generating strategic oversight and plans, and a low-level reasoning agent for detailed executions. Through iterative reinforcement learning with aligned objectives, these agents explore and learn collaboration, leading to improved generalization and robustness. Experimental results demonstrate that ReMA outperforms single-agent RL baselines on complex reasoning tasks, including competitive-level mathematical benchmarks and LLM-as-a-Judge benchmarks. Comprehensive ablation studies further illustrate the evolving dynamics of each distinct agent, providing valuable insights into how the meta-thinking reasoning process enhances the reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
Generate, Discriminate, Evolve: Enhancing Context Faithfulness via Fine-Grained Sentence-Level Self-Evolution
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:Improving context faithfulness in large language models is essential for developing trustworthy retrieval augmented generation systems and mitigating hallucinations, especially in long-form question answering (LFQA) tasks or scenarios involving knowledge conflicts. Existing methods either intervene LLMs only at inference without addressing their inherent limitations or overlook the potential for self-improvement. In this paper, we introduce GenDiE (Generate, Discriminate, Evolve), a novel self-evolving framework that enhances context faithfulness through fine-grained sentence-level optimization. GenDiE combines both generative and discriminative training, equipping LLMs with self-generation and self-scoring capabilities to facilitate iterative self-evolution. This supports both data construction for model alignment and score-guided search during inference. Furthermore, by treating each sentence in a response as an independent optimization unit, GenDiE effectively addresses the limitations of previous approaches that optimize at the holistic answer level, which may miss unfaithful details. Experiments on ASQA (in-domain LFQA) and ConFiQA (out-of-domain counterfactual QA) datasets demonstrate that GenDiE surpasses various baselines in both faithfulness and correctness, and exhibits robust performance for domain adaptation.
Devising a Set of Compact and Explainable Spoken Language Feature for Screening Alzheimer's Disease
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:Alzheimer's disease (AD) has become one of the most significant health challenges in an aging society. The use of spoken language-based AD detection methods has gained prevalence due to their scalability due to their scalability. Based on the Cookie Theft picture description task, we devised an explainable and effective feature set that leverages the visual capabilities of a large language model (LLM) and the Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) model. Our experimental results show that the newly proposed features consistently outperform traditional linguistic features across two different classifiers with high dimension efficiency. Our new features can be well explained and interpreted step by step which enhance the interpretability of automatic AD screening.
Single-Point Supervised High-Resolution Dynamic Network for Infrared Small Target Detection
Aug 04, 2024



Abstract:Infrared small target detection (IRSTD) tasks are extremely challenging for two main reasons: 1) it is difficult to obtain accurate labelling information that is critical to existing methods, and 2) infrared (IR) small target information is easily lost in deep networks. To address these issues, we propose a single-point supervised high-resolution dynamic network (SSHD-Net). In contrast to existing methods, we achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) detection performance using only single-point supervision. Specifically, we first design a high-resolution cross-feature extraction module (HCEM), that achieves bi-directional feature interaction through stepped feature cascade channels (SFCC). It balances network depth and feature resolution to maintain deep IR small-target information. Secondly, the effective integration of global and local features is achieved through the dynamic coordinate fusion module (DCFM), which enhances the anti-interference ability in complex backgrounds. In addition, we introduce the high-resolution multilevel residual module (HMRM) to enhance the semantic information extraction capability. Finally, we design the adaptive target localization detection head (ATLDH) to improve detection accuracy. Experiments on the publicly available datasets NUDT-SIRST and IRSTD-1k demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Compared to other SOTA methods, our method can achieve better detection performance with only a single point of supervision.
STS MICCAI 2023 Challenge: Grand challenge on 2D and 3D semi-supervised tooth segmentation
Jul 18, 2024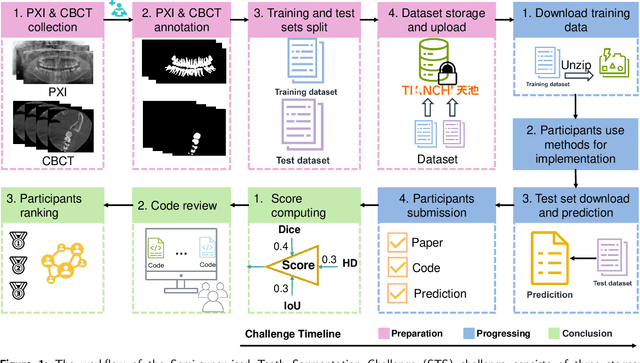
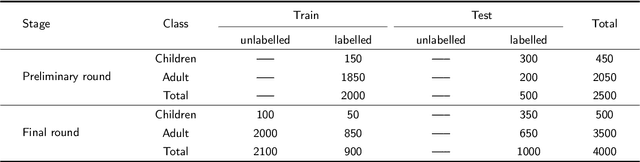
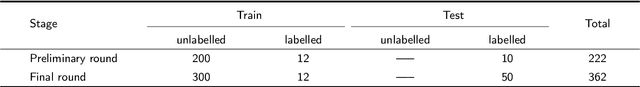
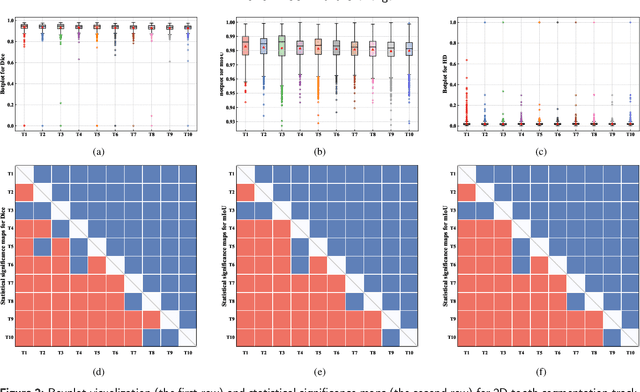
Abstract:Computer-aided design (CAD) tools are increasingly popular in modern dental practice, particularly for treatment planning or comprehensive prognosis evaluation. In particular, the 2D panoramic X-ray image efficiently detects invisible caries, impacted teeth and supernumerary teeth in children, while the 3D dental cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) is widely used in orthodontics and endodontics due to its low radiation dose. However, there is no open-access 2D public dataset for children's teeth and no open 3D dental CBCT dataset, which limits the development of automatic algorithms for segmenting teeth and analyzing diseases. The Semi-supervised Teeth Segmentation (STS) Challenge, a pioneering event in tooth segmentation, was held as a part of the MICCAI 2023 ToothFairy Workshop on the Alibaba Tianchi platform. This challenge aims to investigate effective semi-supervised tooth segmentation algorithms to advance the field of dentistry. In this challenge, we provide two modalities including the 2D panoramic X-ray images and the 3D CBCT tooth volumes. In Task 1, the goal was to segment tooth regions in panoramic X-ray images of both adult and pediatric teeth. Task 2 involved segmenting tooth sections using CBCT volumes. Limited labelled images with mostly unlabelled ones were provided in this challenge prompt using semi-supervised algorithms for training. In the preliminary round, the challenge received registration and result submission by 434 teams, with 64 advancing to the final round. This paper summarizes the diverse methods employed by the top-ranking teams in the STS MICCAI 2023 Challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge