Xiaobing Liu
Goku: Flow Based Video Generative Foundation Models
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces Goku, a state-of-the-art family of joint image-and-video generation models leveraging rectified flow Transformers to achieve industry-leading performance. We detail the foundational elements enabling high-quality visual generation, including the data curation pipeline, model architecture design, flow formulation, and advanced infrastructure for efficient and robust large-scale training. The Goku models demonstrate superior performance in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, setting new benchmarks across major tasks. Specifically, Goku achieves 0.76 on GenEval and 83.65 on DPG-Bench for text-to-image generation, and 84.85 on VBench for text-to-video tasks. We believe that this work provides valuable insights and practical advancements for the research community in developing joint image-and-video generation models.
Infinity: Scaling Bitwise AutoRegressive Modeling for High-Resolution Image Synthesis
Dec 05, 2024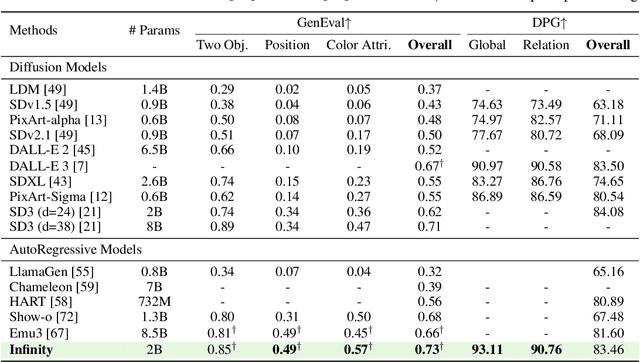

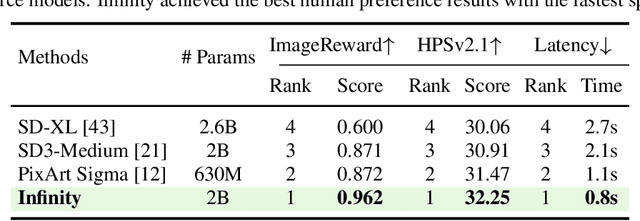

Abstract:We present Infinity, a Bitwise Visual AutoRegressive Modeling capable of generating high-resolution, photorealistic images following language instruction. Infinity redefines visual autoregressive model under a bitwise token prediction framework with an infinite-vocabulary tokenizer & classifier and bitwise self-correction mechanism, remarkably improving the generation capacity and details. By theoretically scaling the tokenizer vocabulary size to infinity and concurrently scaling the transformer size, our method significantly unleashes powerful scaling capabilities compared to vanilla VAR. Infinity sets a new record for autoregressive text-to-image models, outperforming top-tier diffusion models like SD3-Medium and SDXL. Notably, Infinity surpasses SD3-Medium by improving the GenEval benchmark score from 0.62 to 0.73 and the ImageReward benchmark score from 0.87 to 0.96, achieving a win rate of 66%. Without extra optimization, Infinity generates a high-quality 1024x1024 image in 0.8 seconds, making it 2.6x faster than SD3-Medium and establishing it as the fastest text-to-image model. Models and codes will be released to promote further exploration of Infinity for visual generation and unified tokenizer modeling.
One Backward from Ten Forward, Subsampling for Large-Scale Deep Learning
Apr 27, 2021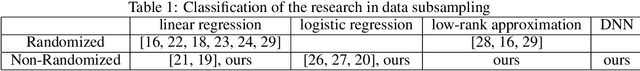
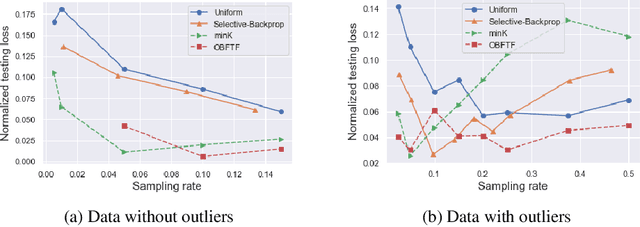

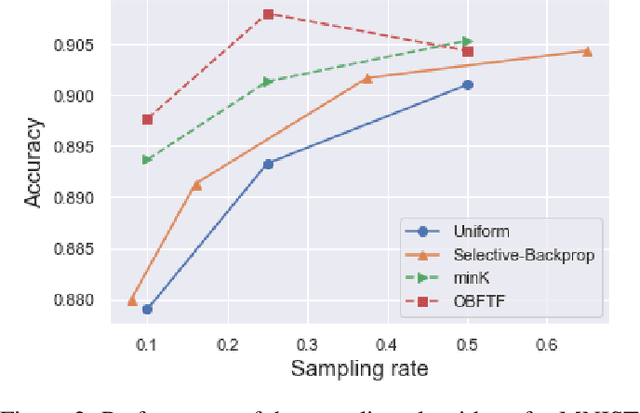
Abstract:Deep learning models in large-scale machine learning systems are often continuously trained with enormous data from production environments. The sheer volume of streaming training data poses a significant challenge to real-time training subsystems and ad-hoc sampling is the standard practice. Our key insight is that these deployed ML systems continuously perform forward passes on data instances during inference, but ad-hoc sampling does not take advantage of this substantial computational effort. Therefore, we propose to record a constant amount of information per instance from these forward passes. The extra information measurably improves the selection of which data instances should participate in forward and backward passes. A novel optimization framework is proposed to analyze this problem and we provide an efficient approximation algorithm under the framework of Mini-batch gradient descent as a practical solution. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework and algorithm on several large-scale classification and regression tasks, when compared with competitive baselines widely used in industry.
Deep Retrieval: An End-to-End Learnable Structure Model for Large-Scale Recommendations
Jul 12, 2020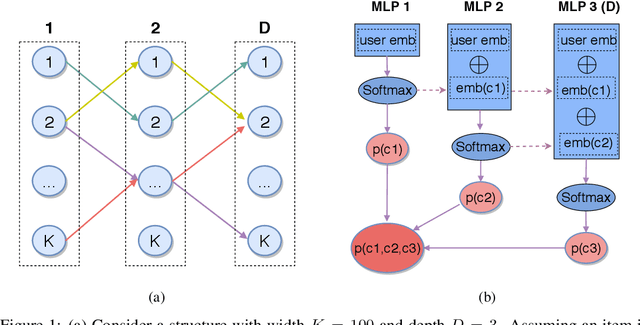
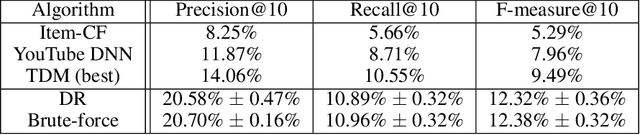
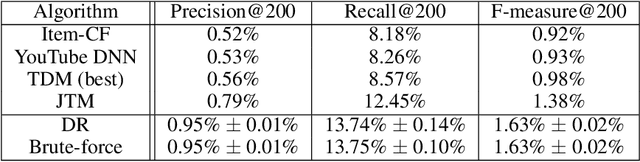
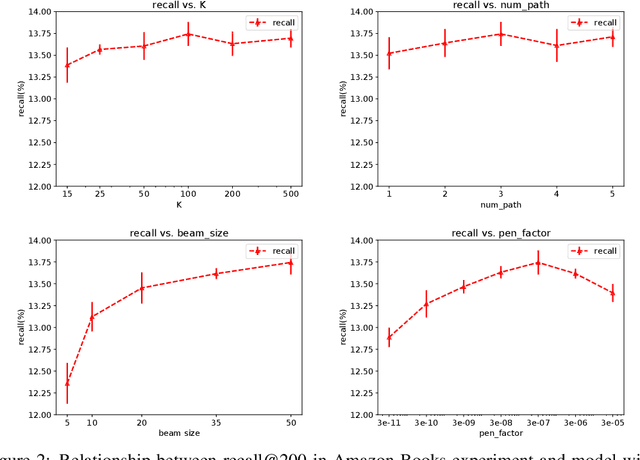
Abstract:One of the core problems in large-scale recommendations is to retrieve top relevant candidates accurately and efficiently, preferably in sub-linear time. Previous approaches are mostly based on a two-step procedure: first learn an inner-product model and then use maximum inner product search (MIPS) algorithms to search top candidates, leading to potential loss of retrieval accuracy. In this paper, we present Deep Retrieval (DR), an end-to-end learnable structure model for large-scale recommendations. DR encodes all candidates into a discrete latent space. Those latent codes for the candidates are model parameters and to be learnt together with other neural network parameters to maximize the same objective function. With the model learnt, a beam search over the latent codes is performed to retrieve the top candidates. Empirically, we showed that DR, with sub-linear computational complexity, can achieve almost the same accuracy as the brute-force baseline.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Online Advertising in Recommender Systems
Sep 10, 2019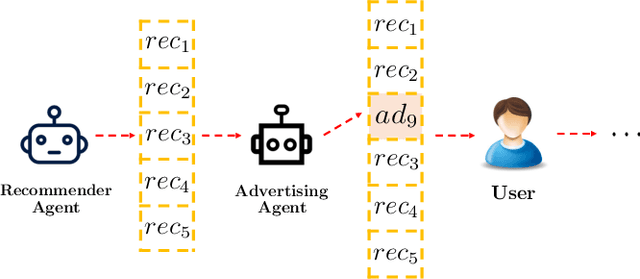

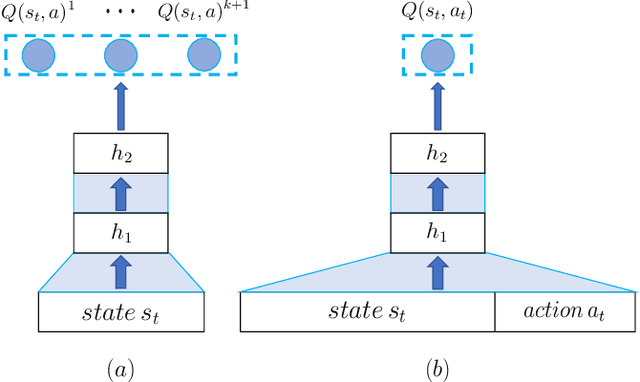
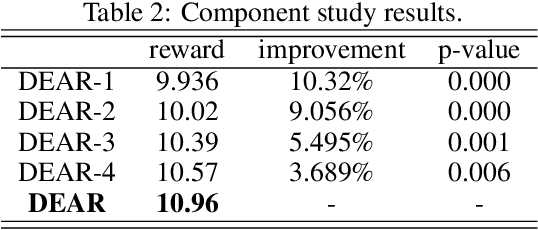
Abstract:With the recent prevalence of Reinforcement Learning (RL), there have been tremendous interests in utilizing RL for online advertising in recommendation platforms (e.g. e-commerce and news feed sites). However, most RL-based advertising algorithms focus on solely optimizing the revenue of ads while ignoring possible negative influence of ads on user experience of recommended items (products, articles and videos). Developing an optimal advertising algorithm in recommendations faces immense challenges because interpolating ads improperly or too frequently may decrease user experience, while interpolating fewer ads will reduce the advertising revenue. Thus, in this paper, we propose a novel advertising strategy for the rec/ads trade-off. To be specific, we develop a reinforcement learning based framework that can continuously update its advertising strategies and maximize reward in the long run. Given a recommendation list, we design a novel Deep Q-network architecture that can determine three internally related tasks jointly, i.e., (i) whether to interpolate an ad or not in the recommendation list, and if yes, (ii) the optimal ad and (iii) the optimal location to interpolate. The experimental results based on real-world data demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Lingvo: a Modular and Scalable Framework for Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling
Feb 21, 2019
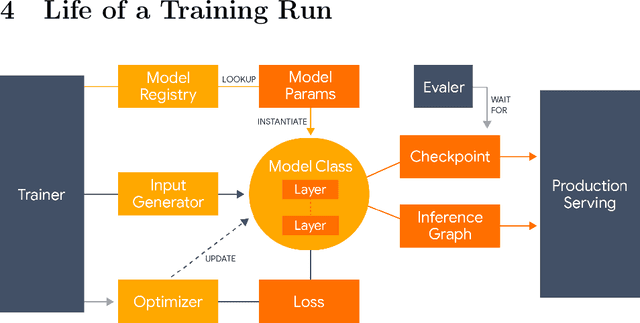
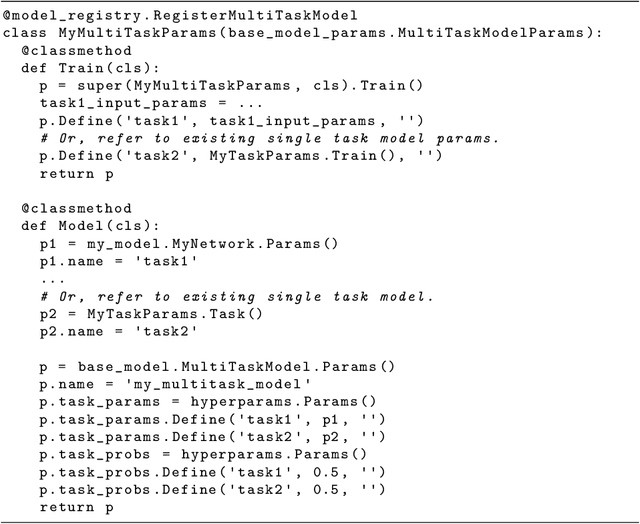
Abstract:Lingvo is a Tensorflow framework offering a complete solution for collaborative deep learning research, with a particular focus towards sequence-to-sequence models. Lingvo models are composed of modular building blocks that are flexible and easily extensible, and experiment configurations are centralized and highly customizable. Distributed training and quantized inference are supported directly within the framework, and it contains existing implementations of a large number of utilities, helper functions, and the newest research ideas. Lingvo has been used in collaboration by dozens of researchers in more than 20 papers over the last two years. This document outlines the underlying design of Lingvo and serves as an introduction to the various pieces of the framework, while also offering examples of advanced features that showcase the capabilities of the framework.
Understanding and Improving Recurrent Networks for Human Activity Recognition by Continuous Attention
Oct 07, 2018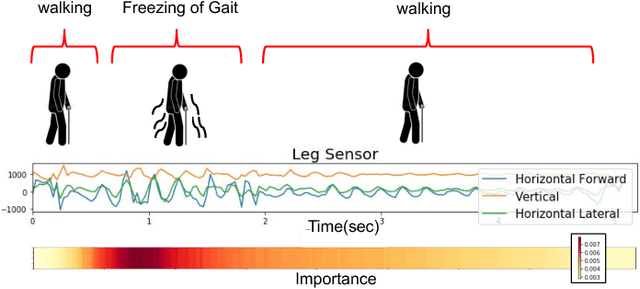
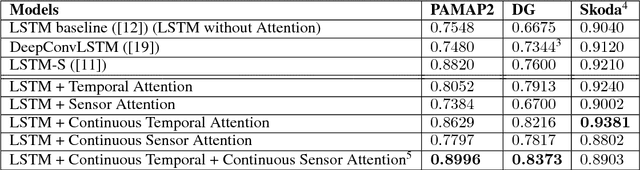
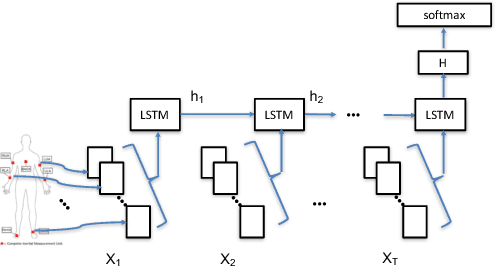
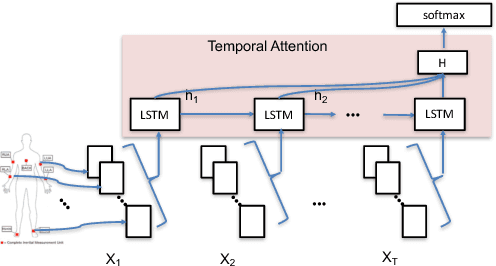
Abstract:Deep neural networks, including recurrent networks, have been successfully applied to human activity recognition. Unfortunately, the final representation learned by recurrent networks might encode some noise (irrelevant signal components, unimportant sensor modalities, etc.). Besides, it is difficult to interpret the recurrent networks to gain insight into the models' behavior. To address these issues, we propose two attention models for human activity recognition: temporal attention and sensor attention. These two mechanisms adaptively focus on important signals and sensor modalities. To further improve the understandability and mean F1 score, we add continuity constraints, considering that continuous sensor signals are more robust than discrete ones. We evaluate the approaches on three datasets and obtain state-of-the-art results. Furthermore, qualitative analysis shows that the attention learned by the models agree well with human intuition.
* 8 pages. published in The International Symposium on Wearable Computers (ISWC) 2018
Scalable and accurate deep learning for electronic health records
May 11, 2018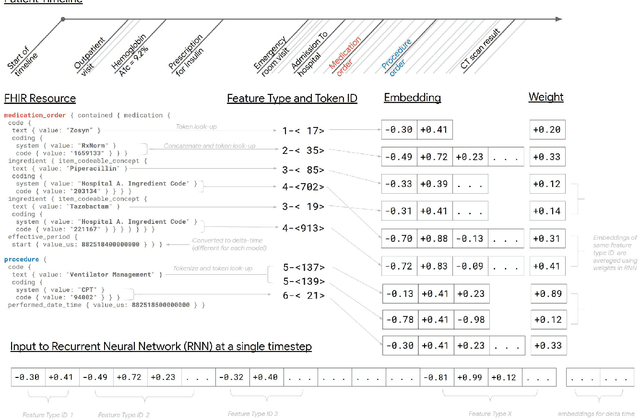
Abstract:Predictive modeling with electronic health record (EHR) data is anticipated to drive personalized medicine and improve healthcare quality. Constructing predictive statistical models typically requires extraction of curated predictor variables from normalized EHR data, a labor-intensive process that discards the vast majority of information in each patient's record. We propose a representation of patients' entire, raw EHR records based on the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. We demonstrate that deep learning methods using this representation are capable of accurately predicting multiple medical events from multiple centers without site-specific data harmonization. We validated our approach using de-identified EHR data from two U.S. academic medical centers with 216,221 adult patients hospitalized for at least 24 hours. In the sequential format we propose, this volume of EHR data unrolled into a total of 46,864,534,945 data points, including clinical notes. Deep learning models achieved high accuracy for tasks such as predicting in-hospital mortality (AUROC across sites 0.93-0.94), 30-day unplanned readmission (AUROC 0.75-0.76), prolonged length of stay (AUROC 0.85-0.86), and all of a patient's final discharge diagnoses (frequency-weighted AUROC 0.90). These models outperformed state-of-the-art traditional predictive models in all cases. We also present a case-study of a neural-network attribution system, which illustrates how clinicians can gain some transparency into the predictions. We believe that this approach can be used to create accurate and scalable predictions for a variety of clinical scenarios, complete with explanations that directly highlight evidence in the patient's chart.
* Published version from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41746-018-0029-1
Google's Neural Machine Translation System: Bridging the Gap between Human and Machine Translation
Oct 08, 2016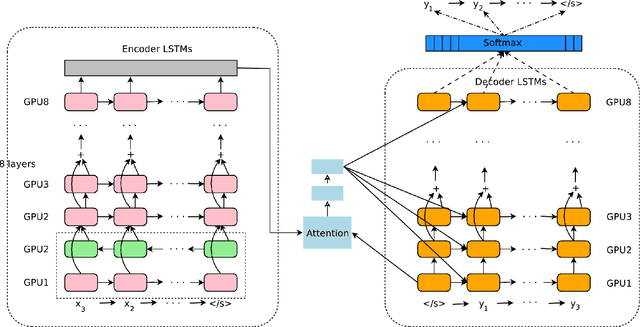
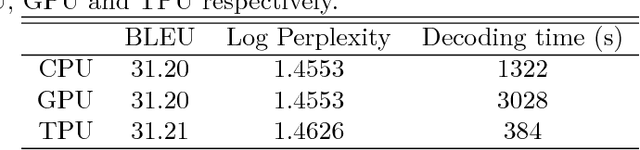
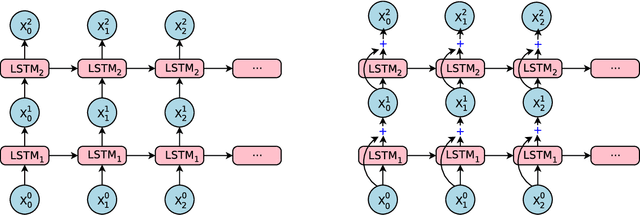
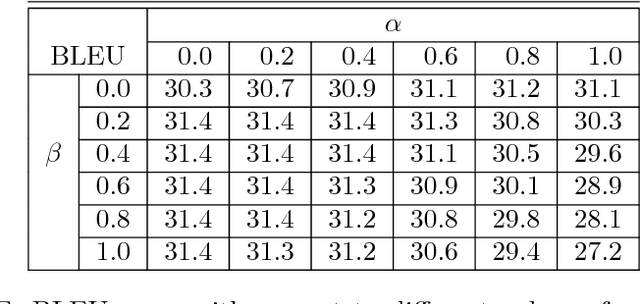
Abstract:Neural Machine Translation (NMT) is an end-to-end learning approach for automated translation, with the potential to overcome many of the weaknesses of conventional phrase-based translation systems. Unfortunately, NMT systems are known to be computationally expensive both in training and in translation inference. Also, most NMT systems have difficulty with rare words. These issues have hindered NMT's use in practical deployments and services, where both accuracy and speed are essential. In this work, we present GNMT, Google's Neural Machine Translation system, which attempts to address many of these issues. Our model consists of a deep LSTM network with 8 encoder and 8 decoder layers using attention and residual connections. To improve parallelism and therefore decrease training time, our attention mechanism connects the bottom layer of the decoder to the top layer of the encoder. To accelerate the final translation speed, we employ low-precision arithmetic during inference computations. To improve handling of rare words, we divide words into a limited set of common sub-word units ("wordpieces") for both input and output. This method provides a good balance between the flexibility of "character"-delimited models and the efficiency of "word"-delimited models, naturally handles translation of rare words, and ultimately improves the overall accuracy of the system. Our beam search technique employs a length-normalization procedure and uses a coverage penalty, which encourages generation of an output sentence that is most likely to cover all the words in the source sentence. On the WMT'14 English-to-French and English-to-German benchmarks, GNMT achieves competitive results to state-of-the-art. Using a human side-by-side evaluation on a set of isolated simple sentences, it reduces translation errors by an average of 60% compared to Google's phrase-based production system.
Wide & Deep Learning for Recommender Systems
Jun 24, 2016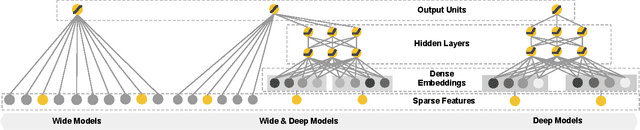
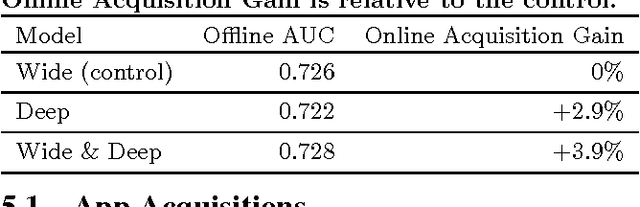

Abstract:Generalized linear models with nonlinear feature transformations are widely used for large-scale regression and classification problems with sparse inputs. Memorization of feature interactions through a wide set of cross-product feature transformations are effective and interpretable, while generalization requires more feature engineering effort. With less feature engineering, deep neural networks can generalize better to unseen feature combinations through low-dimensional dense embeddings learned for the sparse features. However, deep neural networks with embeddings can over-generalize and recommend less relevant items when the user-item interactions are sparse and high-rank. In this paper, we present Wide & Deep learning---jointly trained wide linear models and deep neural networks---to combine the benefits of memorization and generalization for recommender systems. We productionized and evaluated the system on Google Play, a commercial mobile app store with over one billion active users and over one million apps. Online experiment results show that Wide & Deep significantly increased app acquisitions compared with wide-only and deep-only models. We have also open-sourced our implementation in TensorFlow.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge