Yifei Hu
Anjelica
ALPBench: A Benchmark for Attribution-level Long-term Personal Behavior Understanding
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have highlighted their potential for personalized recommendation, where accurately capturing user preferences remains a key challenge. Leveraging their strong reasoning and generalization capabilities, LLMs offer new opportunities for modeling long-term user behavior. To systematically evaluate this, we introduce ALPBench, a Benchmark for Attribution-level Long-term Personal Behavior Understanding. Unlike item-focused benchmarks, ALPBench predicts user-interested attribute combinations, enabling ground-truth evaluation even for newly introduced items. It models preferences from long-term historical behaviors rather than users' explicitly expressed requests, better reflecting enduring interests. User histories are represented as natural language sequences, allowing interpretable, reasoning-based personalization. ALPBench enables fine-grained evaluation of personalization by focusing on the prediction of attribute combinations task that remains highly challenging for current LLMs due to the need to capture complex interactions among multiple attributes and reason over long-term user behavior sequences.
OpenOneRec Technical Report
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:While the OneRec series has successfully unified the fragmented recommendation pipeline into an end-to-end generative framework, a significant gap remains between recommendation systems and general intelligence. Constrained by isolated data, they operate as domain specialists-proficient in pattern matching but lacking world knowledge, reasoning capabilities, and instruction following. This limitation is further compounded by the lack of a holistic benchmark to evaluate such integrated capabilities. To address this, our contributions are: 1) RecIF Bench & Open Data: We propose RecIF-Bench, a holistic benchmark covering 8 diverse tasks that thoroughly evaluate capabilities from fundamental prediction to complex reasoning. Concurrently, we release a massive training dataset comprising 96 million interactions from 160,000 users to facilitate reproducible research. 2) Framework & Scaling: To ensure full reproducibility, we open-source our comprehensive training pipeline, encompassing data processing, co-pretraining, and post-training. Leveraging this framework, we demonstrate that recommendation capabilities can scale predictably while mitigating catastrophic forgetting of general knowledge. 3) OneRec-Foundation: We release OneRec Foundation (1.7B and 8B), a family of models establishing new state-of-the-art (SOTA) results across all tasks in RecIF-Bench. Furthermore, when transferred to the Amazon benchmark, our models surpass the strongest baselines with an average 26.8% improvement in Recall@10 across 10 diverse datasets (Figure 1). This work marks a step towards building truly intelligent recommender systems. Nonetheless, realizing this vision presents significant technical and theoretical challenges, highlighting the need for broader research engagement in this promising direction.
CLAMP: Crowdsourcing a LArge-scale in-the-wild haptic dataset with an open-source device for Multimodal robot Perception
May 27, 2025


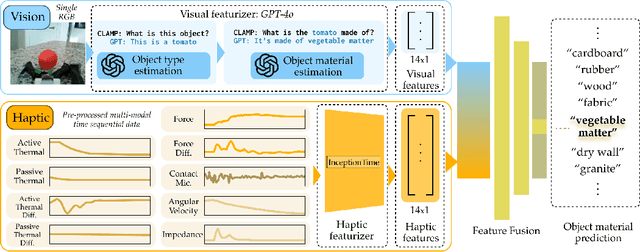
Abstract:Robust robot manipulation in unstructured environments often requires understanding object properties that extend beyond geometry, such as material or compliance-properties that can be challenging to infer using vision alone. Multimodal haptic sensing provides a promising avenue for inferring such properties, yet progress has been constrained by the lack of large, diverse, and realistic haptic datasets. In this work, we introduce the CLAMP device, a low-cost (<\$200) sensorized reacher-grabber designed to collect large-scale, in-the-wild multimodal haptic data from non-expert users in everyday settings. We deployed 16 CLAMP devices to 41 participants, resulting in the CLAMP dataset, the largest open-source multimodal haptic dataset to date, comprising 12.3 million datapoints across 5357 household objects. Using this dataset, we train a haptic encoder that can infer material and compliance object properties from multimodal haptic data. We leverage this encoder to create the CLAMP model, a visuo-haptic perception model for material recognition that generalizes to novel objects and three robot embodiments with minimal finetuning. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of our model in three real-world robot manipulation tasks: sorting recyclable and non-recyclable waste, retrieving objects from a cluttered bag, and distinguishing overripe from ripe bananas. Our results show that large-scale, in-the-wild haptic data collection can unlock new capabilities for generalizable robot manipulation. Website: https://emprise.cs.cornell.edu/clamp/
AgentThink: A Unified Framework for Tool-Augmented Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Autonomous Driving
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) show promise for autonomous driving, yet their struggle with hallucinations, inefficient reasoning, and limited real-world validation hinders accurate perception and robust step-by-step reasoning. To overcome this, we introduce \textbf{AgentThink}, a pioneering unified framework that, for the first time, integrates Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning with dynamic, agent-style tool invocation for autonomous driving tasks. AgentThink's core innovations include: \textbf{(i) Structured Data Generation}, by establishing an autonomous driving tool library to automatically construct structured, self-verified reasoning data explicitly incorporating tool usage for diverse driving scenarios; \textbf{(ii) A Two-stage Training Pipeline}, employing Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to equip VLMs with the capability for autonomous tool invocation; and \textbf{(iii) Agent-style Tool-Usage Evaluation}, introducing a novel multi-tool assessment protocol to rigorously evaluate the model's tool invocation and utilization. Experiments on the DriveLMM-o1 benchmark demonstrate AgentThink significantly boosts overall reasoning scores by \textbf{53.91\%} and enhances answer accuracy by \textbf{33.54\%}, while markedly improving reasoning quality and consistency. Furthermore, ablation studies and robust zero-shot/few-shot generalization experiments across various benchmarks underscore its powerful capabilities. These findings highlight a promising trajectory for developing trustworthy and tool-aware autonomous driving models.
Goku: Flow Based Video Generative Foundation Models
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces Goku, a state-of-the-art family of joint image-and-video generation models leveraging rectified flow Transformers to achieve industry-leading performance. We detail the foundational elements enabling high-quality visual generation, including the data curation pipeline, model architecture design, flow formulation, and advanced infrastructure for efficient and robust large-scale training. The Goku models demonstrate superior performance in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, setting new benchmarks across major tasks. Specifically, Goku achieves 0.76 on GenEval and 83.65 on DPG-Bench for text-to-image generation, and 84.85 on VBench for text-to-video tasks. We believe that this work provides valuable insights and practical advancements for the research community in developing joint image-and-video generation models.
GraphRPM: Risk Pattern Mining on Industrial Large Attributed Graphs
Nov 11, 2024Abstract:Graph-based patterns are extensively employed and favored by practitioners within industrial companies due to their capacity to represent the behavioral attributes and topological relationships among users, thereby offering enhanced interpretability in comparison to black-box models commonly utilized for classification and recognition tasks. For instance, within the scenario of transaction risk management, a graph pattern that is characteristic of a particular risk category can be readily employed to discern transactions fraught with risk, delineate networks of criminal activity, or investigate the methodologies employed by fraudsters. Nonetheless, graph data in industrial settings is often characterized by its massive scale, encompassing data sets with millions or even billions of nodes, making the manual extraction of graph patterns not only labor-intensive but also necessitating specialized knowledge in particular domains of risk. Moreover, existing methodologies for mining graph patterns encounter significant obstacles when tasked with analyzing large-scale attributed graphs. In this work, we introduce GraphRPM, an industry-purpose parallel and distributed risk pattern mining framework on large attributed graphs. The framework incorporates a novel edge-involved graph isomorphism network alongside optimized operations for parallel graph computation, which collectively contribute to a considerable reduction in computational complexity and resource expenditure. Moreover, the intelligent filtration of efficacious risky graph patterns is facilitated by the proposed evaluation metrics. Comprehensive experimental evaluations conducted on real-world datasets of varying sizes substantiate the capability of GraphRPM to adeptly address the challenges inherent in mining patterns from large-scale industrial attributed graphs, thereby underscoring its substantial value for industrial deployment.
EVLM: An Efficient Vision-Language Model for Visual Understanding
Jul 19, 2024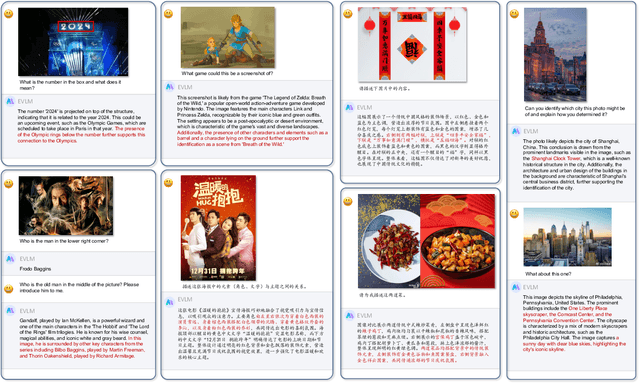
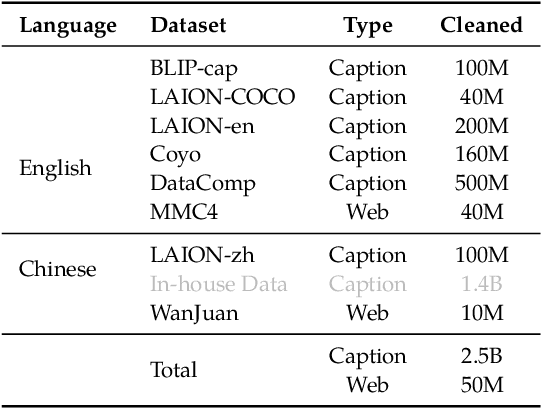
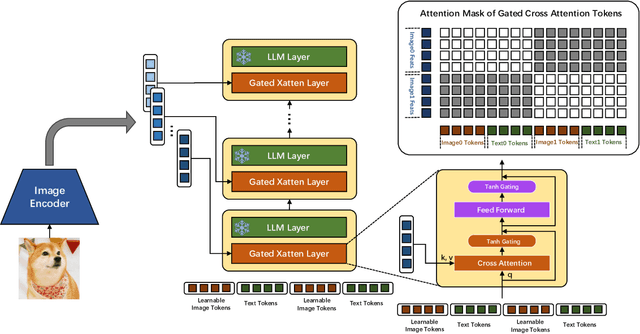

Abstract:In the field of multi-modal language models, the majority of methods are built on an architecture similar to LLaVA. These models use a single-layer ViT feature as a visual prompt, directly feeding it into the language models alongside textual tokens. However, when dealing with long sequences of visual signals or inputs such as videos, the self-attention mechanism of language models can lead to significant computational overhead. Additionally, using single-layer ViT features makes it challenging for large language models to perceive visual signals fully. This paper proposes an efficient multi-modal language model to minimize computational costs while enabling the model to perceive visual signals as comprehensively as possible. Our method primarily includes: (1) employing cross-attention to image-text interaction similar to Flamingo. (2) utilize hierarchical ViT features. (3) introduce the Mixture of Experts (MoE) mechanism to enhance model effectiveness. Our model achieves competitive scores on public multi-modal benchmarks and performs well in tasks such as image captioning and video captioning.
MORPHeus: a Multimodal One-armed Robot-assisted Peeling System with Human Users In-the-loop
Apr 09, 2024Abstract:Meal preparation is an important instrumental activity of daily living~(IADL). While existing research has explored robotic assistance in meal preparation tasks such as cutting and cooking, the crucial task of peeling has received less attention. Robot-assisted peeling, conventionally a bimanual task, is challenging to deploy in the homes of care recipients using two wheelchair-mounted robot arms due to ergonomic and transferring challenges. This paper introduces a robot-assisted peeling system utilizing a single robotic arm and an assistive cutting board, inspired by the way individuals with one functional hand prepare meals. Our system incorporates a multimodal active perception module to determine whether an area on the food is peeled, a human-in-the-loop long-horizon planner to perform task planning while catering to a user's preference for peeling coverage, and a compliant controller to peel the food items. We demonstrate the system on 12 food items representing the extremes of different shapes, sizes, skin thickness, surface textures, skin vs flesh colors, and deformability.
Misspelling Correction with Pre-trained Contextual Language Model
Jan 08, 2021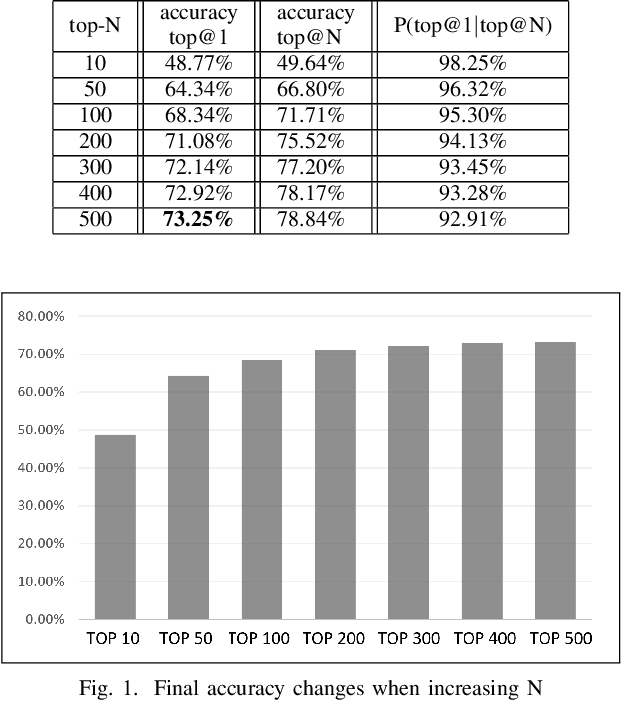

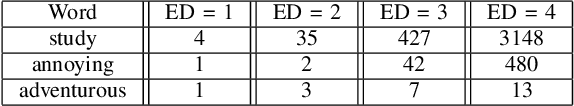
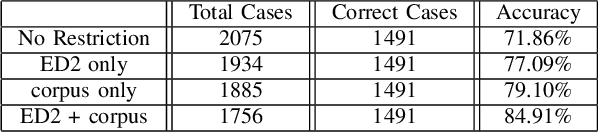
Abstract:Spelling irregularities, known now as spelling mistakes, have been found for several centuries. As humans, we are able to understand most of the misspelled words based on their location in the sentence, perceived pronunciation, and context. Unlike humans, computer systems do not possess the convenient auto complete functionality of which human brains are capable. While many programs provide spelling correction functionality, many systems do not take context into account. Moreover, Artificial Intelligence systems function in the way they are trained on. With many current Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems trained on grammatically correct text data, many are vulnerable against adversarial examples, yet correctly spelled text processing is crucial for learning. In this paper, we investigate how spelling errors can be corrected in context, with a pre-trained language model BERT. We present two experiments, based on BERT and the edit distance algorithm, for ranking and selecting candidate corrections. The results of our experiments demonstrated that when combined properly, contextual word embeddings of BERT and edit distance are capable of effectively correcting spelling errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge