Julia Taylor Rayz
Learning Shortcuts: On the Misleading Promise of NLU in Language Models
Jan 17, 2024Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has enabled significant performance gains in the field of natural language processing. However, recent studies have found that LLMs often resort to shortcuts when performing tasks, creating an illusion of enhanced performance while lacking generalizability in their decision rules. This phenomenon introduces challenges in accurately assessing natural language understanding in LLMs. Our paper provides a concise survey of relevant research in this area and puts forth a perspective on the implications of shortcut learning in the evaluation of language models, specifically for NLU tasks. This paper urges more research efforts to be put towards deepening our comprehension of shortcut learning, contributing to the development of more robust language models, and raising the standards of NLU evaluation in real-world scenarios.
Calibration Error Estimation Using Fuzzy Binning
May 08, 2023



Abstract:Neural network-based decisions tend to be overconfident, where their raw outcome probabilities do not align with the true decision probabilities. Calibration of neural networks is an essential step towards more reliable deep learning frameworks. Prior metrics of calibration error primarily utilize crisp bin membership-based measures. This exacerbates skew in model probabilities and portrays an incomplete picture of calibration error. In this work, we propose a Fuzzy Calibration Error metric (FCE) that utilizes a fuzzy binning approach to calculate calibration error. This approach alleviates the impact of probability skew and provides a tighter estimate while measuring calibration error. We compare our metric with ECE across different data populations and class memberships. Our results show that FCE offers better calibration error estimation, especially in multi-class settings, alleviating the effects of skew in model confidence scores on calibration error estimation. We make our code and supplementary materials available at: https://github.com/bihani-g/fce
COMPS: Conceptual Minimal Pair Sentences for testing Property Knowledge and Inheritance in Pre-trained Language Models
Oct 06, 2022



Abstract:A characteristic feature of human semantic memory is its ability to not only store and retrieve the properties of concepts observed through experience, but to also facilitate the inheritance of properties (can breathe) from superordinate concepts (animal) to their subordinates (dog) -- i.e. demonstrate property inheritance. In this paper, we present COMPS, a collection of minimal pair sentences that jointly tests pre-trained language models (PLMs) on their ability to attribute properties to concepts and their ability to demonstrate property inheritance behavior. Analyses of 22 different PLMs on COMPS reveal that they can easily distinguish between concepts on the basis of a property when they are trivially different, but find it relatively difficult when concepts are related on the basis of nuanced knowledge representations. Furthermore, we find that PLMs can demonstrate behavior consistent with property inheritance to a great extent, but fail in the presence of distracting information, which decreases the performance of many models, sometimes even below chance. This lack of robustness in demonstrating simple reasoning raises important questions about PLMs' capacity to make correct inferences even when they appear to possess the prerequisite knowledge.
A Property Induction Framework for Neural Language Models
May 13, 2022



Abstract:To what extent can experience from language contribute to our conceptual knowledge? Computational explorations of this question have shed light on the ability of powerful neural language models (LMs) -- informed solely through text input -- to encode and elicit information about concepts and properties. To extend this line of research, we present a framework that uses neural-network language models (LMs) to perform property induction -- a task in which humans generalize novel property knowledge (has sesamoid bones) from one or more concepts (robins) to others (sparrows, canaries). Patterns of property induction observed in humans have shed considerable light on the nature and organization of human conceptual knowledge. Inspired by this insight, we use our framework to explore the property inductions of LMs, and find that they show an inductive preference to generalize novel properties on the basis of category membership, suggesting the presence of a taxonomic bias in their representations.
On Information Hiding in Natural Language Systems
Mar 12, 2022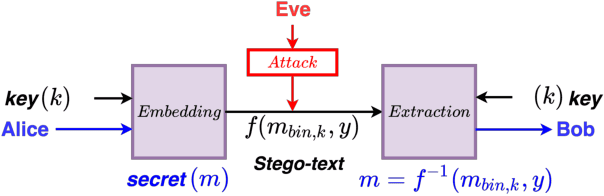
Abstract:With data privacy becoming more of a necessity than a luxury in today's digital world, research on more robust models of privacy preservation and information security is on the rise. In this paper, we take a look at Natural Language Steganography (NLS) methods, which perform information hiding in natural language systems, as a means to achieve data security as well as confidentiality. We summarize primary challenges regarding the secrecy and imperceptibility requirements of these systems and propose potential directions of improvement, specifically targeting steganographic text quality. We believe that this study will act as an appropriate framework to build more resilient models of Natural Language Steganography, working towards instilling security within natural language-based neural models.
Towards The Automatic Coding of Medical Transcripts to Improve Patient-Centered Communication
Sep 22, 2021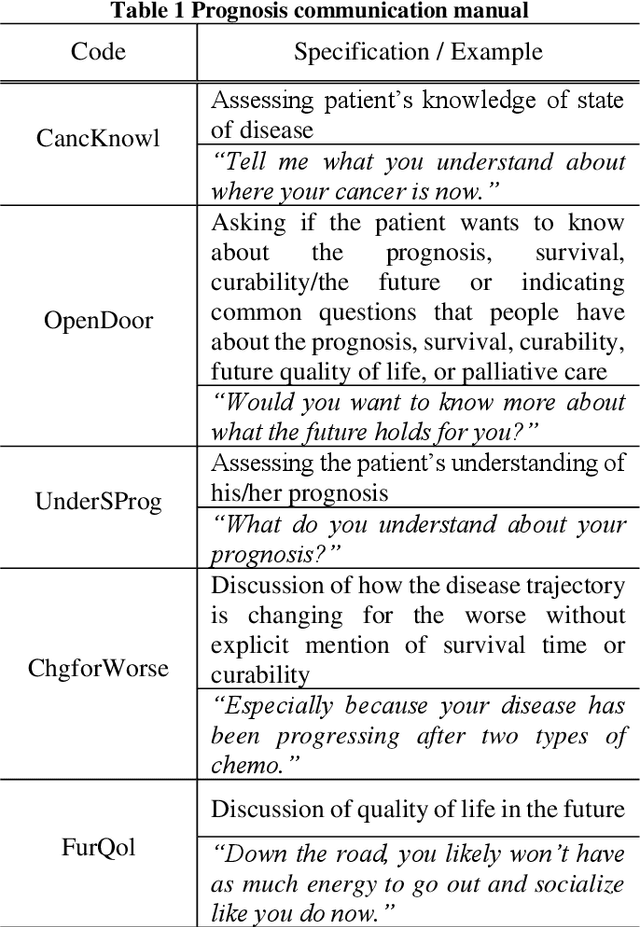
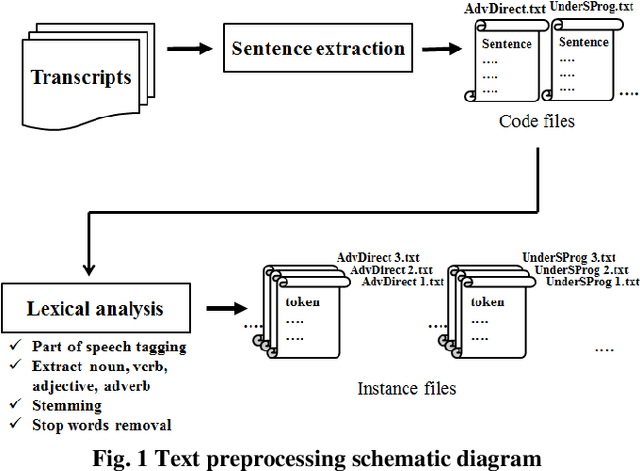
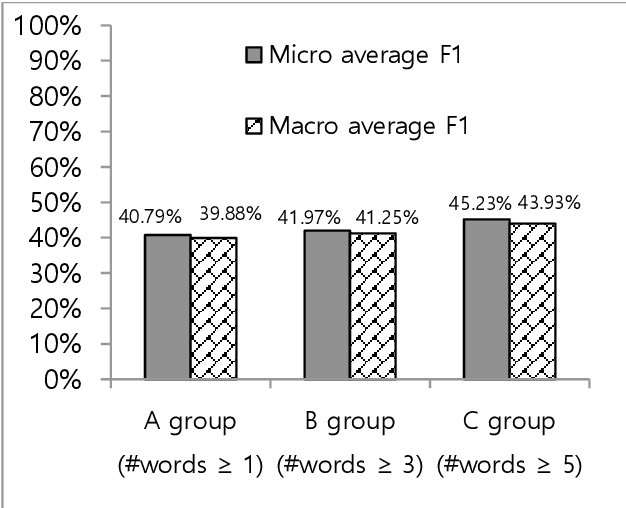
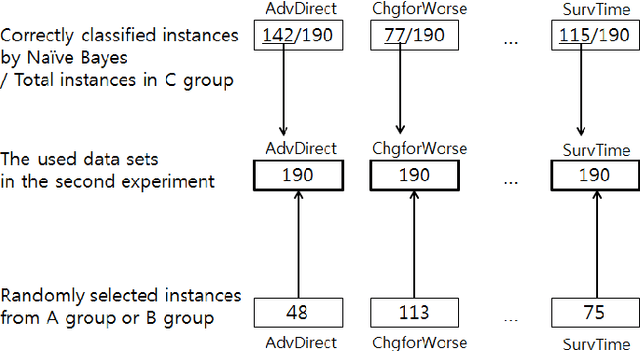
Abstract:This paper aims to provide an approach for automatic coding of physician-patient communication transcripts to improve patient-centered communication (PCC). PCC is a central part of high-quality health care. To improve PCC, dialogues between physicians and patients have been recorded and tagged with predefined codes. Trained human coders have manually coded the transcripts. Since it entails huge labor costs and poses possible human errors, automatic coding methods should be considered for efficiency and effectiveness. We adopted three machine learning algorithms (Na\"ive Bayes, Random Forest, and Support Vector Machine) to categorize lines in transcripts into corresponding codes. The result showed that there is evidence to distinguish the codes, and this is considered to be sufficient for training of human annotators.
Do language models learn typicality judgments from text?
May 06, 2021



Abstract:Building on research arguing for the possibility of conceptual and categorical knowledge acquisition through statistics contained in language, we evaluate predictive language models (LMs) -- informed solely by textual input -- on a prevalent phenomenon in cognitive science: typicality. Inspired by experiments that involve language processing and show robust typicality effects in humans, we propose two tests for LMs. Our first test targets whether typicality modulates LM probabilities in assigning taxonomic category memberships to items. The second test investigates sensitivities to typicality in LMs' probabilities when extending new information about items to their categories. Both tests show modest -- but not completely absent -- correspondence between LMs and humans, suggesting that text-based exposure alone is insufficient to acquire typicality knowledge.
Low Anisotropy Sense Retrofitting (LASeR) : Towards Isotropic and Sense Enriched Representations
Apr 22, 2021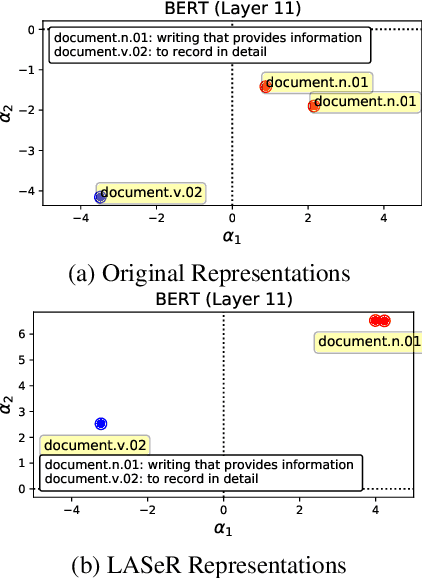
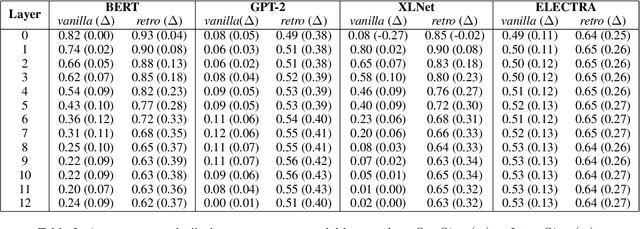
Abstract:Contextual word representation models have shown massive improvements on a multitude of NLP tasks, yet their word sense disambiguation capabilities remain poorly explained. To address this gap, we assess whether contextual word representations extracted from deep pretrained language models create distinguishable representations for different senses of a given word. We analyze the representation geometry and find that most layers of deep pretrained language models create highly anisotropic representations, pointing towards the existence of representation degeneration problem in contextual word representations. After accounting for anisotropy, our study further reveals that there is variability in sense learning capabilities across different language models. Finally, we propose LASeR, a 'Low Anisotropy Sense Retrofitting' approach that renders off-the-shelf representations isotropic and semantically more meaningful, resolving the representation degeneration problem as a post-processing step, and conducting sense-enrichment of contextualized representations extracted from deep neural language models.
Fuzzy Classification of Multi-intent Utterances
Apr 22, 2021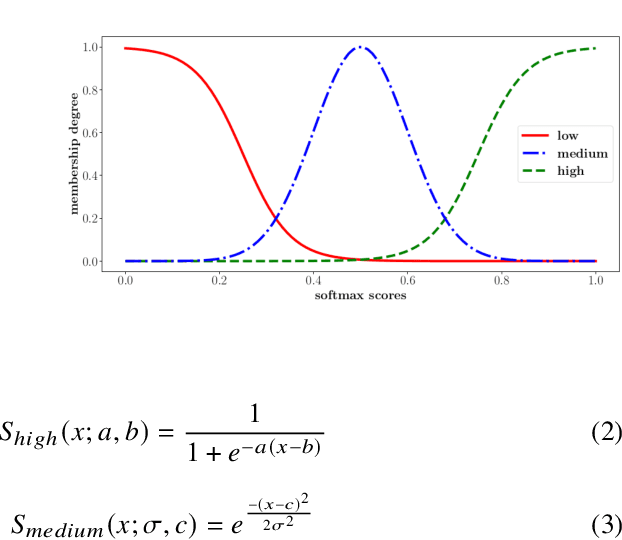
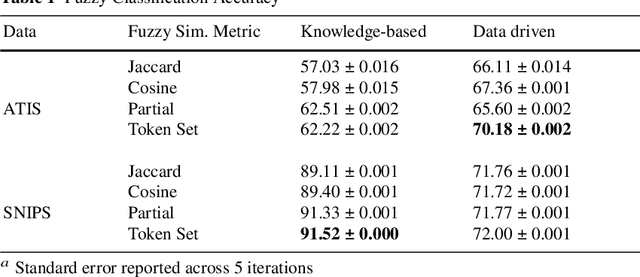
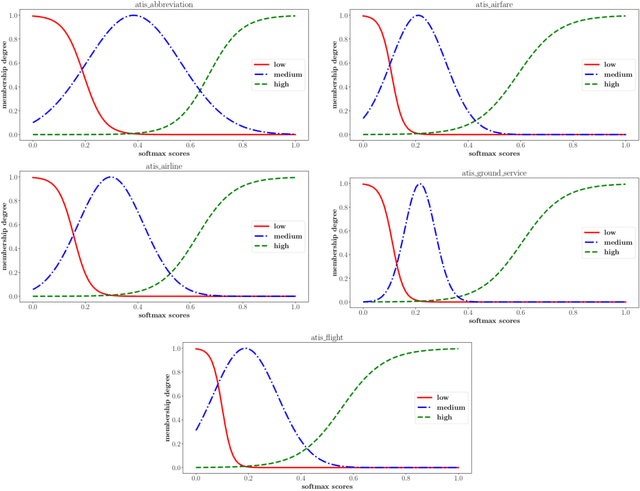
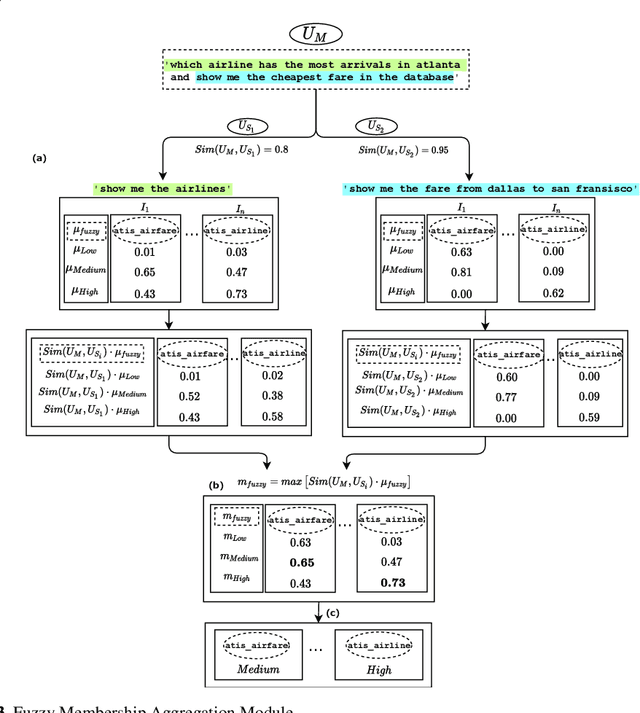
Abstract:Current intent classification approaches assign binary intent class memberships to natural language utterances while disregarding the inherent vagueness in language and the corresponding vagueness in intent class boundaries. In this work, we propose a scheme to address the ambiguity in single-intent as well as multi-intent natural language utterances by creating degree memberships over fuzzified intent classes. To our knowledge, this is the first work to address and quantify the impact of the fuzzy nature of natural language utterances over intent category memberships. Additionally, our approach overcomes the sparsity of multi-intent utterance data to train classification models by using a small database of single intent utterances to generate class memberships over multi-intent utterances. We evaluate our approach over two task-oriented dialog datasets, across different fuzzy membership generation techniques and approximate string similarity measures. Our results reveal the impact of lexical overlap between utterances of different intents, and the underlying data distributions, on the fuzzification of intent memberships. Moreover, we evaluate the accuracy of our approach by comparing the defuzzified memberships to their binary counterparts, across different combinations of membership functions and string similarity measures.
Finding Fuzziness in Neural Network Models of Language Processing
Apr 22, 2021



Abstract:Humans often communicate by using imprecise language, suggesting that fuzzy concepts with unclear boundaries are prevalent in language use. In this paper, we test the extent to which models trained to capture the distributional statistics of language show correspondence to fuzzy-membership patterns. Using the task of natural language inference, we test a recent state of the art model on the classical case of temperature, by examining its mapping of temperature data to fuzzy-perceptions such as "cool", "hot", etc. We find the model to show patterns that are similar to classical fuzzy-set theoretic formulations of linguistic hedges, albeit with a substantial amount of noise, suggesting that models trained solely on language show promise in encoding fuzziness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge